Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Uploaded by
acurvz2005Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Uploaded by
acurvz2005Copyright:
Available Formats
REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES
OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT FOR CAMPUSES
LOPEZ, QUEZON CAMPUS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CIEN 20043 Steel & Timber Design February 3, 2024
QUIZ 2: Name: ___________________________
PART 1: Select the correct answer on the provided choices.
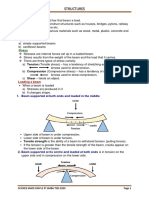
SHEAR STRESS BENDING STRESS DEFLECTION BEAM
SIMPLY SUPPORTED BEAM FIXED END BEAM PROPPED BEAM GIRDER
CANTILIVER BEAM FLOOR LOAD LIVE LOAD DEAD LOAD
MOMENT SHEAR & MOMENT DIAGRAM AXIAL LOAD STRESS
WIDE FLANGE I BEAM FLOOR JOIST COLUMN
1. A structural element that extends horizontally and is supported on only one end.
2. Refers to loads that do, or can, change over time, such as people walking around a building
(occupancy) or movable objects such as furniture.
3. A structure's static, non-moving weight or any permanent components that form an integral
part of it, including self-weight.
4. A type of beam stress produced by distribution of internal forces and moments within the
beam's cross-section as it undergoes deformation.
5. The movement or displacement of a beam or node from its original position due to vertical load.
6. A type of stress in beams that acts coplanar with a given cross-section of the material.
7. A type of beam that is rigidly supported at both ends.
8. The type of beam that supports the beams and provides the main horizontal support for the
structure.
9. A structural element that primarily resists the applied loads from the floor system.
10. A rotational force that occurs when a force is applied perpendicularly to a point at a given
distance away from that point.
11. Type of beams that rest on two supports and is free to move horizontally.
12. A type of steel structural materials that have a wider flange in which the beam can carry more
weight.
13. A type of steel structural material that has a narrow flange.
14. A horizontal structural member that is closely space, and often between beams.
15. Graphs which show the internal shear and bending moment plotted along the length of the
beam.
PART 2: Solve the following.
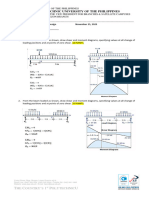
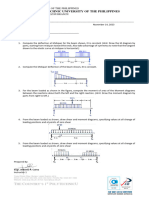
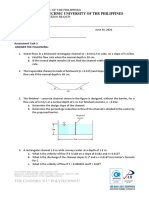
1. A beam 100 mm wide is to be loaded with 3 kN concentrated loads spaced uniformly at 0.40 m
on centers throughout the 5 m span. The following data are given: (15 points)
Allowable bending stress = 24 MPa
Allowable shear stress = 1.24 MPa
Allowable deflection = 1/240 of span
Modulus of elasticity = 18,600 MPa
Weight of wood = 8 kN/m3
a. Find the depth d considering bending stress only.
b. Determine the depth d considering shear stress only.
c. Calculate the depth d considering deflection only.
Prepared By:
Engr. Antonio P. Curva
Instructor 1
Yumul Street, Brgy. Burgos, Lopez Quezon 4316
Direct Line: (042) 3261256, (042) 302-5249 | Telefax No: (042) 841-1890
Website: www.pup.edu.ph | Email: lopez@pup.edu.ph
THE COUNTRY’S 1st POLYTECHNICU
You might also like
- Astm A123-15Document1 pageAstm A123-15AhmadNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument46 pagesBeam DesignAnik Sarker100% (1)
- Quiz 2 KTCDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Beam (Structure) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesBeam (Structure) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHare Krishna jhaNo ratings yet
- Beam StructureDocument6 pagesBeam StructureEdi YantoNo ratings yet
- TDS III Lec 2Document22 pagesTDS III Lec 2Selam MubarekNo ratings yet
- StructuresDocument23 pagesStructuresCarlos MenaNo ratings yet
- CE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument4 pagesCE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignSabarinath MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BEAMDocument25 pagesChapter 1 BEAMDawit TesfayNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure)Document6 pagesBeam (Structure)Alfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Shear StrengthDocument6 pagesShear StrengthSleepy SpettoNo ratings yet
- Kashif Khan ReportDocument11 pagesKashif Khan ReportSaadNo ratings yet
- Shear and MomentDocument16 pagesShear and MomentSHie LaNo ratings yet
