Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen - Bio 1 Final Examination
Uploaded by
Grace LimatoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen - Bio 1 Final Examination
Uploaded by
Grace LimatoCopyright:
Available Formats
1ST TERM FINAL EXAMINATION
GR11- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Name : Mary Grace R. Limato Score: __________
Grade Level & Section: 11- Prophet Elijah Date: 11-18-21
Teacher: Mrs. Marlyn C. Lemosnero
I. ENUMERATION.
1. The cell theory is universal for all living things, no matter how complex, tiny or huge it is. The
theory can be summed up into 3 basic components, what are those? (6 points)
a. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things.
b. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
c. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2.. What are those cell organelles and their function? (3pts each)
a. Ribosomes - responsible for making protein through amino acids,responsible
for making protein through amino acids.
b. Golgi Apparatus - transports and modifies proteins in eukaryotic cells
c. Lysosomes - break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small
molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell
d. Nucleus - it stores the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates
the cell's activities,which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein
synthesis, and reproduction.
d. Mitochondria - which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein
synthesis, and reproduction
f. Chloroplasts - energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for
growth
g. Cytoplasm - energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for growth
h. Nucleulos - ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis and ribosome biogenesis
i. Nucleus - it stores the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates
the cell's activities,which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein
synthesis, and reproduction.
3. What are the two types of cells? (2pts each)
A. Eukaryotic cell
B. Prokaryotic cell
4. Refer to #3, Give the similarities and differences of those cells using Venn diagram. (10 pts.)
Please use the back page for your answers.
5. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that
produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of
precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that
produces two identical (clone) cells. The cell cycle has two major phases, what are those
phases? (2pts each)
A.interphase
B.mitotic phase
6. The three stages of interphase are called: (1pt. each)
A. G1 phase (first gap)
B. S phase (new DNA synthesis)
C. G2 phase (second gap)
7. Give the two types of cell division and their phases. (17pts) Please use the back page for
your answer.
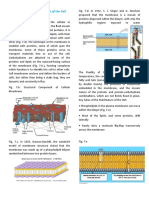
8. Give the components and functions of the plasma membrane. (2pts each)
Component Function
1. cholesterol provides stability to the plasma membrane
by limiting the
movement of the phospholipids,reduces
fluidity.
2. carbohydrates participates in cell recognition and
adhesion,stick out from the
plasma membrane to define the cell's
characteristics and help
cells identify chemical signals
3. peripheral proteins Provides the framework, attached to the
intracellular or extracellular surface of the
lipid bilayer.
4. Integral proteins serves as channels or pumps to move
materials into or
out of the cell, penetrate the hydrophobic
core of the lipid bilayer
5. Pospholipids work to provide pathways for various
substances across
membranes,protects the cells
II. ESSAY.
9. Why is it Mitosis and Meiosis are important? (5pts.each)
Mitosis is required for growth , repair and
replacement of new cells in our body.Meiosis is required for
production of gametes or sex cells in the reproductive organs.If there
is no mitosis there would be no cell growth and cell reproduction and
if meiosis does not occur, it will result in a doubling of chromosomes
in each successive generation, which will result in the formation of
abnormalities.So remember, Mitosis is what helps us grow and
Meiosis is why we are all unique!
10. Explain transport mechanisms of active transport cell. (9pts.)
Living cells need certain substances that exist inside the
cell in concentrations greater than they exist in the extracellular
space. Moving substances up their electrochemical gradients
requires energy from the cell. Active transport uses energy stored in
ATP to fuel this transport. Active transport of small molecularsized
materials uses integral proteins in the cell membrane to move the
materials.These proteins are analogous to pumps. Some pumps,
which carry out primary active transport, couple directly with ATP to
drive their action. In co-transport, energy from primary transport can
be used to move another substance into the cell and up its
concentration gradient.
