Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASEXUAL AND SEXUALREPRODUCTIO Ext
Uploaded by
Makanaka Sambureni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesOriginal Title
ASEXUAL AND SEXUALREPRODUCTIO ext - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesASEXUAL AND SEXUALREPRODUCTIO Ext
Uploaded by
Makanaka SambureniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
1
REPRODUCTION
• reproduction is the ability of living organisms to produce a new generation of
themselves
• reproduction results in the continuation of a species thus preventing extinction
• reproduction may be sexual or asexual
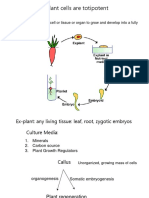
Asexual reproduction in plants
• It is the process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring
from one parent.
• Does not involve gametes or fertilization
• Some of the cells of the parent organism divide by a kind of cell division
called mitosis.
Examples of asexual reproduction
• Binary fission in bacteria
• Spore formation in fungi
• Reproduction by budding in yeast cells
• Production of potato tubers
• Production of new plants from runners
Advantages of asexual reproduction to a population of species in the wild:
➢ It is fast allowing organisms to colonise large areas quickly.
➢ Offspring are well-suited to parents’ environment, large numbers of offspring
are produced
➢ Only one parent needed hence plants grow quickly.
➢ Food is usually present in large vegetative structures: hence this gives the new
plants a better chance of survival. A rapid development of buds into
daughter plants can take place.
➢ It is an easy process as no external agents e.g. insects and wind for
pollination and fertilization are required, so plants grow more quickly.
➢ It takes less energy investment since sex structures don’t have to be
produced.
2
➢ The daughter plants resemble the parent plant in all aspects. Hence it
preserves all the desirable characteristics, as these are passed on directly
without any change.
Advantages to crop production:
➢ Preserves the desirable characteristics e.g. large and attractive flowers, good
flavor, high yields, etc.
➢ Offspring’s characteristics are known
➢ Offspring are guaranteed.
➢ Some plants are only propagated asexually because they don’t produce
viable seeds e.g. bananas, sugarcane, potato, etc. Seedless varieties of fruits
are also a result of vegetative propagation.
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction to a population of species in the wild:
o No variation possible from generation to generation, so no chances of
evolution. No improvement is possible.
o Since all offspring are clones (identical), they may all be wiped out by same
pests/diseases. Hence prone to extinction.
o Lack of dispersal can lead to competition for nutrients, water, oxygen, carbon
dioxide, light and space since plants are overcrowded.
o There is very little adaptation to changing environments. A population could
be wiped out by unfavourable conditions like extreme temperatures, frost
and disease.
o undesirable characteristics are passed on to offspring
o Difficult to produce large numbers of plants that could be produced from
seeds even if this method is rapid.
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction to crop production
• Plants gradually lose their vigour as there is no genetic variation.
3
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
• Sexual reproduction is a process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two
gametes (sex cells) to form a zygote and the production of offspring that are
genetically different from each other.
• The number of chromosomes in a species is fixed and is the same in all of its
body cells e.g. human cells contain 46 chromosomes; garden pea cells
contain 14; mice contain 40, etc. The number of chromosomes in each body
cell of a plant or animal is called the diploid number. The chromosomes
always appear in pairs: hence the diploid number is always an even number.
• Two parents are needed to produce new organisms in sexual reproduction.
This involves sex cells or gametes. These are formed in the reproductive
organs.
• In animals the male gametes are sperm cells and the female gametes are
egg cells (ova). In flowering plants the male gametes are nuclei inside pollen
grains and female gametes are inside the ovules.
• Gametes) contain only half the diploid number of chromosomes. This number
is called the haploid number.
• During sexual reproduction, the nuclei of male and female gametes (haploid
cells) fuse to form a new diploid cell called a zygote. This fusion of gamete
nuclei to form a zygote is termed fertilization.
Advantages of sexual reproduction to a population of a species
➢ Brings about variation in the offspring
➢ More genetic diversity: There is good chance that at least some of the
offspring be resistant to certain diseases or adapted to certain environments:
Offspring can adapt to new environments better
➢ There are higher chances of evolution
➢ It helps natural selection to remove harmful mutations from the population
➢ In plants seeds are dispersed from one parent plant so there is less
overcrowding and less competition for resources
4
Advantages of sexual reproduction to crop production
• Ability to influence offspring favorably by selective breeding.
• A disease is less likely to affect all the individuals in a population
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction
➢ Two parents are needed and fertilization is required.
