Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Yearly Exam Key Notes
Uploaded by
Anthony.sabaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Yearly Exam Key Notes
Uploaded by
Anthony.sabaCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Science Yearly Study Guide Notes:
Topic 3 - Am I Not Healthy Enough?
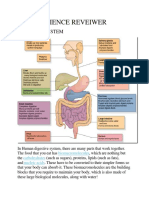
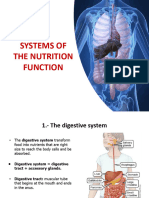
Digestion:
- Digestion begins at the mouth and finishes at the anus.
- Chewing (mechanical digestion) breaks down food while mixing with saliva creating
bolus (made by the tongue).
- The esophagus has wave like muscles known as peristalsis, which force food down.
- The stomach is a hollow organ which holds food while being mixed with gastric acids
to continue the process of breaking it down into a useable form. Cells in the lining of
the stomach create strong acids that are responsible for the breakdown process.
- In the small intestine, food absorption takes place. Chyme is released in small
amounts from the stomach to the small intestine through another sphincter.
Peristalsis continues in the small intestine, churning the chime and mixing it with
intestinal secretions. These secretions include enzymes that further digest proteins,
fats and carbohydrates.
- All the nutrients made are then released into the bloodstream and distributed to the
cells of the body. These nutrients are carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
- Villi (finger-like projections) lie in the tubes of the small intestine.
- They come in contact with the digested food passing through the small intestine and
efficiently help with absorption of nutrients (Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins) as
they increase surface area. The molecules (nutrients) will move from the wall of the
small intestine into the blood vessels.
- Gallbladder Produces bile.
- The Pancreas Converts food into fuel for the body’s cells and also produces insulin to
allow absorption of glucose.
- The Liver processes the nutrients absorbed from the small intestine.
- The Large Intestine. Absorbs water from the remaining indigestible food and
removes waste products from the body.
- Anus removes things the body doesn’t need.
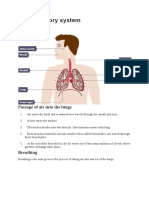
Respiration:
- Respiration I is NOT breathing.
- The Nose inhales and exhales air, warms and moistens. (like a filter) Cilia and mucus
line the nasal cavity and trap bacteria and foreign particles that enter through the
nose.
-
- The Pharynx allows air to pass from the mouth to the lungs.
- The Larynx (voice box), is a passageway for air to enter the lungs.
- The Epiglottis is a flap that protects the trachea against food absorption. (Stops the
food from going down the windpipe)
- The Trachea is hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs. It
provides airflow to and from the lungs.
- The Lungs are air filled organs like sponges, having two sides. Right lung and left
lung. Within the lung, there are tubular branches called bronchi, which then they
divide into smaller grape like trees called alveoli.
- When air enters the lungs they expand, and deflate when you exhale.
- The Alveoli are tiny grape like sacs that lie in the lungs at the end of the respiratory
tree. Gas exchange takes place because they have very thin walls.
- The diaphragm is the primary muscle used in the process of inspiration, or
inhalation. The diaphragm opens when you breathe.
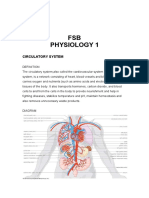
Circulation:
- The Heart is made of strong muscle tissues and is protected by your rib cage.
- The Heart Consists of four hollow chambers – two ventricles and two atria.
- It consists of the right and left atrium.
- From here it is pumped through yet another valve and into the aorta, the vessel in
which it begins its journey around the body.
- The heart contains valves that make sure that blood only flows in the right direction.
There are four valves in the human heart, one at the exit of each chamber.
- The two chambers at the bottom of the heart are called VENTRICLES.
- Heart valves are made of flaps of skin that only open in one direction. If blood tried
to flow backwards, the valve would snap shut, preventing the flow in that direction.
- Red Blood Cells. Carry oxygen bound to haemoglobin.`
- Blood vessels enter and leave the heart.
- Once in the heart the blood moves from the right atrium, through one way valve,
into the lower chamber, the right ventricle.
- Blood first enters the heart through the right atrium.
