Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Sheet: Colligative Properties
Uploaded by
KENNETH POLOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practice Sheet: Colligative Properties
Uploaded by
KENNETH POLOCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Practice Sheet: Colligative Properties
2
3 1. Caffeine, C8H10N4O2, is a stimulant found in tea and coffee. A sample of the
4 substance was dissolved in 45.0 g of chloroform, CHCl3, to give a 0.0946 m
5 solution. How many grams of caffeine were in the sample?
2. Concentrated aqueous ammonia contains 1.00 mol NH3 dissolved in 2.44 mol H2O.
What is the mole fraction of NH3 in concentrated aqueous ammonia? What is the
molal concentration of NH3?
3. A solution was prepared by dissolving 0.915 g of sulfur , S8, in 100.0 g of acetic
acid, HC2H3O2. Calculate the freezing point and boiling point of the solution.
4. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is used as an antioxidant in processed foods. (It
prevents fats and oils from becoming rancid.) A solution of 2.500 g BHT in 100.0
g of benzene has a freezing point of 4.880 ° C. What is the molecular weight of
BHT?
5. Assume that water and ethanol mix to form an ideal solution, i.e. their mixtures
obey Raoult's Law at all concentrations. The vapor pressure of pure water at 25°
C is 23.8 torr and the vapor pressure of pure ethanol at 25° C is 58.9 torr. For a
mixture of ethanol and water in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.200, what
is the vapor pressure of the solution and what is the mole fraction of ethanol in the
vapor?
6. Ehylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) is a low volatility liquid commonly sold as
antifreeze to be mixed with water in car radiators. By adding a nonvolatile solute
to the water in the radiator, not only is the freezing point of the resulting solution
substantially lower than the freezing point of water, the boiling point is raised
substantially. Thus a water/ethylene glycol mixture protects the radiator both from
freezing and from boiling over. Calculate the freezing and boiling points of a
mixture of water and ethylene glycol obtained by mixing 2.00 kg ethylene glycol
(M.W. = 62.0682 g/mol) and 2.00 kg of water.
7. A 1.14 g sample of a molecular substance dissolved in 100 g of camphor. The
resulting solution is observed to start freezing at a temperature of 177.3 ° C. What
is the molar mass of the solute?
8. Calculate the Osmotic pressure at 50 degrees Celsius of a glucose solution C6H12O6
that has 60 grams of glucose dissolved in enough water to make 1500 ml.
1. Answer: molality = (moles solute)/(mass solvent)
So, moles solute = (molality)(mass solvent) = (0.0946 mol/kg)(0.045 kg) = 0.004257 mol.
mass of solute = (moles)(molar mass) = (0.004257 mol)(194.194 g/mol) = 0.827 g
2. Answer: XNH3 = (moles NH3)/(total moles) = (1.00 moles NH3)/(3.44 moles) = 0.291
mass of H2O = 2.44 mol(18.02 g/mol) = 43.97 g
molality NH3 = (moles NH3)/(mass solvent) = (1.00 mol)/(0.04397 kg) = 22.7 mol/kg
3. Answer: Calculate molality first: moles solute = 0.915 g(1 mol/ 256.528 g) =0.003567 mol
molality = (moles solute)/(mass solvent) = (0.003567 mol)/(0.100 kg) = 0.03567 mol/kg
(1) Tf = Kfm = (3.59 ° C/m)(0.03567 m) = 0.1281° C
Tf = Tf° - Tf = 16.60° C - 0.1281° C = 16.47° C
(2) Tb = Kbm = (3.08 ° C/m)(0.03567 m) = 0.1099° C
Tb = Tb° + Tb = 118.5° C + 0.1099° C = 118.6° C
4. Answer: (1) Tf = Tf° - Tf = 5.455° C - 4.880° C = 0.575° C
(2) Tf = Kfm so..... m = Tf/ Kf = (0.575° C)/(5.065 ° C/m) = 0.1135 mol/kg
(3) molality = (moles solute)/(mass solvent) so.... moles solute = (molality)(mass solvent)
= (0.1135 mol/kg)(0.100 kg) = 0.01135 mol
(4) molar mass = (mass)/(moles) = (2.500 g)/(0.01135 mol) = 220 g/mol
5 Answer. P(ethanol) = (.200)(58.9 torr) = 11.78 torr
P(water) = (.800)(23.8 torr) = 19.04 torr
P(total) = 11.78 torr + 19.04 torr = 30.82 torr +2 points
Xvapor(ethanol) = (11.78 torr)/(30.82 torr) = 0.382
6. moles of ethylene glycol = (2000 g)(1 mol/62.0692 g) = 32.2 mol
molality = (moles solute)/(mass solvent) = (32.2 mol)/(2.00 kg) = 16.1 m
Tb = (16.1 m)(.512 ° C/m) = 8.25 ° C, so the boiling point is 108.25 ° C.
