Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
JAN CAMILLE LENONOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
JAN CAMILLE LENONCopyright:
Available Formats
PHARMACOLOGY SEM 01 | CYC 02
LECTURE AUF-CON
NCM 0106 MODULE 12 & 13 – DRUGS ACTING ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
○ Composed of plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes
OUTLINE and platelets
I Concept Review ○ Plasma: 90% water, 10% solutes
A Cardiovascular System
B Congestive Heart Failure
II Drugs Acting on the CVS CONCEPTS
A Cardiac Glycosides
B Antianginals ● CONDUCTION OF ELECTRICAL IMPULSES
C Antidysrhythmics ○ SA node “primary pacemaker”: 60-80 bpms
○ AV node “secondary pacemaker”: 40-60 bpms
○ Bundle of His (right and left bundle branches)
CONCEPT REVIEW
○ Purkinje Fibers
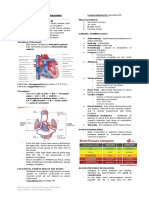
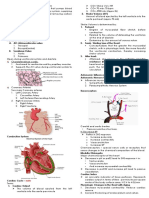
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ● Stimulates the heart to contract
PARTS
📌 REMEMBER: AV node can act as the primary
pacemaker if the SA node is malfunctioning
(bradycardia)
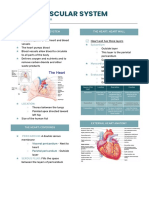
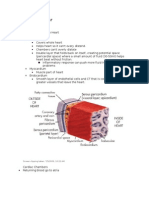
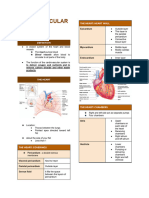
● HEART
○ Composed mainly by myocardium (heart
● CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE
muscles)
○ Arterial blood pressure: determined by
○ Covered externally by the pericardium, lined
peripheral resistance and cardiac output
internally by the endocardium
○ High blood viscosity = high resistance
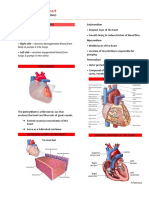
○ 4 Chambers: LA, LV, RA, RV
○ Longer blood vessel = higher resistance
● Atria: receiving chambers
○ Blood vessel radius increases = lesser
● Ventricles: pumping chambers
resistance produced
○ 4 Valves: Tricuspid and Mitral Valves,
○ Cardiac Output (CO)
Pulmonary and Aortic Semilunar Valves
● Volume of blood pumped by either
○ Perfused through the coronary arteries
ventricles of the heart each minute
● Prevents backflow of blood
○ Stroke Volume (SV)
● Right Coronary Artery, Left Anterior
● Volume of blood pumped per ventricle
Descending Artery, Left Circumflex Artery
each time the heart contracts
● BLOOD FLOW
○ Heart Rate
○ Superior (upper) and Inferior (lower) Vena
● Number of times the heart contracts each
Cava → Right Atrium → Tricuspid valve → Right
minute
Ventricle → Pulmonary semilunar valves →
○ Formula
Pulmonary trunk → Pulmonary artery (lungs,
● CO = HR x Stroke Volume (amount of blood
carrying unoxygenated blood) → Pulmonary
ejected by the ventricle every after
veins → Left Atrium → Bicuspid valve → Left
heartbeat) - 70mL per beat
Ventricle → Aortic semilunar valve → Aorta →
● Normal CO = 4-8 L/m
rest of the body
○ Three Factors affecting Stroke Volume
● BLOOD VESSELS
● Preload: force exerted by blood against
○ Arteries → Arterioles → Capillaries → Venules →
the ventricles at the end of diastole
Veins
○ Blood flow force that stretches the
○ Largest in lumen chena: veins
ventricle
○ Largest lumen in diameter: great veins
○ Higher preload = higher cardiac
○ Thicker wall: arteries
output
○ A lot of medication have their effect on arteries
● Contractility: force of ventricular
specifically of the smooth muscle layer that is
contractions
why the arteries are capable of performing
○ Higher Preload and contractility =
vasoconstriction and vasodilation that is not
higher stroke volume
present in veins
● BLOOD
NCM 0106| Surname, Name|1
MODULE 12 & 13 – DRUGS ACTING ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
● Afterload: resistance to ventricular ejection ● Left atrium will return the blood/fluid to the
of blood caused by opposing pressures in lungs
the aorta and systemic circulation ● Nursing Intervention: Do not place patient
○ Afterload increases = flat in bed, dapat orthopneic position
decreased/weaker stroke volume ○ Pulmonary edema