- The walls of the atria and ventricles have different thickness. The atria haverelatively
thin muscular outside walls while the ventricles have outside walls that are very
muscular and thick.
- From here the blood is pumped through another one way valve into the pulmonary
artery to travel in the lungs.
- The right side of your Heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The left side
of the heart receives the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body.
- All four chambers work like pumps and push blood throughout your body.
- Blood Vessels allow blood to flow quickly from one region to another and then allow
- it to come back to your heart. Cellular Respiration:
- Has a hollow area that allows for easy flow of food.
- Three main types of Blood Vessels including capillaries, arteries and veins.
- Cellular respiration is the series of reactions that occur in an organism’s cells to
release energy from the energy-rich sugar glucose.
- Word formula for cellular Respiration:
- Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (Energy)
Photosynthesis:
- Word Formula:
- Carbon Dioxide + Water (Light) (Chlorophyll) → Glucose + Oxygen
Plant Transport System:
- Plants have two types of transport tubes, which start in the roots and travel up the
stems to the leaves.
- Root Structure: Function is to absorb water and nutrients. Anchors plant into
ground.
- Xylem Structure: Function is to carry water and minerals to plant (eg.
Photosynthesis, hydrogen)
- Phloem Structure: Transports the food (Glucose) made in leaves to all the plant cells.
- Stem: Transports food and water. And holds plant upright.
- Flower: Pollen, Reproduction – make seeds.
- Leaves: Photosynthesis. They release oxygen and enter carbon dioxide.
Revision Tasks:
- Revision Booklet Link: Link
You might also like
- Earth and Life Science 1Document24 pagesEarth and Life Science 1John Jacob Ezekiel CaisNo ratings yet
- Body Systems RevisionDocument11 pagesBody Systems Revisionamie122auNo ratings yet
- Normal AnatomyDocument4 pagesNormal AnatomyDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Biology 4th QuarterDocument6 pagesBiology 4th QuarterYeizmin KimNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: - Left AtriumDocument14 pagesScience Reviewer: - Left AtriumJasmineLouiseEspañolNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 Body OrgansDocument62 pagesSCIENCE 4 Body OrgansjamjamNo ratings yet
- Normal Anatomy 2Document6 pagesNormal Anatomy 2Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - Body SystemsDocument6 pagesScience Notes - Body SystemsSarvika DusheNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument13 pagesDigestive System GuidegemNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter No 5 Life Process Notes by Harshit Nagar The Green Board NotesDocument7 pagesBio Chapter No 5 Life Process Notes by Harshit Nagar The Green Board NotesNeetu NagarNo ratings yet
- Summary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionDocument29 pagesSummary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionwendyNo ratings yet
- g7 Advance Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesg7 Advance Science ReviewerEzequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Natural 6ºprimariaDocument6 pagesThe Digestive System Natural 6ºprimariaPatry sanchezNo ratings yet
- Bio RespirationDocument4 pagesBio RespirationBrian Voyd RebitoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 - Module 1Document7 pagesSCIENCE 9 - Module 1cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- 3 Human Body SystemsDocument66 pages3 Human Body SystemsThe KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration and the human respiratory systemDocument8 pagesRespiration and the human respiratory systemshreyasNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY ReviewerDocument18 pagesBIOLOGY ReviewerAngela Nicole ManasNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document2 pagesScience 9Mark Nelson OfrasioNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument14 pagesSciencesheanellerenzsantosNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument29 pagesCardioKrystal Kaye AczonNo ratings yet
- Annatomy Notes For Bpe StudDocument14 pagesAnnatomy Notes For Bpe StudYoga KalyanamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ReviewDocument53 pagesUnit 4 ReviewRoberta BansahNo ratings yet
- The human body systemsDocument47 pagesThe human body systemsErl D. MelitanteNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes for CBSE Class 10 Science Notes for Chapter 6 Life ProcessesDocument71 pagesRevision Notes for CBSE Class 10 Science Notes for Chapter 6 Life Processesparashakthi PRNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument7 pagesScience ReviewPia louise RamosNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorNo ratings yet