Tf = (16.1 m)(1.858 ° C/m) = 29.9 ° C, so the freezing point is -29.9 ° C.
7. (1) molality = Tf/Kf = (179.5 ° C - 177.3 ° C)/(40 ° C/m) = 0.055 m
(2) moles solute = (molality)(mass solvent) = (0.055 m)(0.100 kg) = 0.0055 m
(3) molar mass = mass/moles = (1.14 g)/(0.0055 mol) = 207g/mol +2 points
8.
1. Convert grams of glucose to moles of glucose by dividing the mass by the molecular weight of
glucose(180)
60 grams glucose X 1 mole glucose / 180 grams glucose = 0.333 moles glucose
2. Convert milliliters of solution to liters
1500 ml X 1 liter / 1000 ml = 1.500 liter
3. Determine the Molarity of the solution.
Molarity = 0.333 mole / 1.500 liter = 0.222 moles / liter
4. Convert the Celsius temperature to Kelvin.
K = C + 273 = 50 + 273 = 323 K
5. Calculate the Osmotic Pressure using the formula
Osmotic Pressure = (0.222) (0.0821) (323) = 5.89 atmospheres
You might also like
- Chem 11Document5 pagesChem 11Jen Karen BolidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Properties of Solutions Exercise 1Document26 pagesChapter 13 Properties of Solutions Exercise 1janeNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument6 pagesChemRoselyn BunquinNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties and AnswerDocument3 pagesColligative Properties and AnswerTai PanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Document16 pagesLiquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 HomeworkDocument36 pagesChapter 15 HomeworkJoey Chang0% (1)
- Boiling Point Elevation Worksheet SolutionsDocument7 pagesBoiling Point Elevation Worksheet SolutionsDaniela Mae BiongNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 117 AnswersDocument2 pagesWorksheet 9 117 AnswersMaxiNo ratings yet
- 2lesson 5 Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument25 pages2lesson 5 Colligative Properties of Solutionsrachelle tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Tanpa JudulDocument3 pagesDokumen Tanpa JudulNia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Phypharm ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhypharm ReviewerjaspergarcesdiegoNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties WS FP AnswersDocument3 pagesColligative Properties WS FP AnswersVIENA ANGYANGNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesSolutions: Lecture NotesMisa AmaneNo ratings yet
- Chem w5-6Document7 pagesChem w5-6Shevanie Lei AmamenceNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument44 pagesColligative PropertiesCacey Daiwey Calixto100% (1)
- Molailty and ColligativeDocument12 pagesMolailty and Colligativeimmatofuloverx32428No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties.: Unit 4Document52 pagesColligative Properties.: Unit 4RafaelNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument23 pagesColligative PropertiesPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties NotesDocument5 pagesColligative Properties Notesjehov cantera100% (1)
- Wa0001Document17 pagesWa0001HimanshuNo ratings yet
- CHM 1102 Worksheet 6 2021Document2 pagesCHM 1102 Worksheet 6 2021kevin persaudNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 2Document4 pagesChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 2maxime namaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Chemistry - SolutionsDocument33 pagesClass 12 - Chemistry - SolutionsSlaying LegendNo ratings yet
- Vidyamandir Classes Dilute Solution AssignmentDocument5 pagesVidyamandir Classes Dilute Solution AssignmentPhani PadmasriNo ratings yet
- Solving Chemistry ProblemsDocument1 pageSolving Chemistry ProblemsCharlene L. PulmaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesWorksheet 6 Colligative Propertiesani illuriNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES WORKSHEETDocument3 pagesSOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES WORKSHEETCindy GallosNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument27 pagesColligative PropertiesKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- WRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIDocument21 pagesWRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIAshleyNo ratings yet
- Tugas RutinDocument15 pagesTugas RutinElvi ZurryyatiNo ratings yet