○ Left ventricle has to pump harder due
to the presence of resistance DRUGS ACTING ON THE CVS
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE A. CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
Digitalis
● Due to cardiac abnormalities or conditions that
place increase demand on the heart; heart ● Have been in use as early as 1200 AD
compensates → Heart muscle weakens and ● Naturally occurring come from purple and white
enlarges → Loses its ability to pump blood to the foxglove plants, which can be poisonous
lungs and systemic circulation → Left or right ● Inhibits the Na-K pump that leads to increased
failure → Continuous increase, forceful intracellular Na
contractions → Compensatory mechanism fails → ○ Leads to calcium influx that causes more
Congestive heart failure → Cardiac arrest (if not efficient cardiac muscle fiber contractions
treated) ● Also used to correct CHF, atrial fibrillation (rapid
uncoordinated atrial contraction) and atrial flutter
(200-300 bpm)
STAGES OF HEART FAILURE (PUMP FAILURE)
● FOUR EFFECTS OF DIGITALIS ON THE HEART
STAGE CHARACTERISTICS ACCORDING TO STAGE ○ (+) Inotropic
High risk to heart failure without symptoms ● Influences the contraction; more forceful
A
of structural heart disease contraction
● Increased CO
Some cardiac changes such as decreased
ejection fraction without symptoms of heart ○ (-) Chronotropic
failure ● Slows down the heart rate
B
○ (-) Dromotropic
Ejection fraction: how much is expelled from ● Slower conduction of signals from SA node
the heart; 50-70%: normal
● Decrease conduction of heart cells
Structural heart disease with symptoms of through AV node
heart failure such as fatigue, shortness of ○ Increase stroke volume
C
breath, edema, and decrease in physical
activity DIGOXIN (LANOXIN)
Severe structural heart disease and marked
D ● A secondary drug of choice for heart failure
symptoms of heart failure at rest
● Indications: Heart Failure, Atrial Fibrillation (rapid
Right Sided Heart Failure beating)
●
● Route: PO and IV
○ Mainly systemic s/sx
● t ½: 36 hours (once a day)
● Abdominal pain, fatigue, bloating, nausea,
dependent pitting edema, ankle edema, ● Low protein binding power
ascites, jaundice, hepatomegaly, ● 30% metabolized by the liver
decreased urine output (lesser blood sa ● 65% excreted by the kidneys unchanged
kidneys), increase CVP, HPN ● Serum level for dysrhythmias: 0.8-2.0 ng/ml
● Serum level for heart failure: 0.5 – 1.0 mg/ml
● Right atrium will return blood/fluid to the
systemic circulation ● Toxic level: >2-3 ng/ml
● Contraindications: Ventricular Fibrillation (fast AV
○ Peripheral edema
Left Sided Heart Failure node; hypokalemia)
●
● SIDE EFFECTS
○ Mainly respiratory s/sx
● Dyspnea, orthopnea, fatigue, restlessness, ○ N/V, diarrhea, abdominal pain, confusion,
crackles, peripheral cyanosis, dry weakness, blurred vision
non-productive cough, frothy blood tinged ● ADVERSE REACTIONS
mucus ○ Bradycardia, Cardiac Dysrhythmias,
Thrombocytopenia
NCM 0106 | Surname, Name|2
MODULE 12 & 13 – DRUGS ACTING ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
● Prior Nursing Intervention: read ECG ● Drugs used to treat Angina Pectoris (a condition of
acute cardiac/chest pain caused by inadequate
DIGITALIS TOXICITY (CARDIOTOXICITY) myocardial perfusion due to either plaque
formation or coronary artery spasms)
● Signaled by emerging side effects ○ Could lead to Myocardial Infarction or a heart
● Serum levels exceeds 3 ng/ml attack
● Elderly are more prone to develop toxicity ● Three types of Angina Pectoris
○ Because the elderly have degenerating ○ Stable Angina (Classis): Predictable, occurs
excretory system, the liver ages, thus having following physical exertion or stress
higher chances of not excreting excess level of ○ Unstable Angina (Preinfarction)
digitalis ● Unpredictable, may occur even at rest.