➢ Growth to maturity is slow; not as rapid and efficient as other forms of
reproduction.
➢ Plant reproduction depends on external agencies for pollination and
dispersal.
➢ Offspring are not guaranteed that is, not every act of sexual reproduction is
guaranteed to produce an offspring.
➢ Lots of genetic material is wasted e.g. a lot of sperms are produced yet only
one is required to fertilise an egg.
➢ There is a chance for mutations to happen.
➢ Energy must be consumed to find a suitable mate.
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument13 pagesAsexual Reproductionkritishaa8100No ratings yet
- Heirloom Seeds: An Introduction to Organic Heirloom Seeds, Growing Them, and Their BenefitsFrom EverandHeirloom Seeds: An Introduction to Organic Heirloom Seeds, Growing Them, and Their BenefitsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in Plantsnell jaesNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Advs and DisadvsDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction Advs and DisadvsMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesReproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual Reproductionstephenalfa7No ratings yet
- (Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDocument125 pages(Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDavis ShamolmolNo ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument27 pagesMethods of ReproductionMark Hernand GalapateNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument40 pagesPerpetuation of LifeDionne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Reproduction IntroductionDocument4 pagesLesson 9 - Reproduction IntroductionlemoniteNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Reproduction in OrganismDocument18 pagesChapter - 1 Reproduction in OrganismDr.MonikaShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction 11 061653Document22 pagesAnimal Reproduction 11 061653HeavenNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Yr12Document56 pagesBiology Notes Yr12Marc GiangrassoNo ratings yet
- MicropropagationDocument30 pagesMicropropagationBrigitte ReyesNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION NOTES For ExamDocument11 pagesREPRODUCTION NOTES For ExamdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Complete Year 12 HSC Biology SummaryDocument45 pagesComplete Year 12 HSC Biology SummaryClaudiaNo ratings yet
- To Reviewgen BioDocument19 pagesTo Reviewgen Bioguia.mareeseNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument49 pages5.1.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionploysaejiwNo ratings yet
- To Ti Potency & PlasticityDocument14 pagesTo Ti Potency & PlasticityNasir Hussain FarazNo ratings yet
- Science 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideDocument21 pagesScience 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Reproduction 28 For Presentation 29Document120 pagesPlant and Animal Reproduction 28 For Presentation 29Elizaga ElizagaNo ratings yet
- HSC Biology Notes Module 5Document44 pagesHSC Biology Notes Module 5gemma.ie6No ratings yet
- OrganogenesisDocument65 pagesOrganogenesisNavodit GoelNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionPew Collado PlaresNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument17 pagesPlant Reproductionshaim xd.No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 16 Reproduction - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument9 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 16 Reproduction - CIE Biology IGCSEStudy GuyNo ratings yet
- Selectivebreedingpowerpoint 130416182435 Phpapp01Document18 pagesSelectivebreedingpowerpoint 130416182435 Phpapp01priarun18No ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument56 pagesMethods of ReproductionJhigo Villar Franco PascualNo ratings yet
- Asexual Repro NotesDocument23 pagesAsexual Repro NotesMs ZoyaNo ratings yet
- Ms. Reeta Kaul Science Facilitator at M.L.Khanna D.A.V Public School, DwarkaDocument42 pagesMs. Reeta Kaul Science Facilitator at M.L.Khanna D.A.V Public School, DwarkaHu la laNo ratings yet
- Vegetative PropagationDocument4 pagesVegetative PropagationHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Culture: Used For 1. Micropropagation 2. RegenerationDocument21 pagesPlant Tissue Culture: Used For 1. Micropropagation 2. RegenerationAysha MohideenNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesREPRODUCTIONElisa EstebanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Spectrum SquareDocument15 pagesReproduction Spectrum SquareAgastya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualDocument26 pagesBiology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualGeorge EskandarNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION L1 (Prashant Kirad)Document46 pagesREPRODUCTION L1 (Prashant Kirad)superherosunny13No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 - Reproduction & InheritanceDocument18 pagesBiology Unit 3 - Reproduction & Inheritancethisismashael07No ratings yet
- HSC Biology Module 5Document21 pagesHSC Biology Module 5adneeniqbal259No ratings yet