- Major Organ Systems (Form 1)Document29 pagesMajor Organ Systems (Form 1)protyushNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human LungDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human LungRosal ClarinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems GuideDocument14 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systems GuideJustine GacayanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Reviewer First QRTDocument4 pagesScience 9 Reviewer First QRTAshleyNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemEvansNo ratings yet
- Respiratory & Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory SystemYaSHVaRDHaN DaGaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument3 pagesANAPHYmichelle magandamNo ratings yet
- 10th Life ProcessDocument10 pages10th Life ProcessSunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - ReadingDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy - ReadingzuzanamNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument9 pagesHuman Body SystemsTiara Dwi PangestutiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemRafael Quieta Claro Jr.No ratings yet
- B2 Tissues and Organs Ict LessonDocument2 pagesB2 Tissues and Organs Ict LessonCharlie BlakeNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Wave Like Contraction. Detoxification and PhagocytosisDocument2 pagesDigestive System: Wave Like Contraction. Detoxification and PhagocytosisLourdes BaesNo ratings yet
- Frog Organ SystemDocument33 pagesFrog Organ SystemReineil PanguitoNo ratings yet
- Respiration, Transport and ExcretionDocument14 pagesRespiration, Transport and ExcretionAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - 2Document7 pagesChapter 6 - 2Prit mistryNo ratings yet
- Biology - Unit 3: Dissolved SubstancesDocument11 pagesBiology - Unit 3: Dissolved SubstancesTahirNo ratings yet
- BPED-2 Valenzuela Angelo Joseph ValenzuelaDocument11 pagesBPED-2 Valenzuela Angelo Joseph ValenzuelaAngelo Joseph ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Sci Notes Ch6 VT VaibhavPDF - 230609 - 132019Document9 pagesSci Notes Ch6 VT VaibhavPDF - 230609 - 132019Riya JainNo ratings yet
- Bio-Pt 2Document10 pagesBio-Pt 2Ralph jhenzel UtonNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRoland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument78 pagesPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionssannsannNo ratings yet
- Human Body'S Systems: Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHuman Body'S Systems: Circulatory SystemsrathinakumarNo ratings yet
- FSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFSB Physiology 1: Circulatory SystemSkylar0.comNo ratings yet
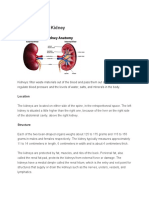
- Anatomy of The KidneyDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Kidneycatherine kate gulengNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems 3Document21 pagesHuman Body Systems 3JuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory System ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Human Respiratory System ExplainedshashaNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiologytedy_berNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument21 pagesHuman Body Systemsilmioangelo100% (4)
- Human Body SystemsDocument21 pagesHuman Body Systemsveeramani100% (3)
- 8350business Studies Operations NotesDocument27 pages8350business Studies Operations NotesAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Bio ImagesDocument1 pageBio ImagesAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- 2571business Studies Finance Notes ATARnotesDocument32 pages2571business Studies Finance Notes ATARnotesAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- 3297agrippina The Younger Study NotesDocument24 pages3297agrippina The Younger Study NotesAnthony.saba100% (1)
- Module 7 - Infectious Dieases - IQ4 - Dot Point 7 - Aboriginal Knowledge - RESPECTDocument3 pagesModule 7 - Infectious Dieases - IQ4 - Dot Point 7 - Aboriginal Knowledge - RESPECTAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- HSC CORE 1 Nishans Official NotesDocument26 pagesHSC CORE 1 Nishans Official NotesAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Sparta Religion - III - IV - VDocument8 pagesSparta Religion - III - IV - VAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Tacitus Source Study - TextbookDocument3 pagesTacitus Source Study - TextbookAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Core 1: How Are Priority Issues For Australia's Health Identified?Document13 pagesCore 1: How Are Priority Issues For Australia's Health Identified?Anthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- HSC Ancient - Pompeii & Herculaneum-3Document20 pagesHSC Ancient - Pompeii & Herculaneum-3Anthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Pompeii StudyDocument35 pagesPompeii StudyAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- Augustan-Age-notes Anthony SabaDocument23 pagesAugustan-Age-notes Anthony SabaAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- 3297agrippina The Younger Study NotesDocument24 pages3297agrippina The Younger Study NotesAnthony.saba100% (1)
