Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Leakage Current
Surface Leakage Current
Uploaded by
alvin meOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Leakage Current
Surface Leakage Current
Uploaded by
alvin meCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide to modern insulation testing The origin of insulation
2.1.1 Surface leakage current IRiss
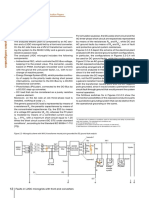
Surface leakage current flows on the surface of insulation between connection points of
applied voltage. This current causes an error in insulation resistance measurement and
could be eliminated by using a guard terminal. According to Figure 1 it flows through
resistors Riss1 and Riss2. The current does not depend on time.
U
I Riss = Eq. 2
Riss1 + Riss2
2.1.2 Insulation leakage current IRiso
This current flows through insulation. The insulation resists with resistance Riso (Figure
1). The insulation leakage current does not depend on time.
U
I Riso = Eq. 3
Riso
2.1.3 Polarization absorption current IRCpi
The absorption or de-absorption current starts from a lower level than capacitance
charging current but has a much longer time constant (up to several minutes). This is
caused by ions and dipoles re-aligning themselves within the insulation. When an
electric field is applied some ions are able to move, and some dipoles align themselves
within the field. These effects reverse themselves slowly when the test voltage is
removed, caused by particles returning to their natural random state. In the model this
phenomena is represented as an additional Rpi - Cpi combination in parallel with Riso.
The current IRCpi charges the capacitor Cpi. At the beginning the capacitor is not
charged, i.e. no polarized insulator, and the current starts with value U/Rpi. The
capacitor starts to charge and the current becomes smaller. Finally the capacitor is
completely charged, i.e., the insulator completely polarized, and the current does not
flow any more. The polarization absorption current depends on time according to
Equation 4.
t
−
U R C
I RCpi = e pi pi Eq. 4
Rpi
Other currents could mask the polarization absorption current; therefore, the
polarization current measurement could be problematic.
It is often easier to measure the opposite process: the dielectric discharge. In this case
the measurement starts with fully charged capacitor Cpi. The connection leads are
shorted and the depolarization current is observed.
2.1.4 Capacitance charging current ICiso
The capacitance charging current ICiso charges the capacitor Ciso. Ciso represents the
capacitance between metal parts connected to the measuring instrument inputs that are
You might also like
- Bansal Current Electricity PDFDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricity PDFUttiya SangiriNo ratings yet
- Ac Bald or Motors Above Nema FrameDocument48 pagesAc Bald or Motors Above Nema Framejahosolaris5512No ratings yet
- Maintenance and Check Electrical MotorsDocument7 pagesMaintenance and Check Electrical MotorsalexfrizNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Gas Insulated Substation DescriptionDocument24 pagesGas Insulated Substation DescriptionAnonymous BZQOJwWIh6No ratings yet
- Bansal Current ElectricityDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricitysudhanva mattupalli100% (1)
- Research and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksDocument88 pagesResearch and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksRajendra Prasad Shukla67% (3)
- Current Electricity. MiaDocument42 pagesCurrent Electricity. MiaVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics ProjectDocument21 pages12th Physics ProjectPratik Sharma47% (19)
- GTP - 12PX0.5,6PX0.75,2PX0.5,10PX0.5Document3 pagesGTP - 12PX0.5,6PX0.75,2PX0.5,10PX0.5santhoshNo ratings yet
- 1guide To DC Testing of InsulationDocument10 pages1guide To DC Testing of InsulationNeeraj pathakNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document15 pagesLab Report 3WaleedSubhan100% (1)
- 2.basic ElectronicsDocument209 pages2.basic ElectronicsJayanthi Krishnasamy BalasundaramNo ratings yet
- IAC Current Report 1Document7 pagesIAC Current Report 1ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Lab4 PDFDocument21 pagesLab4 PDFJoseph Lawrence CelesteNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearDocument13 pagesElectrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- RLC Physics PracticalDocument10 pagesRLC Physics PracticalVacker Guzel83% (6)