- Biological Diversity: Reproduction and SurvivalDocument37 pagesBiological Diversity: Reproduction and SurvivalNick YamNo ratings yet
- Digos City National High School Senior High School Quarter 2 (Week 2) Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesDigos City National High School Senior High School Quarter 2 (Week 2) Earth and Life Sciencejanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsphemelomashumbaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction 1Document92 pagesAsexual Reproduction 1Zerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument22 pagesMethods of ReproductionAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization in PlantsDocument24 pagesDouble Fertilization in PlantsAshmit Srinjoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- 10 Somatic Embryo and Synthetic SeedDocument28 pages10 Somatic Embryo and Synthetic SeedDivyacrotu MajumderNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ReproductionDocument77 pagesIGCSE ReproductionTonkaaw KatayouwongchareonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Notes PDFDocument26 pagesGen Bio 2 Notes PDFDALA, ALLYZA ISABELLE A.No ratings yet
- E. Animal ReproductionDocument18 pagesE. Animal ReproductionJudy Ann CastorNo ratings yet
- Asexual V Sexual ReproductionDocument16 pagesAsexual V Sexual ReproductionFi SonnetNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument44 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionAntonio BulaonNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentDocument22 pagesPlant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentNix TanNo ratings yet
- Q2 Lesson 3 Part 1Document81 pagesQ2 Lesson 3 Part 1mrfwbsttr9No ratings yet
- Questions Plants AnimalsDocument10 pagesQuestions Plants AnimalsPrince LancelotNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 ReproductionDocument23 pagesLesson1 ReproductionshusuishigakiNo ratings yet
- Class 12-Biology (CHSE &CBSE) Chapter-01: Reproduction in OrganismsDocument6 pagesClass 12-Biology (CHSE &CBSE) Chapter-01: Reproduction in OrganismsAbhipsa dash nikyNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plants ReproductionDocument95 pagesAnimal and Plants ReproductionMark Repollo100% (1)
- Q4 Week 3 - ELSDocument7 pagesQ4 Week 3 - ELSAgatha KimNo ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument26 pagesMethods of Reproductioncmillica1176No ratings yet
- AsexualDocument4 pagesAsexualAR JAY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiDocument27 pagesChapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiAbcNo ratings yet
- Angles Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocument2 pagesAngles Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesLogic Gates Practice QuestionsMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Demonstrative Adjectives (Autosaved)Document14 pagesDemonstrative Adjectives (Autosaved)Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Markscheme AnswersDocument31 pagesMid Year Markscheme AnswersMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document3 pagesTask 3Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument21 pagesAsexual ReproductionMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Industry Pt3 - Employment StructuresDocument5 pagesIndustry Pt3 - Employment StructuresMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Commercial LayersDocument25 pagesCommercial LayersMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in HumansMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 20 January - Proper Nouns 1Document1 pageWednesday 20 January - Proper Nouns 1Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Thursday 21 January Common Noun Vs Proper NounDocument1 pageThursday 21 January Common Noun Vs Proper NounMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Task 2Document4 pagesTask 2Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geography TestDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Geography TestMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 20 January - Proper Nouns 1Document1 pageWednesday 20 January - Proper Nouns 1Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Specimen P2 Section BDocument10 pagesCambridge English Specimen P2 Section BMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Acfrogcams41lkykrvhmog3fx7sg FQFL Uxxhoasnl2bs66zvjxojromg1n Hp4daxoytgkbeqk Ihcwpshf9m1cdmbie Ukaqqaacjeeyoygnwjbhbjj 1fabpf0bshp9egrftitquxxumlehnDocument10 pagesAcfrogcams41lkykrvhmog3fx7sg FQFL Uxxhoasnl2bs66zvjxojromg1n Hp4daxoytgkbeqk Ihcwpshf9m1cdmbie Ukaqqaacjeeyoygnwjbhbjj 1fabpf0bshp9egrftitquxxumlehnMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Industry Pt2 - Factors Influencing Industry LocationDocument7 pagesIndustry Pt2 - Factors Influencing Industry LocationMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- ClassTT 1HDocument1 pageClassTT 1HMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Science Stage 8 Sample Paper 1 Mark Scheme - tcm143-595704Document12 pagesScience Stage 8 Sample Paper 1 Mark Scheme - tcm143-595704Makanaka Sambureni100% (7)
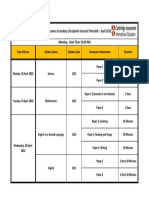