You might also like
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 6 Structural Components of The Cell Membrane Activity 1: What'S in The Cell Membrane?Document7 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 6 Structural Components of The Cell Membrane Activity 1: What'S in The Cell Membrane?Mark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 7Document5 pagesGen Bio Module 7Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- General Biology: ActivityDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: Activityjulianne tanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To PhysiologyMiaIsabelleAntonioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Week7 BiologyDocument5 pagesWeek7 BiologyMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substances Through Cell MembranesDocument34 pagesTransport of Substances Through Cell MembranesSanchezNo ratings yet
- Prelim - ProbSet 1Document2 pagesPrelim - ProbSet 1Alixandra Isobel De VeraNo ratings yet
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zoneNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #3-Structure Components of The Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #3-Structure Components of The Cell MembraneGi GiNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesCell and Tissue Characteristicsgreenflames09100% (1)
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDocument18 pagesBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- Notes Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesNotes Human AnatomyLeslie Ann MesolisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellDocument94 pagesChapter 3 Cellmohamedshilleh7No ratings yet
- General Biology: 1-3 (Second Grading)Document8 pagesGeneral Biology: 1-3 (Second Grading)Dhexter Masungsong MirandaNo ratings yet
- Bio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Document6 pagesBio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Mia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Bio 49 Activity 1Document6 pagesBio 49 Activity 1Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Biology 1Document3 pages1st Summative Test Biology 1julzhaideNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL CellsDocument8 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL Cellsansarish94No ratings yet
- NSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer KeyDocument43 pagesNSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer Keygian leepsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Ibd A09-Ppt Individu Topik 1-Robi KholiqDocument29 pagesIbd A09-Ppt Individu Topik 1-Robi KholiqDiniSylvanaNo ratings yet
- NOTES Unit 3 - The CellDocument7 pagesNOTES Unit 3 - The CellCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- Local Media2437312247486514219Document29 pagesLocal Media2437312247486514219Olive Vergara MuscaNo ratings yet
- Week 1, LAS 1:: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument3 pagesWeek 1, LAS 1:: Structure/Function Cell PartKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane DeutschDocument5 pagesPlasma Membrane DeutschSafeer SefiNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembraneKim Antonette50% (2)
- Biology Notes 1st QuarterDocument25 pagesBiology Notes 1st QuarterJascha Isaac PangandianNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology TestDocument6 pagesCellular Biology TestlinhNo ratings yet
- Cells: Developmental Biology ReviewerDocument13 pagesCells: Developmental Biology ReviewerCarmela LipoNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Topic 1 CellsDocument10 pagesIb Biology Topic 1 Cellswee100% (1)
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- Handout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesHandout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeayaanNo ratings yet
- Biology AML NMAT ReviewerDocument15 pagesBiology AML NMAT ReviewerJocelyn Mae CabreraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument3 pagesLaboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyynaNo ratings yet
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument14 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- IB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsDocument5 pagesIB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsTiffani Choy100% (1)
- Parts of The Cell and FunctionsDocument31 pagesParts of The Cell and FunctionsMary Joy Llosa Redulla100% (1)
- 4) Cell MembraneDocument17 pages4) Cell Membranescobi doNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Cell Review AssignmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Cell Review Assignmentsarahmohammed801No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyjsfowen18No ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- MICRO - 1S02 - Cell Parenchyma and StromaDocument8 pagesMICRO - 1S02 - Cell Parenchyma and StromajandaniellerasNo ratings yet