○ S/Sx: Confusion, Irregular pulse, N/V, Diarrhea, ● Occurs frequently over the course of a day
Vision Changes, Appetite Loss with progressive severity
○ Gastrointestinal distress: Anorexia and/or ○ Variant (Prinzmetal, Vasospastic): occurs
diarrhea (earliest signs), salivation and during rest
abdominal pain ● Typical pain is described as originating in the
○ Neurological effects: restlessness, irritability, center of the chest, radiating to the left arm and
headache, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, and neck
/or confusion, visual disturbances (blurred or ● Decreased blood flow, decreased oxygen
colored vision, halo vision, amblyopia, and myocardium leading to pain lasting for a few
diplopia minutes
○ Cardiac effects: cardiac dysrhythmias, - - ● S/sx: tightness, pressure in the center of the chest
● Phenytoin and Lidocaine are effective in treating and pain radiating down the left arm, neck (severe
digoxin toxicity induced ventricular dysrhythmias AP)
○ Controls only the symptoms brought about by
the toxicity but not correct the toxicity THREE TYPES OF ANTIANGINALS
● Antidote: Digoxin-Immune Fab (Digifab, Digibind)
○ These antidotes bind with digitalis compound = ● Increase blood flow either by increasing oxygen
excreted together = lower digoxin level supply od by decreasing oxygen demand by
myocardium
DIGOXIN DRUG INTERACTIONS
NITRATES
● (+) potent diuretics – digitalis toxicity
○ Diuretics: Furosemide (Lasix), ● Developed in 1840s
Hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril) ● First agents used to relieve angina
○ Furosemide and thiazides promote K loss ● Act on smooth muscle and the blood vessels
(hypokalemia) causing relaxation and dilation
● (+) Cortisone preparations – digitalis toxicity ○ Promotes generalized and coronary
○ Promotes Na retention and K loss when taken vasodilation
systematically ● Decreases preload and afterload and reduces
● (+) Antacids, bulk forming laxatives – decreased myocardial oxygen demand
digitalis absorption ● NITROGLYCERIN (NTG)
○ Most used nitrate
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES ○ Preparations: Sublingual (SL) tablets, ointment,
transdermal patch, extended release capsules,
● Obtain drug history aerosol sprays
● Record baseline PR at the apical pulse for one full
○ NTG SL → internal jugular vein → right atrium
minute; withhold drug if pulse is > 60 bpm
○ Side Effects: HA, postural hypotension, dizziness,
● Recommend potassium rich food sources as weakness and faintness, myocardial ischemia
permitted in diet (rebound effect), reflex tachycardia, and
● Monitor serum digoxin levels (0.8 – 2 ng/ml) syncope
● Instruct to report signs and symptoms of toxicity
○ Drug Interactions
● (+) other vasodilators = risk for
B. ANTIANGINALS hypotension greatly increases
NCM 0106 | Surname, Name|3
MODULE 12 & 13 – DRUGS ACTING ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
● (+) heparin = antagonized heparin effect
when given NTG is given as an IV dose ● Blocks Beta receptors → decrease effects of
○ NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES sympathetic NS → block release of catecholamines
● Monitor vital signs (NE/Epi) → decrease HR and BP
● Have client sit and lie down during ● Blocks Beta 1 and Beta 2 receptors
administration ● For classic angina (anti-angina) decrease HR,
● Offer sips of water before giving sublingual decrease myocardial contractility → decrease
nitroglycerin oxygen consumption → decrease pain of angina
○ Dryness of the oral mucosa might
● Decreases sympathetic nervous stimulation of
affect the absorption of the
cardiac muscles
medication
● Decreased HR leads to decreased cardiac muscle
● If chest pain persists after 3 doses of NTG
oxygen demand which can reduce angina
SL, instruct client to do to nearest hospital
● Non-selective beta blockers
● Tolerance to nitrates may develop die to
○ Blocks Beta 1 & 2
continued increase in dosage and
○ Decrease HR, bronchoconstriction
prolonged use