- Unit-V Circuit BreakersDocument88 pagesUnit-V Circuit BreakersRamesh VajrapuNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 2: ObjectiveDocument12 pagesExperiment # 2: ObjectiveAizaz Khan ZäziíììNo ratings yet
- TP 2: Studying Rectifiers and Semi-ConductorsDocument5 pagesTP 2: Studying Rectifiers and Semi-ConductorsZiad FAwalNo ratings yet
- NROSCI 1012 - Lecture 7Document4 pagesNROSCI 1012 - Lecture 7HonzaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Edward Felton - SectionDocument10 pagesName: - Edward Felton - SectionedNo ratings yet
- 5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DC (Aina P. Marandang)Document17 pages5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DC (Aina P. Marandang)Klint Suerte CanillaNo ratings yet
- NPN & PNP by Dr. Vijendra LingwalDocument25 pagesNPN & PNP by Dr. Vijendra LingwalDastaaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1-3Document6 pagesExperiment 1-3Mitrayosna MishraNo ratings yet
- Importance of Testing: Insulation Resistance Test (IR Test)Document4 pagesImportance of Testing: Insulation Resistance Test (IR Test)P Bhanuvas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument12 pagesElectricity Notesvedaradha41No ratings yet
- EI2203 EDC 2marksDocument14 pagesEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliNo ratings yet
- Physics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022Document71 pagesPhysics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022TahmidNo ratings yet
- 2 Mark 16 MarkedcDocument18 pages2 Mark 16 MarkedccoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- GENERATOR Testing Final Npti 20 DecDocument101 pagesGENERATOR Testing Final Npti 20 DecAshok PalakondaNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Capsule 30Document23 pagesPhysics Final Capsule 30Cybermatic AmanNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 EEE4002 ETH VL2023240103046 2023-10-31 Reference-Material-IDocument74 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 EEE4002 ETH VL2023240103046 2023-10-31 Reference-Material-Isimran goelNo ratings yet
- 03 Diode Rectifier ProjectDocument11 pages03 Diode Rectifier ProjectManju NathNo ratings yet
- Reverse Bias:: P-N Junction DiodeDocument2 pagesReverse Bias:: P-N Junction DiodeKalam Hasnain AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01Document10 pagesLesson 01Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Question BankDocument17 pagesElectronic Devices Question BankrammanoharNo ratings yet
- 5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DCDocument17 pages5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DCKlint Suerte CanillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Diode CircuitsDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Diode Circuitseee3 semNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics IIESDocument210 pagesBasic Electronics IIESAkshay ThokeNo ratings yet
- Edc 2 Marks QBDocument18 pagesEdc 2 Marks QBAnonymous lt2LFZHNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsDocument22 pagesDiffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsnagarajudbpNo ratings yet
- 12 - Current ElectricityDocument24 pages12 - Current Electricitykesha bagadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance: I. AC Voltages and CircuitsDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance: I. AC Voltages and CircuitsramjiNo ratings yet
- Phy 103Document11 pagesPhy 103Yin KuzNo ratings yet
- 478 - Phs 242 NotesDocument61 pages478 - Phs 242 NotesSovan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Exp. No. - 3 Step Response of RLC CircuitDocument9 pagesExp. No. - 3 Step Response of RLC CircuitEsh-war RajNo ratings yet
- 9 - Electronic Devices PDFDocument28 pages9 - Electronic Devices PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Lab5 2Document21 pagesLab5 2Sindbad HooNo ratings yet
- EDC Unit I 2 MarksDocument4 pagesEDC Unit I 2 MarksmuthaiNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitDocument9 pagesRC CircuitRohishkumarReddy MittaNo ratings yet
- Phy1004w Buffler M&ie&m3Document117 pagesPhy1004w Buffler M&ie&m3Hawksmoor1888No ratings yet