- BucklingDocument7 pagesBucklingMohammad BurhanNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesBeam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Spardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresDocument18 pagesSpardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresSpradha Mehta100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Edge Beam-Column-Slab Connections Subjected To Earthquake Loading PDFDocument20 pagesReinforced Concrete Edge Beam-Column-Slab Connections Subjected To Earthquake Loading PDFPrabu RengarajanNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument64 pagesEngineering MaterialsDARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- BeamsDocument4 pagesBeamsAbhi ANo ratings yet
- (5.3) Shear and Moment in BeamsDocument62 pages(5.3) Shear and Moment in BeamsIan Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- Beam 1Document5 pagesBeam 1saheed tijaniNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document16 pagesModule 3Hyurinshiro TetsuyaNo ratings yet
- Arch Wires Used in OrthodonticsDocument47 pagesArch Wires Used in Orthodonticsavanthika krishnaraj100% (1)
- @ETCONp Construction Material LDocument90 pages@ETCONp Construction Material LMekuannint DemekeNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure)Document4 pagesBeam (Structure)OgwoGPNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General IntroductionDocument45 pages1.1 General IntroductionEr Vivek MathapatiNo ratings yet
- Capacity Design Criteria For Connections in Precast StructuresDocument9 pagesCapacity Design Criteria For Connections in Precast StructuresMariana Angélica ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Capacity Design Criteria For Connections in Precast StructuresDocument10 pagesCapacity Design Criteria For Connections in Precast Structuresdamavand28No ratings yet
- Ass Unit 2Document17 pagesAss Unit 2Samreen Khan100% (1)
- BENDINGDocument13 pagesBENDINGAlfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Buckling PhenomenaDocument305 pagesBuckling PhenomenaManoj PradhanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Stressed Elective EngineeringDocument7 pagesPre-Stressed Elective EngineeringJonas FernandezNo ratings yet
- Som Study Notes 59Document29 pagesSom Study Notes 59Anubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document59 pagesUnit 3P S HARSHITA100% (1)
- Flexural Behaviour of RCC Beams: S TejaswiDocument5 pagesFlexural Behaviour of RCC Beams: S TejaswiJdjdjsjsNo ratings yet
- Failure in Beams Subjected To Point LoadDocument45 pagesFailure in Beams Subjected To Point LoadPriyam AndhariaNo ratings yet
- Bending: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument76 pagesBending: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchNalinikanta SinghNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Space TrussDocument356 pagesBehavior of Space TrussMrAgidasNo ratings yet
- Teori Dasar StrukturDocument32 pagesTeori Dasar StrukturPAK RINo ratings yet
- RCCDocument22 pagesRCClakshitaNo ratings yet
- 03 Shear Strength CapacityDocument13 pages03 Shear Strength CapacityAquila1952No ratings yet
- JL-89-January-February Lateral Stability of Long Prestressed Concrete Beams-Part 1Document20 pagesJL-89-January-February Lateral Stability of Long Prestressed Concrete Beams-Part 1Dong-Yong KimNo ratings yet
- Prestress Lecture NotesfsfsfsDocument153 pagesPrestress Lecture NotesfsfsfsAlzhammer ManupacNo ratings yet
- Falcon RCD ColumnsDocument4 pagesFalcon RCD ColumnsJerome Adduru100% (1)
- Beam DeflectionDocument15 pagesBeam DeflectionrizaregularNo ratings yet
- Distribution System: BAP 203 Building Material and Construction Technology VDocument20 pagesDistribution System: BAP 203 Building Material and Construction Technology VshubhangiNo ratings yet
- "How To Differentiate Between Short and Slender Column": Goburdhun Yogesh ID: 1515419Document14 pages"How To Differentiate Between Short and Slender Column": Goburdhun Yogesh ID: 1515419Yogesh GoburdhunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reinforced Concrete Design Part 2Document4 pagesIntroduction To Reinforced Concrete Design Part 2jhess QuevadaNo ratings yet
- PSD Test NotesDocument21 pagesPSD Test Notesmuhfil MuhfilNo ratings yet
- FBSMC Module 2Document12 pagesFBSMC Module 2GEETIKANo ratings yet