○ Ex: Propranolol (Inderal), Nadolol (Cogard),
● Ointment: do not use finger, instead use
Pindolol (Visken)
gloves of tongue depressor
○ Contraindications: Asthma because of the
● Transderm patch: do not touch the
broconstricting effect
medication portion
○ S/E: bronchospasm, psychotic response,
○ Rotate sites: thighs and arms can be
impotence, bradycardia, hypotension
used
● Selective beta blockers (Cardioselective)
○ Avoid hairy areas (may shave to
○ Blocks Beta 1
increase absorption)
○ Decrease HR
● Do not apply on the chest in the vicinity of
○ Ex: Atenolol (Tenormin), Metoprolol (Neobloc,
defibrillator-cardioverter paddle
Lopressor)
● Avoid alcohol ingestion
○ S/E: decrease HR (bradycardia), decrease BP
● Store bottle away from light
(hypotension)
○ Might lose potency
● Burning and stinging sensation means the
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
drug is potent
● Instruct client not to discontinue these ● Also known as CCBs
drugs without healthcare provider’s ● First introduced in 1982 for the treatment of stable
approval = withdrawal symptoms may be and variant angina, hypertension and certain
severe dysrhythmias
● NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL WAYS ● Calcium
○ Avoid heavy meals, smoking, ○ Increases myocardial contractions
extremes weather changes, ○ Increased workload of the heart
strenuous exercise, emotional upset ○ Increases oxygen need/consumption
○ Moderate exercise, rest, relaxation ● Calcium-channel blockers - blocks Ca
techniques ○ Exert dilating effect on coronary arteries and
● Perform pain assessment peripheral blood vessels by inhibiting calcium
● Monitor blood pressure, report hypotension → coronary vasodilation and increase blood
● If NTG patch is about to be discontinued, flow and lower BP
taper down dose prior to discontinuation ○ Negative inotropics and decreases afterload
of drug which help decrease cardiac oxygen demands
● Wear gloves when applying transdermal ● CCBs relax coronary artery spasms and peripheral
preparations arterioles
● Advise patient to refrain from doing ● CCBs are negative inotropes and decreases
activities requiring alertness afterload which help decrease cardiac oxygen
● Educate patient about orthostatic demand
hypotension ● Examples
○ “-dipine”
BETA BLOCKERS ○ Amlodipine, Nifedipine, Nicardipine, Felodipine
NCM 0106 | Surname, Name|4
MODULE 12 & 13 – DRUGS ACTING ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
○ **Verapamil HCl, Diltiazem HCl TYPES OF ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC DRUGS
● Routes: PO, IV
● Common side effects: Hypotension, Bradycardia, CLASS 1 - NA CHANNEL BLOCKERS – FAST
Dizziness, Headache
● Decreases Na ion influx which decreases
C. ANTIDYSRHYTHMICS conduction velocity and suppresses automaticity
● 1A
● Cardiac Dysrhythmia (Arrhythmia) ○ Slows conduction and prolong repolarization
○ Any deviation from the normal rate and pattern ○ Ex: Quinidine, Procainamide
(normal sinus rhythm) of the heartbeat; ● 1B
bradycardia, tachycardia, irregular heart ○ Slows conduction and shortens repolarization
rhythm ○ Ex: Lidocaine HCl
○ Often follow a myocardial infarction or as a ● 1C
result of hypoxia or hypercapnia ○ Prolongs conduction with little effect on
○ Dysrhythmia (distured heart rhythm) repolarization
○ Arrhythmia (absence of rhythm) ○ Ex: Propafenone
○ Atrial dysrhythmia - prevent proper filling of
ventricles and decrease the CO by ⅓ CLASS 2 - BETA BLOCKERS
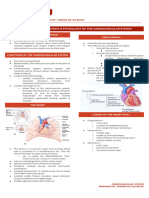
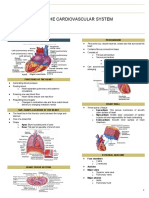
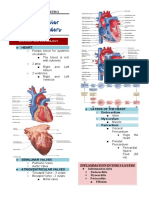
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG) ● Block sympathetic activity → decrease
contractility, BP, AV node conduction, and enhance
repolarization
● Decreases conduction velocity, automaticity and
refractory time
● Ex: Propranolol (Inderal)
CLASS 3 - POTASSIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
● Drugs that prolong repolarization
● Prolong action potential and delay repolarization
and refractory period