- The Meme Wall Percent Composition & Empirical & Molecular FormulasDocument36 pagesThe Meme Wall Percent Composition & Empirical & Molecular FormulasAL - 12LJ 682103 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Energetics CalculationsDocument21 pages5.1 Energetics CalculationsFairy QinNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties PDFDocument13 pagesPhysical Properties PDFrushdiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Rutin LarutanDocument2 pagesTugas Rutin LarutanPutri AfrianiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 solutions freezing and boiling pointsDocument2 pagesClass 12 solutions freezing and boiling pointsmanasvNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - CustodioDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - CustodioIvy CustodioNo ratings yet
- Karen Ann v. BACUS - Activity No.3 - CalorimetryDocument7 pagesKaren Ann v. BACUS - Activity No.3 - CalorimetryKaren Ann V. BACUSNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesColligative Properties Cheat SheetRishi Sinha25% (4)
- Example Problems Solns and Colligatives 2013 PDFDocument1 pageExample Problems Solns and Colligatives 2013 PDFShina Yang MadaleNo ratings yet
- Collprop PresDocument14 pagesCollprop PresLynet Claire GuiquingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Practice Exercises SolutionsDocument25 pagesChapter 13 Practice Exercises SolutionsBelaFistaNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument7 pagesSolutions: Short Answer Type QuestionsPadmalaya paloNo ratings yet
- XII SolutionsDocument3 pagesXII SolutionsAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 PracticeDocument2 pagesChapter 12 PracticeSarah ViscoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 (Ch10) - 2020Document3 pagesHomework 1 (Ch10) - 2020Keiko CheungNo ratings yet
- Solution: M Number of Moles Ofsolute Volume of Solution (L) Weight Molecular Weight MDocument3 pagesSolution: M Number of Moles Ofsolute Volume of Solution (L) Weight Molecular Weight Mlove youNo ratings yet
- TR KIMIA - Yogi Sihite PDFDocument23 pagesTR KIMIA - Yogi Sihite PDFYogi SihiteNo ratings yet
- WK4 Umbao L Cana GC2Document5 pagesWK4 Umbao L Cana GC2Master Of BlankNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument3 pagesSolutionsTanmay sinhaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoDocument8 pagesWeek 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document43 pagesCH 2Tamanna GaurNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document43 pagesCH 2TechView TeamTamilNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Jawaban Kimia Dasar Chapter 12Document5 pagesSoal Dan Jawaban Kimia Dasar Chapter 12cacaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 NCERTDocument44 pagesCH 2 NCERTsPaRkLiNg wAtErNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mass from Freezing Point DepressionDocument2 pagesMolecular Mass from Freezing Point DepressionAshwin JambhulkarNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet 14.1 Solutions UpdatedDocument2 pagesProblemSet 14.1 Solutions Updatedkatherine ramirezNo ratings yet
- Mass Percentage Solutions Chapter 2Document40 pagesMass Percentage Solutions Chapter 2Mo RafeeusshanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Energy ChangesDocument6 pagesCalculating Energy ChangesCaughtIn144pNo ratings yet
- 4 Calculations Used in Analytical Chemisty: 4A Some Important Units of MeasurementDocument7 pages4 Calculations Used in Analytical Chemisty: 4A Some Important Units of MeasurementMichelle MariposaNo ratings yet
- Art. Robert SteckerDocument1 pageArt. Robert SteckerKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Exercise Intensity LevelsDocument2 pagesExercise Intensity LevelsKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Redemption Song Lyrics: Bob MarleyDocument3 pagesRedemption Song Lyrics: Bob MarleyKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
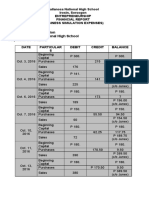
- Business Simulation Gallanosa National High School G4-Stem 2Document1 pageBusiness Simulation Gallanosa National High School G4-Stem 2KENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument2 pagesCommunication BarriersKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Review of Epic Play 'Si Bulusan nan si AgingayDocument1 pageReview of Epic Play 'Si Bulusan nan si AgingayKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Q&aDocument1 pageQ&aKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Writing The HeadlineDocument3 pagesWriting The HeadlineKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Volleyball Rules & Regulations: Basic Principles of The GameDocument11 pagesVolleyball Rules & Regulations: Basic Principles of The GameKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Set UpsDocument1 pageSet UpsKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- José Rizal PDFDocument2 pagesJosé Rizal PDFKENNETH POLO100% (1)
