Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8analytic Geometry 2 OC PDF
Uploaded by
Jevan CalaqueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8analytic Geometry 2 OC PDF
Uploaded by
Jevan CalaqueCopyright:
Available Formats
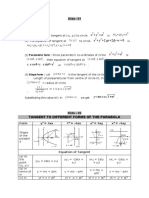
CERTCDAVAO ANALYTIC GEOMETRY 2
Conic Sections Parabola
- The locus of the point that moves such that its distance
from a fixed point called the focus is always equal to its
distance from a fixed line called the directrix. The intersection
of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a
generating straight line of that surface.
y r
Directrix
focus
d1
Latus rectum, 4a
vertex 2a
d2
x
a0 a
GENERAL EQUATION: 2a
Ax2 Bxy Cy2 Dx Ey F 0
2a
In modern mathematics, conics is defined as the locus of a
point which moves in such a way that the ratio of its distance
from a fixed point (focus) and a fixed line (directrix) is constant. General Equation of Parabola
The constant ratio is called eccentricity.
(A or B is zero)
Circle : ( If eccentricity, e = 0 )
when B=0
Ellipse : ( If eccentricity, e < 1 )
Ax 2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0
Parabola : ( If eccentricity, e = 1 ) or
2
Hyperbola : ( If eccentricity, e > 1 ) x + Cx + Dy + E = 0
Two ways of determining the type of conics from the given when A=0
general equation:
By 2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0
By Comparing Coefficients of the quadratic terms, (B = or
0):
y 2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0
From: Ax2 Cy2 Dx Ey F 0
Latus Rectum, LR
If,
Latus rectum is a chord passing through the focus and
A C , the conic is a CIRCLE parallel to the directrix or perpendicular to the axis.
A C , the conic is an ELLIPSE
LR = 4a
A or C is zero, the conic is a PARABOLA
A & C opposite sign, the conic is a HYPERBOLA Vertex at (h, k)
By Discriminant: (y - k )2 4a(x - h)
or
2 2
From: Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 (x - h)2 = 4a(y - k)
If, the discriminant, B2 4AC 0 , the conic is:
B2 4AC 0, the conic is an ellipse if A C Ellipse
2 The locus of points, or path traced out, in a plane such
B 4AC 0, the conic is a circle if A C that the sum of the distances from the moving point to two
B2 4AC 0, the conic is a parabola fixed points remains constant. The two fixed points are then
called foci. The constant sum is the length of the major axis
B2 4AC 0, the conic is a hyperbola
that is equal to 2a. It can also be defined as the locus of the
point that moves such that the ratio of its distance from a fixed
Circle point, called the focus, and a fixed line, called the directrix, is
- A simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of constant and is less than one (1).
those points in a plane which are the same distance from a
given point called the center. The common distance of the focus y focus
points of a circle from its center is called its radius.. vertex
d d vertex
General Equation (A = B)
d4
Ax 2 +Ay 2 +Cx + Dy+ E = 0 b a
Minor axis, 2b
d3
Latus rectum
Latus rectum
or
Directrix
Directrix
c c
x
2 2 0
x + y + Cx + Dy + E = 0 d1
d2
b
Standard Equations center
Center at (h, k) P (x, y)
a a
(x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r 2 Major axis, 2a
Center at (0, 0)
This study source was2downloaded
2 2 by 100000839416317 from CourseHero.com on 05-21-2022 09:48:04 GMT -05:00
x +y =r
CERTCDAVAO: 0932 328 8053
https://www.coursehero.com/file/74612470/8analytic-geometry-2-OCpdf/
CERTCDAVAO ANALYTIC GEOMETRY 2
General Equation (A B) Standard Equations
2
Ax + By + Cx + Dy + E = 0 2 “a” may be greater, equal, or less than “b” Center at (0, 0):
or x2 y2 y2 x2
2
2 1 or 2
2 1
x 2 +By 2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0 a b a b
Elements of Ellipse: Center at (h, k):
2 2 2
a b c
x h y k
2 2
1
a2 b2
d3 c
Eccentricity , e 1 .0 or
d4 a
y k x h
2 2
1
a 2b2 a2 b2
d LR
e a
Equation of Asymptote
d1 + d2 = 2a y - k = m (x - h)
where (h, k) is the center of the hyperbola and m is the slope.
m = b/a if the axis is horizontal and m = a/b if the axis is
Standard Equations ( a > b )
vertical. Use (+) for upward asymptote and (-) for downward
Center at (0, 0): asymptote.
x2 y2 x2 y2
2
2 1 or 2
2 1 How to Solve Problems Involving Conics
a b b a
1. Given the equations of any conic, find the certain elements
(center, eccentricity, focus, latus rectum, vertex, etc.)