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint General Timetable May 2022Document1 pageCambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint General Timetable May 2022Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Acfrogafik4uldv02q6kmm Amg3fkzzdgaluacxpwxxoyri8aw3lcl7itaakx3p4z6vnfw U Icvkdnmjfodu4po4gk25rpu8nggy3gzqqwlmoc084l Visb1sg7cq5lh88xw6va Fu7elpzkwnrDocument8 pagesAcfrogafik4uldv02q6kmm Amg3fkzzdgaluacxpwxxoyri8aw3lcl7itaakx3p4z6vnfw U Icvkdnmjfodu4po4gk25rpu8nggy3gzqqwlmoc084l Visb1sg7cq5lh88xw6va Fu7elpzkwnrMakanaka Sambureni100% (1)
- Arbitral Award - Wicks Vs COTTCODocument10 pagesArbitral Award - Wicks Vs COTTCOMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science P2 2016Document24 pagesCambridge Science P2 2016Makanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English 2017 Paper 1 Section ADocument12 pagesCambridge English 2017 Paper 1 Section AMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - General PaperDocument1 pageSocial Studies - General PaperMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Heroes Day PresentationDocument6 pagesHeroes Day PresentationMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Transport and CommunicationDocument1 pageTransport and CommunicationMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Chisz Entrance Assessment Section BDocument1 pageChisz Entrance Assessment Section BMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Vertical Isolation VCBEnglishDocument1 pageVertical Isolation VCBEnglishdip461No ratings yet
- Introduction To Reproduction PDFDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Reproduction PDFLmssvNo ratings yet
- Zetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFDocument234 pagesZetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFAntonNo ratings yet
- Wjec Biology SpectificaionDocument93 pagesWjec Biology SpectificaionLucy EvrettNo ratings yet
- Genie Z45/22Document58 pagesGenie Z45/22jonny david martinez perezNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainDocument3 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainPkNo ratings yet
- 100 Years of Hydrodynamic PDFDocument28 pages100 Years of Hydrodynamic PDFnikodjoleNo ratings yet
- Streamline SWR (S) - Rev - 00-04-2019 PDFDocument2 pagesStreamline SWR (S) - Rev - 00-04-2019 PDFarjun 11No ratings yet
- Icpc11 - Thermodynamics and Fluid MechanicsDocument22 pagesIcpc11 - Thermodynamics and Fluid MechanicsAPARNANo ratings yet
- HardikDocument21 pagesHardikGohil HardikNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesMagneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Movimiento Circular, Momentun Lineal y EnergíaDocument92 pagesMovimiento Circular, Momentun Lineal y EnergíaJulio César Macías ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Only Milling Since 1967Document16 pagesCompany Profile: Only Milling Since 1967PavelNo ratings yet
- The Failed Rotator CuffDocument307 pagesThe Failed Rotator Cufforthofitness2017No ratings yet
- AVR Brosure Basler Decs 100Document2 pagesAVR Brosure Basler Decs 100NikolayNo ratings yet
- TOP233YDocument24 pagesTOP233YJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Food - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonDocument9 pagesFood - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonRotten AnarchistNo ratings yet
- Non-Pen MountDocument17 pagesNon-Pen MountT BagNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Adam HakimiNo ratings yet
- What's The Use of Neuroticism?: G. Claridge, C. DavisDocument18 pagesWhat's The Use of Neuroticism?: G. Claridge, C. DavisNimic NimicNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones Postoperatorias en Esofagectomía Por Cáncer. Evaluación de 215 Casos Según Definiciones Del Grupo de Consenso InternacionalDocument7 pagesComplicaciones Postoperatorias en Esofagectomía Por Cáncer. Evaluación de 215 Casos Según Definiciones Del Grupo de Consenso InternacionalPaulo RoseroNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Technical BrochurDocument7 pagesKomatsu Technical BrochurBenjamin MossoNo ratings yet
- NARS Fall 2011 Press File PDFDocument19 pagesNARS Fall 2011 Press File PDFheather_dillowNo ratings yet
- Faujifood Pakistan PortfolioDocument21 pagesFaujifood Pakistan PortfolioPradeep AbeynayakeNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning: VocabularyDocument9 pagesFood Poisoning: VocabularyHANG WEI MENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Daphne Alpha Cleaner Series: Lubricant Product InformationDocument2 pagesDaphne Alpha Cleaner Series: Lubricant Product InformationChart ChNo ratings yet
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocument10 pagesCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Cholera: Submitted ToDocument17 pagesAssignment On Cholera: Submitted ToEhesanulHaqueSaifNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Fire Loads For An Educational Building - A Case StudyDocument4 pagesEstimation of Fire Loads For An Educational Building - A Case StudyEditor IJSETNo ratings yet
- Scuba Diving - Technical Terms MK IDocument107 pagesScuba Diving - Technical Terms MK IJoachim MikkelsenNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)