- 8ACV Study Guide Notes: What Do I Need To Know For The Exam?Document5 pages8ACV Study Guide Notes: What Do I Need To Know For The Exam?Anthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- iCell: Compare Animal, Plant and Bacteria CellsDocument3 pagesiCell: Compare Animal, Plant and Bacteria CellsAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
- English Studies Stage 6 2017 Sample Work Year 12 Billy Elliot Extended Response DarcyDocument1 pageEnglish Studies Stage 6 2017 Sample Work Year 12 Billy Elliot Extended Response DarcyAnthony.sabaNo ratings yet
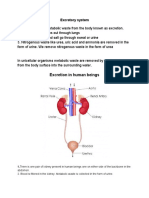
- Excretory system waste removalDocument4 pagesExcretory system waste removalKAbirNo ratings yet
- Guideline SummaryDocument9 pagesGuideline SummarymanmeetNo ratings yet
- Frog External Anatomy RevDocument18 pagesFrog External Anatomy RevMike DelivaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageLECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemJeremiah AndalNo ratings yet
- Fitness Exercises Mvpa ParticipationsDocument20 pagesFitness Exercises Mvpa ParticipationsJei Diao VillosoNo ratings yet
- Pe 02 Module 4Document26 pagesPe 02 Module 4EliNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System ExplainedDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory System ExplainedfidANo ratings yet
- Stomach and Intestine Lesson 15Document25 pagesStomach and Intestine Lesson 15Nicholson SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation PDFDocument47 pagesBlood and Circulation PDFeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Alternative Names: SleepwalkingDocument3 pagesAlternative Names: SleepwalkingRohanNo ratings yet
- Student Sleep and GPA HoursDocument4 pagesStudent Sleep and GPA HoursCharles XavierNo ratings yet
- Ojas Pranayam - KrishanjiDocument3 pagesOjas Pranayam - KrishanjiraychoslanchevNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An OrientationDocument59 pagesThe Human Body: An OrientationShery Han Bint HindawiNo ratings yet
- Edid6508group 3 Storyboardcorrectedversion1Document35 pagesEdid6508group 3 Storyboardcorrectedversion1api-349780383No ratings yet
- Raspored 2020-2021 Medicinski Engleski IIIDocument5 pagesRaspored 2020-2021 Medicinski Engleski IIIGracia GrabarićNo ratings yet
- Endo & Exogenous Pacemakersin Biological RhythmsDocument2 pagesEndo & Exogenous Pacemakersin Biological RhythmsMiss_M90No ratings yet
- Blood Groups: DR - Agus Alim Abdullah, SPPK (K)Document59 pagesBlood Groups: DR - Agus Alim Abdullah, SPPK (K)Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- Our Digestive System: A Concise GuideDocument35 pagesOur Digestive System: A Concise GuidecelineNo ratings yet
- Umj 1x Dovangiova 3330 1 ManuskripDocument8 pagesUmj 1x Dovangiova 3330 1 ManuskripNursaniahNo ratings yet
- 11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyDocument3 pages11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyAkashNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion GuideDocument28 pagesBlood Transfusion GuideChristina DienteNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 QUIZ EndocrineDocument3 pagesGRADE 10 QUIZ EndocrineShielo Marie CabañeroNo ratings yet
- Leslie Kaminoff's Anatomy of Yoga breathing reviewDocument11 pagesLeslie Kaminoff's Anatomy of Yoga breathing reviewgingergarlicNo ratings yet
- The human body facts guide: Cells, organs, systems & moreDocument6 pagesThe human body facts guide: Cells, organs, systems & moreجنید سلیم چوہدری100% (4)
- Lesson 07 PDFDocument14 pagesLesson 07 PDFIhsan UllahNo ratings yet
- Bing Soal Us SmaDocument4 pagesBing Soal Us SmaElma FatmiNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Oxygen AdvantageJOHN0% (1)
- Mouth Breathing and Facial Morphological PatternDocument6 pagesMouth Breathing and Facial Morphological PatternAlejandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Sleep Phenotypes in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderDocument35 pagesSleep Phenotypes in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderPierluigi CongedoNo ratings yet