● Increases the refractory period, and prolongs the
action potential duration
● Ex: Amiodarone HCl (Cordarone)
CLASS 4 - CA CHANNEL BLOCKERS
● P wave - atrial depolarization (contraction) ● Inhibit movement of calcium ions decreasing
● QRS wave - ventricular depolarization (contraction) excitability and contractility of the myocardium
● T wave - ventricular repolarization (relaxation) ● Most effective at the SA and AV nodes to reduce
● PQ interval - atrial repolarization (relaxation) rate of contraction
● Dilate coronary arteries and increase blood flow to
5 PHASES OF A HEARTBEAT the myocardium
Travel of the cardiac action potential across the heart ● Decreasing excitability and is a negative inotropic
PHASE EVENT agent
0 Rapid depolarization caused by Na influx ● Ex: Verapamil (Calan), Diltiazem (Cardizem)
● SIDE EFFECTS
Initial repolarization which coincides with
1 ○ Cardiovascular depression, hypotension,
the termination of Na ions influx
bradycardia, confusion, nausea and vomiting
2 Plateau associated with the influx of Ca ions
● NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Rapid repolarization caused by the influx of ○ Obtain baseline VS and ECG
3
K ions
● Hypotension and bradycardia
4 Resting membrane potential ○ Perform objective pain assessment
○ Monitor cardiac enzymes/markers
NCM 0106 | Surname, Name|5
You might also like
- 12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- RT 105 Finals NotesDocument24 pagesRT 105 Finals NotesLouiseNo ratings yet
- Cardio Renal MedicationsDocument14 pagesCardio Renal MedicationsHarly E. DeniegaNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument9 pagesCARDIOVASCULARcsfcfssfNo ratings yet
- CMS RNDocument88 pagesCMS RNday alcoberNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument28 pagesCardioMerald PerdigonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System OverviewDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System OverviewJanet Floreno VillasanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs and the Renin-Angiotensin SystemDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Drugs and the Renin-Angiotensin SystemAngel DiangNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemFisco DessereiNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Group 1Document92 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Group 1Jefferson AdralesNo ratings yet
- The Heart - Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartDocument10 pagesThe Heart - Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartLol lolNo ratings yet
- Med Surg MidtermDocument17 pagesMed Surg Midtermjhan grabierNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy and Blood FlowDocument11 pagesHeart Anatomy and Blood FlowAysha AishaNo ratings yet
- KNES320 NotesDocument55 pagesKNES320 NotesOlamide GNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysioDocument9 pagesCardiac Physiosakuragi jakeNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology & Urine Formation: Biology 25 A. SantiagoDocument39 pagesCardiovascular Physiology & Urine Formation: Biology 25 A. Santiagoapi-3826751No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 10Document34 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 10weissNo ratings yet
- 28-31 Cardiovascular ProblemsDocument34 pages28-31 Cardiovascular ProblemsdelarakrishnafaithpNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Physiology Circulatory System: BIOL212 11/8Document96 pagesCardiac Physiology Circulatory System: BIOL212 11/8mary ann aquinoNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR LECTURE: TERMINOLOGY AND CIRCULATIONDocument7 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR LECTURE: TERMINOLOGY AND CIRCULATIONAnabelle RicoNo ratings yet
- Guyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 14 PDFDocument4 pagesGuyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 14 PDFOsman NazirNo ratings yet