- What Is The Term Used in The Construction Industry To Mitigate TheDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Term Used in The Construction Industry To Mitigate TheEliza Mae AquinoNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2018-19 MEE1006 ETH TT201 VL2018191005146 Reference Material I Deformation of SoildsDocument21 pagesFALLSEM2018-19 MEE1006 ETH TT201 VL2018191005146 Reference Material I Deformation of SoildsSHUBHAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Form Active StructuresDocument48 pagesForm Active StructuressampathNo ratings yet
- Video1.2 Introduction To StructuresDocument28 pagesVideo1.2 Introduction To StructuresNguyễn An KhoaNo ratings yet
- Structures: Types of BeamsDocument6 pagesStructures: Types of BeamsDanzel YonasiNo ratings yet
- Ce133p 2 WSD NSCP 2015Document2 pagesCe133p 2 WSD NSCP 2015RapNo ratings yet
- Unit1 From Mechanics of Materials by B C PunmiaDocument120 pagesUnit1 From Mechanics of Materials by B C Punmiasimalaravi75% (8)
- Introduction To Steel DesignDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Steel DesignkumuthaNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainFrom EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- Adjusted 2nd Sem Class ScheduleDocument2 pagesAdjusted 2nd Sem Class Scheduleacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Class List SteelDesign 2016-17Document1 pageClass List SteelDesign 2016-17acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Grade - Sheet TimberDocument2 pagesGrade - Sheet Timberacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 KTCDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Theroy Quiz 1 KTCDocument3 pagesTheroy Quiz 1 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Theroy Quiz 3 KTCDocument4 pagesTheroy Quiz 3 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Class List Theory1 2016-17Document1 pageClass List Theory1 2016-17acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Theroy Quiz 1Document1 pageTheroy Quiz 1acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Deformable BodiesDocument73 pagesFundamentals of Deformable Bodiesacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Theroy Quiz 2 KTCDocument1 pageTheroy Quiz 2 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Evaluation Instrument For Student Intern - FinalDocument4 pagesEvaluation Instrument For Student Intern - Finalacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Structural Theory 1 (Method of Superposition)Document30 pagesStructural Theory 1 (Method of Superposition)acurvz2005No ratings yet
- GradeSheet 4Document3 pagesGradeSheet 4acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Alpha Phi Omega: Philippines, Incorporated Zeta Xi Chapter & Zeta Xi Alumni Association 202Document1 pageAlpha Phi Omega: Philippines, Incorporated Zeta Xi Chapter & Zeta Xi Alumni Association 202acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 With KTCDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 With KTCacurvz2005100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Deformable Bodies Questionaire - Summer 2021-2022Document8 pagesFundamentals of Deformable Bodies Questionaire - Summer 2021-2022acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Questionaire - Summer 2021-2022 KTCDocument15 pagesStrength of Materials Questionaire - Summer 2021-2022 KTCacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Deformable BodiesDocument73 pagesFundamentals of Deformable Bodiesacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: T C 1 P UDocument11 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: T C 1 P Uacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Assessement Task 3 - Flow in Open ChannelDocument2 pagesAssessement Task 3 - Flow in Open Channelacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics QuestionnaireDocument15 pagesEngg Mechanics Questionnaireacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Structural Theory 1 (Three Moment Equation)Document44 pagesStructural Theory 1 (Three Moment Equation)acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Assessement Task 2 - Fluid Flows in PipeDocument3 pagesAssessement Task 2 - Fluid Flows in Pipeacurvz2005100% (1)
- Structural Theory 1 (Moment Area Method)Document38 pagesStructural Theory 1 (Moment Area Method)acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Flow in Open Channel - Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesFlow in Open Channel - Sample Problemsacurvz2005No ratings yet