- Festivals PDFDocument2 pagesFestivals PDFKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Written Report (Different Growth Stages of LowLand Rice)Document5 pagesWritten Report (Different Growth Stages of LowLand Rice)KENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Ceer 2019. PhysicsDocument14 pagesCeer 2019. PhysicsKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Translocation and Transport in PlantsDocument2 pagesTranslocation and Transport in PlantsKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument3 pagesTranspirationKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Wilhelmy Plate - WikipediaDocument2 pagesWilhelmy Plate - Wikipediaprecious omokhaiyeNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4067211Document53 pagesSSRN Id4067211mnpxzdsqs8No ratings yet
- Brand Guidelines ShortDocument9 pagesBrand Guidelines ShortFarhan SaeedNo ratings yet
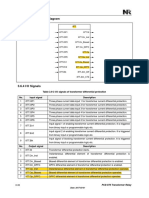
- 3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryDocument2 pages3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryAC DCNo ratings yet
- Understanding Schmitt TriggersDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Schmitt TriggersfernandofortunaNo ratings yet
- API 579 FFS in CodeCalc/PVEliteDocument4 pagesAPI 579 FFS in CodeCalc/PVEliteSajal Kulshrestha100% (1)
- On Completion 211 International School ProjectDocument2 pagesOn Completion 211 International School ProjectVed BaralNo ratings yet
- 15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILDocument8 pages15.production and Productivity Improvement Measures at MOIL-MOILkatta_sridharNo ratings yet
- Harga Juta Freeze 15ml - Google ShoppingDocument1 pageHarga Juta Freeze 15ml - Google Shopping17 - M Naradeen Janitra Pua UpaNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân - Giảng Viên ĐHSPHN - 0904731900 Facebook Page: Miss Ngân Panda English ClassDocument16 pagesNguyễn Thị Kim Ngân - Giảng Viên ĐHSPHN - 0904731900 Facebook Page: Miss Ngân Panda English ClassactuallynhatNo ratings yet
- Cec 208 Lecture Notes 1Document9 pagesCec 208 Lecture Notes 1Zaid Habibu100% (1)
- Electrical Input Components: Operación de SistemasDocument5 pagesElectrical Input Components: Operación de Sistemasgalvis1020No ratings yet
- Ceramage: Light-Curing Microhybrid CompositeDocument3 pagesCeramage: Light-Curing Microhybrid CompositeVero GrambergNo ratings yet
- Loraine Chemutai Koskei LAW/MG/1139/09/19 Enviromental and Natural Resource Law - Cat2 Hazardous WasteDocument4 pagesLoraine Chemutai Koskei LAW/MG/1139/09/19 Enviromental and Natural Resource Law - Cat2 Hazardous Wasteloraine koskeiNo ratings yet
- LPS Training - 2015 Update FINALDocument65 pagesLPS Training - 2015 Update FINALAsriSaffuan86% (7)
- Pseudo-Chomsky ThreeDocument4 pagesPseudo-Chomsky ThreeTyler ShortNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication Self Reflection #1Document5 pagesInterpersonal Communication Self Reflection #1monicawoods705No ratings yet
- Fauziah Ratna Hapsari: About MeDocument3 pagesFauziah Ratna Hapsari: About MeFauziah Ratna HapsariNo ratings yet
- 2019-10-01 Kitchen Garden PDFDocument110 pages2019-10-01 Kitchen Garden PDFLaura GrėbliauskaitėNo ratings yet
- Are Humans Really Beings of LightDocument14 pagesAre Humans Really Beings of LightmazhmiNo ratings yet
- Planning Commentary OfficialDocument7 pagesPlanning Commentary Officialapi-550981792No ratings yet
- Interesting Facts About AquariusDocument9 pagesInteresting Facts About AquariusFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- CSE2005 Lab Assessment-2: OS Process and Thread ManagementDocument29 pagesCSE2005 Lab Assessment-2: OS Process and Thread ManagementTanumay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofit in Hospitals Using Fluid ViscousDocument6 pagesSeismic Retrofit in Hospitals Using Fluid ViscousDeyanira Sayuri Yangali HerreraNo ratings yet
- Preent Simple TenseDocument3 pagesPreent Simple TenseHenrique Pires SantosNo ratings yet
- Colorcoat HPS200 Ultra Harmoniplus DoPDocument1 pageColorcoat HPS200 Ultra Harmoniplus DoPCesar SNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 3Document27 pagesLecture3 3himan123No ratings yet
- Group 7 - English For TOEFL PreparationDocument26 pagesGroup 7 - English For TOEFL PreparationNindySJaNo ratings yet
- Pravesh 5Document3 pagesPravesh 5VIVEK SHAKYANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 2Document4 pagesChemistry Lab Report 2Sahaj SinghNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Chemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)From EverandChemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)No ratings yet