Center at (h, k):
Reduce the equation to standard form and apply the
x h y k
2 2
necessary formulas.
1
a2 b2
2. Given only the points, find the equation. (3 points for
or circle, 3 points and axis for parabola, four points for ellipse and
x h y k
2 2
hyperbola)
1 Substitute the given points to the general equation
b2 a2
and solve for A, B, C, etc.
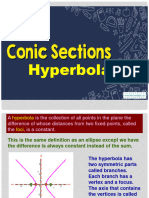
Hyperbola
The locus of a point which moves so that the difference of 3. Given some elements, find the equation. (center and
its distance between the two fixed points is constant. This point radius for circle; vertex and a for parabola; center, a, and b for
is known as the foci. The constant difference is the length of ellipse and hyperbola)
the transverse axis that is equal to 2a. It may also be defined Reduce the equation to standard form.
as the locus of the point that moves such that the ratio of its
distance from a fixed point, called the focus, and fixed line, Transformation of Coordinates (Shifting Axes)
called the directrix, is constant and is greater than one (1).
asymptote asymptote
y
Directrix
Directrix
d4
vertex d3 d1
vertex
Conjugate axis, 2b
d2
Latus rectum
b
Latus rectum
focus focus
x
b
center Coordinates of the point P in the new and old coordinate
d d
systems are tied by the equations:
a a
x' x a
Transverse axis, 2a
c c
y' y b
General Equation of Hyperbola
(A and B have opposite signs)
Ax 2 -By 2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0 Polar Coordinate System
or (r, )
2 2
x - By + Cx + Dy + E = 0 r
Elements of Hyperbola O
x
2 2 2
c a b Pole Axis
d3 c Sign Convention
Eccentricity , e 1 .0
d4 a is positive (+) if measured counterclockwise
is negative (-) if measured clockwise
a 2b2 r is positive (+) if measured at the terminal side of
d LR r is negative (-) if measured at the extension through O
e a
from the terminal side of
d2 - d1 = 2a
This study source was downloaded by 100000839416317 from CourseHero.com on 05-21-2022 09:48:04 GMT -05:00
CERTCDAVAO: 0932 328 8053
https://www.coursehero.com/file/74612470/8analytic-geometry-2-OCpdf/
CERTCDAVAO ANALYTIC GEOMETRY 2
Distance Between Two Points D. x2 – 10x + 8y + 41 = 0
The distance between two given points can be solve 11. Determine the equation of the parabola with axis vertical,
vertex is at (−1, −1) and passing through (2, 2).
using cosine law.
A. x^2 + 2x – 3y - 2 = 0
(r2, 2) d B. x^2 – 4x + 2y - 1 = 0
C. x^2 + 4x – y - 2 = 0
r2 D. x^2 – 5x + 2y - 6 = 0
= 2 - 1 (r1, 1)
r1 12. A cable suspended from supports that are the same height
O and 600 feet apart has sag of 100 feet. If the cable hangs in
x the form of a parabola, find its equation.
Pole
A. y^2=900x C. x^2=400y
d r12 r22 2r1r2 cos 2 1 B. y^2=400x D. x^2=900y
13. Find the location of the center of the ellipse:
Relationship Between Polar and Cartesian Coordinate 2 2
16x 25y 64x 50y 311 0
Systems A. (3, 2) C. (2, 1)
2 2 2
x
(r, ) r x y B. (4, 5) D. (1, 2)
y 14. An ellipse has its vertices at (-2,-3) and (8,-3). If one end of
y r tan
x the minor axis is at (3,-7), how far is the nearest focus to the
left of the directrix.