- Basic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Document41 pagesBasic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Hassnain MassidNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMDocument47 pages1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- ECL NotesDocument57 pagesECL Notesvamsee007No ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical ChargeDocument6 pagesCapacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical Chargeankita071291No ratings yet
- Networksshort2011 12pdfDocument10 pagesNetworksshort2011 12pdfvenki249No ratings yet
- 2Document83 pages2Kalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker, Dr. ShahzaddDocument86 pagesCircuit Breaker, Dr. ShahzaddMUHAMMAD NABEEL JABBARNo ratings yet
- Rectifier, Transformer & Filter Design PDFDocument12 pagesRectifier, Transformer & Filter Design PDFajay patelNo ratings yet
- SUPERCAP Basic ConceptDocument145 pagesSUPERCAP Basic ConceptWaldyr Yassuo KamakuraNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocument1 pageMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocument1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocument1 pageElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Ambient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageAmbient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit Breakeralvin meNo ratings yet
- Sensitive Electronic LoadsDocument1 pageSensitive Electronic Loadsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution NetworksDocument1 pageElectrical Distribution Networksalvin meNo ratings yet
- Methods of Test For Cables: Indian StandardDocument2 pagesMethods of Test For Cables: Indian StandardARUN BNo ratings yet
- Computer Simulation of Leakage Current On Ceramic Insulator Under Clean Fog ConditionDocument6 pagesComputer Simulation of Leakage Current On Ceramic Insulator Under Clean Fog ConditionKamello AssisNo ratings yet
- Manual MaDocument21 pagesManual MaSergio RecabarrenNo ratings yet
- Vgs Trafo Dry OutDocument8 pagesVgs Trafo Dry OutvikashNo ratings yet
- Medium Voltage SystemsDocument8 pagesMedium Voltage SystemsRague MiueiNo ratings yet
- SRB 301MCDocument6 pagesSRB 301MCSudheer RawatNo ratings yet
- American National Standard High-Voltage Current-Limiting Motor-Starter Fuses - Conference Test ProceduresDocument13 pagesAmerican National Standard High-Voltage Current-Limiting Motor-Starter Fuses - Conference Test ProceduresJesus SalazarNo ratings yet
- LSZHDocument34 pagesLSZHtwo travellerNo ratings yet
- Chain Pilot - PowerSyntax - 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesChain Pilot - PowerSyntax - 2020 PDFBradley CliftNo ratings yet
- Catalog Hartland RelayDocument16 pagesCatalog Hartland RelayEslam SalamonyNo ratings yet
- TroubleshootingDocument24 pagesTroubleshootingMohammed Aldaffaie100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument19 pagesIntroductionAsif AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 GHA Presentation Englisch SE Nov2011Document49 pages4 GHA Presentation Englisch SE Nov2011ahmed aliNo ratings yet
- Technical Speci Cation: DimensionsDocument2 pagesTechnical Speci Cation: DimensionsOmar Alfredo Del Castillo QuispeNo ratings yet
- User Manual 345Document5 pagesUser Manual 345AmirulHanif AlyahyaNo ratings yet
- 1C 500 MM (2xy) 0.6 1.0 (1.2) KV CABLESDocument2 pages1C 500 MM (2xy) 0.6 1.0 (1.2) KV CABLESanamulk-1No ratings yet
- Luwendran MoodleyDocument7 pagesLuwendran MoodleyDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Unified Facilities Criteria (Ufc) : Electrical Safety, O & MDocument247 pagesUnified Facilities Criteria (Ufc) : Electrical Safety, O & MHassenLNo ratings yet
- Tender of MT Power TransformersDocument17 pagesTender of MT Power TransformersAbdulwahed alsafanyNo ratings yet
- LT Power Cable - Data SheetDocument9 pagesLT Power Cable - Data SheetAnagha DebNo ratings yet
- Micro TempDocument22 pagesMicro TempAgustin ArtalNo ratings yet
- Home Assignments FromDocument7 pagesHome Assignments FromHarsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- TYPE TEST SIAC SPR KEMA - Final TIC 1603-13 V3Document72 pagesTYPE TEST SIAC SPR KEMA - Final TIC 1603-13 V3anbkhn90No ratings yet
- 12 Transformer Factory Tests Briefly Explained - EEPDocument9 pages12 Transformer Factory Tests Briefly Explained - EEPcatalinccNo ratings yet
- Bosch 20182019 Catalog GrindersDocument26 pagesBosch 20182019 Catalog Grindersvidya sagar boddetiNo ratings yet