- BIOL212 Fa 21 Lecture 27 PostedDocument73 pagesBIOL212 Fa 21 Lecture 27 Postedmary ann aquinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemJenny Torreda100% (1)
- NCM 112 - Med SurgDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Med SurgKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- The-Cardiovascular-System Notes MariebDocument7 pagesThe-Cardiovascular-System Notes MariebLol lolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular 1Document7 pagesCardiovascular 1simonedarling100% (2)
- Structure of The Heart TransesDocument6 pagesStructure of The Heart TransesReign SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Tara's Anatomy and Physiology - Aehlert ECGs Made EasyDocument16 pagesTara's Anatomy and Physiology - Aehlert ECGs Made EasyTara McNeillNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 Midterms ReviewerDocument7 pagesNCM 118 Midterms ReviewerKai SamaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Anatomy and Physiologyino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Happ Finals Week 13Document8 pagesHapp Finals Week 13angelaggabao0No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular SystemChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Biology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryDocument13 pagesBiology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryMa. Teresa M. AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and Respiratory Practice QuestionsDocument15 pagesBlood Vessels and Respiratory Practice QuestionsRACHEL VERA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Transport in Plants and Animalstffnllrnt1215No ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument18 pagesHeart Anatomy & Physiologygeng gengNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ATU (Autosaved)Document58 pagesCardiovascular System ATU (Autosaved)maxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Viva Emergencies & EthicsDocument93 pagesViva Emergencies & EthicsPei Xing KwekNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure (Page Print 1-4)Document4 pagesBlood Pressure (Page Print 1-4)hihariv794No ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumansDocument19 pages3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumanslovenialawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 StudentsDocument6 pagesChapter 12 StudentsJohn Paul CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Heart: Dr. Aditya Reza Pratama Dr. Yusuf Arifin Dr. Sasmojo Widito, SP - JP (K)Document34 pagesAnatomy of The Heart: Dr. Aditya Reza Pratama Dr. Yusuf Arifin Dr. Sasmojo Widito, SP - JP (K)Nur FarinahNo ratings yet
- Major Arteries of the Body: Aorta, Carotids, Subclavians & MoreDocument11 pagesMajor Arteries of the Body: Aorta, Carotids, Subclavians & MoreagzbNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy Circulation: BIOL212 10.27.2021 11/1Document69 pagesCardiac Anatomy Circulation: BIOL212 10.27.2021 11/1mary ann aquinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular SystemDocument29 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular SystemDhanica B. FiguracionNo ratings yet
- UPDATED Lesson Guide Dysrhythmias .Docx 118ADocument21 pagesUPDATED Lesson Guide Dysrhythmias .Docx 118ARiri MiguelNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Lecture on Heart ConditionsDocument68 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Lecture on Heart ConditionsShanine Alexia CordovezNo ratings yet
- HLTAAP002 CardiovascularDocument56 pagesHLTAAP002 CardiovascularJesse SimonNo ratings yet
- CH 14 HeartDocument43 pagesCH 14 HeartTricia Rose KnousNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ANAPIYA Finale Part 1Document9 pagesReviewer in ANAPIYA Finale Part 1Llyana paula SuyuNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec CardioDocument12 pagesAnaphy Lec CardioRyan Dave UmayamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument14 pagesCardiovascular Disordergwyneth guintuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular SystemDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Simple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoDocument157 pagesSimple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoRenato Bandeira100% (4)