- IM BSCE 4 - Steel Design Part 1Document86 pagesIM BSCE 4 - Steel Design Part 1acurvz2005No ratings yet
- IM BSCE 3 - Hydraulics 1 Chapter 1 2021-2022Document36 pagesIM BSCE 3 - Hydraulics 1 Chapter 1 2021-2022acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Structural Theory 1 (Double Integration Method)Document22 pagesStructural Theory 1 (Double Integration Method)acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Pennsylvania Crusher Bradford BreakerDocument2 pagesPennsylvania Crusher Bradford Breakerfahrudin100% (1)
- CV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFDocument3 pagesCV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFlevanviet0410100% (1)
- Genuine Parts: Hendrickson Equalizing Beam End BushingsDocument4 pagesGenuine Parts: Hendrickson Equalizing Beam End BushingsCesarNo ratings yet
- Plummer Blocks: Tightening Bolt Oil Fill PlugDocument30 pagesPlummer Blocks: Tightening Bolt Oil Fill Plugmanoj983@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- IRS - Well Pile Foundation Code PDFDocument17 pagesIRS - Well Pile Foundation Code PDFtipsypigNo ratings yet
- Dunham-Bush ManualDocument43 pagesDunham-Bush ManualHernan Humberto Castañeda MendozaNo ratings yet
- Status As of April 30, 2019Document61 pagesStatus As of April 30, 2019Irish EbuenNo ratings yet
- Angelo DelZotto School of Construction ManagementDocument47 pagesAngelo DelZotto School of Construction ManagementGonzalo OviedoNo ratings yet
- Wubye ST Report New EbcsDocument67 pagesWubye ST Report New EbcsKalid KemalNo ratings yet
- Pipe Schedules Chart Imperial and Metric HFT50-WEB-P PDFDocument2 pagesPipe Schedules Chart Imperial and Metric HFT50-WEB-P PDFAnonymous ITKbMGWMNo ratings yet
- Section 09900Document15 pagesSection 09900Im ChinithNo ratings yet
- Government of India Ministry of Railways (Railway Board) : Indian Railways Permanent Way ManualDocument18 pagesGovernment of India Ministry of Railways (Railway Board) : Indian Railways Permanent Way ManualmeenarpNo ratings yet
- Pozzolith 555: Non-Chloride Accelerating AdmixtureDocument3 pagesPozzolith 555: Non-Chloride Accelerating AdmixtureFrancois-No ratings yet
- PCM Bharosha BIM Service ProviderDocument2 pagesPCM Bharosha BIM Service ProviderbhadrakmishraNo ratings yet
- 2.6.1.1 AHU - Construction.checklistDocument5 pages2.6.1.1 AHU - Construction.checklistHiếu Nguyễn100% (1)
- Experiment No. 9 Demonstration of Fluid Flow Through An Orifice I. ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 9 Demonstration of Fluid Flow Through An Orifice I. ObjectiveMark B. BarrogaNo ratings yet
- API Standard 600: Steel Gate Valves-Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends, Bolted BonnetsDocument3 pagesAPI Standard 600: Steel Gate Valves-Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends, Bolted BonnetsPasquale CutriNo ratings yet
- National Plumbing Code of TT PDFDocument86 pagesNational Plumbing Code of TT PDFJeffrey JamesNo ratings yet
- R1 - Detailed Project Report - Rangpo Station - 13.12.2023Document221 pagesR1 - Detailed Project Report - Rangpo Station - 13.12.2023AGNIVO RAYNo ratings yet
- BG-DWG-2021-R0-371 Apartment 05-Sept-21 4-4Document1 pageBG-DWG-2021-R0-371 Apartment 05-Sept-21 4-4Dan Sarmiento100% (1)
- Earthquake Resistance in Japanese PagodasDocument9 pagesEarthquake Resistance in Japanese PagodasSreehari SkNo ratings yet
- 4 - Design of A Two Way Solid Slabs To BS8110Document29 pages4 - Design of A Two Way Solid Slabs To BS8110Ahmed Al-AmriNo ratings yet
- Rooms in The HouseDocument10 pagesRooms in The HouseAnnemary RoNo ratings yet
- Esbe Vta323 HojaDocument1 pageEsbe Vta323 HojaGoheimNo ratings yet
- © Focus Design Partners - Company Portfolio 2019Document42 pages© Focus Design Partners - Company Portfolio 2019AmarHromoNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation of Mahogany Carpel Ash As Cement Replacement in Concrete 2 PDFDocument9 pagesAn Experimental Investigation of Mahogany Carpel Ash As Cement Replacement in Concrete 2 PDFAdler ValdezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Tranverse ShearDocument43 pagesChapter 7 - Tranverse Shearzamspacekl100% (1)
- Ttymuy, MuiDocument41 pagesTtymuy, MuiAjayNo ratings yet
- Staircase 3Document1 pageStaircase 3Kashif KhanNo ratings yet