- The Structural Components of The Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesThe Structural Components of The Cell MembraneJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY LaboratoryDocument5 pagesHISTOLOGY LaboratoryFarida GuialelNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell E-BookDocument21 pagesPlant Cell E-BookSammy ShnayderNo ratings yet
- Cells QSDocument6 pagesCells QSPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 &2 Biology IUDocument5 pagesHomework 1 &2 Biology IUVanessa NguyenNo ratings yet
- C) Glycolipids Make Up About 5%Document9 pagesC) Glycolipids Make Up About 5%Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- Pass Your MBBS Physiology: #InnocentialDocument12 pagesPass Your MBBS Physiology: #InnocentialTapeNo ratings yet
- Basic AntennaDocument8 pagesBasic AntennaKavitha ECE1942No ratings yet
- The Structural Components of The Cell Membrane and Its Functions, With Transport Mechanisms.Document17 pagesThe Structural Components of The Cell Membrane and Its Functions, With Transport Mechanisms.Vieyah Angela VicenteNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentRobert Ladaga33% (3)
- Activity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisDocument9 pagesActivity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 3 - CellDocument13 pages3 - CellGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development, and Facilitating LearningDocument14 pagesChild and Adolescent Development, and Facilitating LearningMichael SantosNo ratings yet
- BIOLS343 TestDocument5 pagesBIOLS343 TestMindificent Education KitNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Test BankDocument21 pagesCH 14 Test BankKrestine MolleNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 6 - CoordinationDocument3 pagesIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 6 - CoordinationHisokagen100% (2)
- Chapter 019Document28 pagesChapter 019Esteban Tabares GonzalezNo ratings yet
- BC Tiempo de Trombina Inserto OWNAG11E05Document6 pagesBC Tiempo de Trombina Inserto OWNAG11E05Isa Mar BCNo ratings yet
- Crown and Root Landmarks, Division Into Thirds, Line Angles and Point AnglesDocument57 pagesCrown and Root Landmarks, Division Into Thirds, Line Angles and Point Anglesamanita238100% (1)
- Chapter Nine - Isolation, Culture and Propagation of Natural Killer CellsDocument11 pagesChapter Nine - Isolation, Culture and Propagation of Natural Killer CellsManoj Kumar pandreNo ratings yet
- Faradic Type CurrentDocument26 pagesFaradic Type CurrentzainabnoorNo ratings yet
- Psyn 102 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPsyn 102 ReviewerP Harvey PuducayNo ratings yet
- Position Paper: A B C D e F G H CDocument11 pagesPosition Paper: A B C D e F G H CNico IonaşcuNo ratings yet
- Gat2 TestDocument5 pagesGat2 Testኣፈወርቂ በላይ ወዲ ቐሺNo ratings yet
- An Electron Transport ChainDocument2 pagesAn Electron Transport ChainArdrian SizibaNo ratings yet
- N9 แนวข้อสอบวิชาภาษาอังกฤษDocument30 pagesN9 แนวข้อสอบวิชาภาษาอังกฤษJO-JO17No ratings yet
- Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure - WikipediaDocument22 pagesGeneralized Tonic-Clonic Seizure - WikipediaAtul MhetreNo ratings yet
- Proyecto EstanciaDocument15 pagesProyecto Estanciaarath jaimesNo ratings yet
- HEMOSTASISDocument6 pagesHEMOSTASIScatuiraneljhayyyNo ratings yet
- CB7 All SheetsDocument38 pagesCB7 All SheetsAryan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- IB Style Test - Topic 8 HL Metabolism, Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesIB Style Test - Topic 8 HL Metabolism, Respiration and Photosynthesisika100% (1)
- A2 Buguina Peaches A.Document7 pagesA2 Buguina Peaches A.Peach Amparo BuguinaNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Document33 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 4Abdullah Yusof AzzamNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Structures and Functions in Living Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument9 pagesTopic 2: Structures and Functions in Living Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For Edexcel Biology IGCSEArfaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Ecg ReadingDocument6 pagesEcg ReadingMarianette CainongNo ratings yet
- BPM 1 Spring 2019 FTM Module - Lecture and DLA Objectives Term 1 Professionalism ObjectivesDocument11 pagesBPM 1 Spring 2019 FTM Module - Lecture and DLA Objectives Term 1 Professionalism ObjectivesNoelani-Mei Ascio50% (2)
- Grade 11 Biology The EyeDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Biology The EyeDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Anti AgingDocument6 pagesAnti AgingZubair Akram JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials and Nanotechnology For Tissue Engineering KrishnanDocument371 pagesBiomaterials and Nanotechnology For Tissue Engineering KrishnanRêmulo FariasNo ratings yet
- Physiology Past PapersDocument11 pagesPhysiology Past PapersIrfan Haider FaniNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Clonin ModelDocument9 pagesClonin ModelNano AlmukasabyNo ratings yet