- Car As R S Te: Blo SeDocument17 pagesCar As R S Te: Blo SeBenedict De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- 06.2 Care of Couples With Fertility ProblemsDocument9 pages06.2 Care of Couples With Fertility ProblemsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 08 - LEC Family Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pages08 - LEC Family Nursing Care PlanJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 05.3 Problems of The Power and Psyche PDFDocument12 pages05.3 Problems of The Power and Psyche PDFJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 06.1 High-Risk Postpartal ClientDocument22 pages06.1 High-Risk Postpartal ClientJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 07 Nursing Role in The Health of Ill Children and Their FamiliesDocument20 pages07 Nursing Role in The Health of Ill Children and Their FamiliesJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- MCN REVIEW FOR MIDTERMSDocument5 pagesMCN REVIEW FOR MIDTERMSJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Levels of clientele in community nursing and key Philippine health lawsDocument1 pageLevels of clientele in community nursing and key Philippine health lawsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 06.1 High-Risk Postpartal ClientDocument22 pages06.1 High-Risk Postpartal ClientJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Care for high-risk pregnant women with diabetesDocument27 pagesCare for high-risk pregnant women with diabetesJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 03 Second Trimester ConditionsDocument7 pages03 Second Trimester ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 01.1 High-Risk Prenatal ClientDocument18 pages01.1 High-Risk Prenatal ClientJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 02 First Trimester ConditionsDocument12 pages02 First Trimester ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 05.2 Problems of The PassageDocument5 pages05.2 Problems of The PassageJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child with Acute ProblemsDocument16 pagesCare of Mother and Child with Acute ProblemsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Level 2 - Prelim Exam Guidelines 2023Document2 pagesLevel 2 - Prelim Exam Guidelines 2023JAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 04 Third Trimester ConditionsDocument11 pages04 Third Trimester ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Requirements Level 2 OPDDocument5 pagesRequirements Level 2 OPDJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Oia Keisha PDFDocument7 pagesOia Keisha PDFJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 2518-Article Text-13816-1-10-20201215Document6 pages2518-Article Text-13816-1-10-20201215JAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Care for high-risk pregnant women with diabetesDocument27 pagesCare for high-risk pregnant women with diabetesJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Le3 Oia PDFDocument12 pagesLe3 Oia PDFJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 2554-Article Text-13960-1-10-20201220Document9 pages2554-Article Text-13960-1-10-20201220JAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Proper HygieneDocument10 pagesMaintaining Proper HygieneJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 07 - LEC Care of The NewbornDocument17 pages07 - LEC Care of The NewbornJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 05 - LEC The Family and Family HealthDocument5 pages05 - LEC The Family and Family HealthJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 16NBSHemoglobinDisorders IJNS2021Document13 pages16NBSHemoglobinDisorders IJNS2021JAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- 04-05 - LEC Intrapartal Care and The Labor PhenomenonDocument29 pages04-05 - LEC Intrapartal Care and The Labor PhenomenonJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3Document3 pagesNCP Format 3JAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Arpèges de Trois Notes: Arpeggios in TripletsDocument3 pagesArpèges de Trois Notes: Arpeggios in TripletspanapapakNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Water and Non-Aqueous SolventsDocument41 pagesDispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Water and Non-Aqueous SolventsSantiago OrtizNo ratings yet
- WordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsDocument21 pagesWordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsNgô Ngọc Hải phươngNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of Basey SamarDocument28 pagesArts and Crafts of Basey SamarTrisha MenesesNo ratings yet
- 3M NLP White PaperDocument12 pages3M NLP White PaperJayampathi SamarasingheNo ratings yet
- Improve Product Packaging at Annual Board MeetingDocument9 pagesImprove Product Packaging at Annual Board Meetingizzat89% (9)
- Telangana Energy Dept Contact NumbersDocument27 pagesTelangana Energy Dept Contact Numbersstarpowerzloans rjyNo ratings yet
- MF ISIN CodeDocument49 pagesMF ISIN CodeshriramNo ratings yet
- LFJ All OrdersDocument195 pagesLFJ All Orderskate jackNo ratings yet
- Orphanage Cum Old Age Home: Amruta Prakash BedmuthaDocument2 pagesOrphanage Cum Old Age Home: Amruta Prakash BedmuthaNamrata Bhandari100% (1)
- Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesGray Iron Castings: Standard Specification Forsafak kahramanNo ratings yet
- From Birth Till Palatoplasty Prosthetic.20Document5 pagesFrom Birth Till Palatoplasty Prosthetic.20Maria FernandaNo ratings yet
- Capacity Based On Shear Parameters As Per IS 6403: C C C C W Q Q Q Q F y y y yDocument5 pagesCapacity Based On Shear Parameters As Per IS 6403: C C C C W Q Q Q Q F y y y yKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Deep Learning Activation Functions When To Use ThemDocument15 pagesFundamentals Deep Learning Activation Functions When To Use ThemfaisalNo ratings yet
- Rate of ChangeDocument22 pagesRate of ChangeTrisha MariehNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Permafrost and Ground-Ice IPA 2005Document159 pagesGlossary of Permafrost and Ground-Ice IPA 2005NatitaGonzàlezDíazNo ratings yet
- T e 2552674 Percy Polls Peculiar Plants Fiction Year 5 Reading Comprehension - Ver - 5Document20 pagesT e 2552674 Percy Polls Peculiar Plants Fiction Year 5 Reading Comprehension - Ver - 5mariam osamaNo ratings yet
- SECURED TRANSACTION BAR CHECKLISTDocument4 pagesSECURED TRANSACTION BAR CHECKLISTatw4377100% (1)
- Weap - ModflowDocument20 pagesWeap - Modflowguive3No ratings yet
- CAPS LESSON PLAN, KAHOOT QUIZ, PPT VIDEODocument3 pagesCAPS LESSON PLAN, KAHOOT QUIZ, PPT VIDEOMandisa MselekuNo ratings yet
- E-Way BillDocument1 pageE-Way BillShriyans DaftariNo ratings yet
- Lifeboat Equipment ListDocument1 pageLifeboat Equipment Listjosua albertNo ratings yet
- CV Jubilee Bubala Environmental SpecialistDocument4 pagesCV Jubilee Bubala Environmental SpecialistNomayi100% (2)
- Mordaunt Short ms907w User ManualDocument12 pagesMordaunt Short ms907w User ManualiksspotNo ratings yet
- Lyrics: Original Songs: - JW BroadcastingDocument56 pagesLyrics: Original Songs: - JW BroadcastingLucky MorenoNo ratings yet
- BISE Sukkur HSC Part 2 Results 2015Document12 pagesBISE Sukkur HSC Part 2 Results 2015ajayNo ratings yet
- Kristine Jane T. Zipagan Assignment: 1. Parts of InfographicsDocument2 pagesKristine Jane T. Zipagan Assignment: 1. Parts of InfographicsChristyNo ratings yet
- Vocabulario Ingles 3 EsoDocument6 pagesVocabulario Ingles 3 EsoPatri ParrasNo ratings yet
- MSDS Slideway Oil Iso VG 68 - 031115Document6 pagesMSDS Slideway Oil Iso VG 68 - 031115Rini SiskayantiNo ratings yet
- Regional Campus The English and Foreign Languages UniversityDocument2 pagesRegional Campus The English and Foreign Languages UniversitySidra KhanNo ratings yet