O
x x r cos A. 7.42 C. 4.28
Pole Axis
y r sin B. 3.21 D. 5.33
15. The major axis of the elliptical path in which the satellite
SAMPLE PROBLEMS moves around the earth is approximately 186,000,000 miles
and the eccentricity of the ellipse is 1/60. Find the maximum
1. What conic section is represented by the equation : x2 + 4y2 + altitude of the satellite.
4xy + 2x – 10 = 0 A. 94, 550,000 C. 84,556,000
A. Ellipse C. Hyperbola B. 105,000,000 D. 96,665,000
B. Parabola D. Circle
16. Find the equation of the ellipse given the following conditions:
2. Identify the graph of the equation : foci (−3, 2) and (5, 2), major axis is 10.
x2 +y2+3x-2y+4=0. A. 9x^2 + 25y^2 – 18x – 100y – 116 = 0
A. Circle C. Ellipse B. 9x^2 + 25y^2 – 18x + 100y – 116 = 0
B. Point D. No graph C. 9x^2 + 25y^2 – 18x – 100y + 116 = 0
D. 9x2 + 25y2 – 18x + 100y + 116 = 0
3. What is the coordinate of the center of the circle
2 2
17. From the given equation of the hyperbola 16y2 – 9x2 + 36x +
x y 18x 10y 25 0 . 96y – 36 = 0. Find the center of the hyperbola.
A. (9, 5) C. (−9, 5) A. 1, -2 C. 3, -4
B. (−5, 9) D. (9, −5) B. 2,-3 D. 3, -2
4. Find the equation of the circle which is tangent to both the x 18. Find the equation of the hyperbola with foci at (−4, 0) and (4,
and y axes and having a radius of 3 units. 0) and passes through (2, 0).
A. x^2 + y^2 – 6x – 6y + 9 = 0 A. 3x^2 – y^2 – 12 = 0
B. x^2 + y^2 + 6x + 6y + 18 = 0 B. 3x^2 – y^2 + 12 = 0
C. x^2 + y^2 – 9 = 0 C. x^2 – 3y^2 – 4 = 0
D. x^2 + y^2 – 18 = 0 D. x^2 – 3y^2 + 12 = 0
5. Determine the value of k so that x2 +y2-8x+10y+k=0 is the 19. The length of the latus rectum of a hyperbola is equal to 18
equation of circle of radius 7. and the distance between the foci is 12. Determine the
A. 8 C. -4 equation of the curve if the conjugate axis is parallel to the y-
B. -8 D. 6 axis.
A. y^2 – 3x^2 = 27 C. y^2 – 2x^2 = 15
6. Find the radius of a circle with center at (4,1) if a chord of B. 3x^2 – y^2 = 27 D.2x^2 – 3y^2 = 27
length 4√2 is bisected at (7,4).
A. 7 C. 2 20. A point moves so that the difference between its distance
B. √26 D. √42 from (0, 5) and (0, −5) is 8, what is the equation of its locus?
A. 9y^2 – 16x^2 = 144
7. A curve has an equation of x2 y2 6x 10y 5 0 . Find the B. 16x^2 – 9y^2 = 144
equation of the tangent line at (1, 0). C. 4y^2 – 9x^2 = 36
A. 2x + 5y + 2 = 0 C. 2x – 5y – 2 = 0 D. 9x^2 – 4y^2 = 36
B. 5x – 2y + 2 = 0 D. 5x + 2y – 2 = 0
21. Find the new coordinate of the point (3, −5) if the axis is
8. Determine the equation of the radical axis of the two circles: translated to a new origin at (−4, 6).
A. (7, −11) C. (−1, 1)
x2 y2 10x 18y 25 0 and x2 y2 2x 4y 1 0 . B. (−7, 11) D. (4, −14)
A. 6x – 11y + 12 = 0
B. 2x + 3y – 3 = 0 22. Find the equation of the curve x2 y2 2x 8y 8 0 if the
C. 3x + 4y – 5 = 0
D. x – y + 2 = 0 origin is moved at (3, −2).
A. x’2 + y’2 – 12x’ + 8y’ + 43 = 0
B. x’2 + y’2 – 8x’ + 12y’ + 43 = 0
9. The vertex of the parabola y2 2x 6y 3 0 is located at: C. x’2 + y’2 + 8x’ – 12y’ + 43 = 0
A. (−3, 3) C. (3, 3) D. x’2 + y’2 + 12x’ – 8y’ + 43 = 0
B. (3, −3) D. (−3, −3)
23. A point has a polar coordinate of (7, 38°). Determine its
10. Find the equation of the parabola with vertex at (5,-2) and equivalent rectangular coordinate.
focus at (5,-4). A. (5.52, 4.31) C. (79.56, 38.64)
A. x2 – 12x + 10y + 40 = 0 B. (38.64, 79.56) D. (4.31, 5.52)
B. x2 – 8x + 4y + 36 = 0
This studyC. x2 was
source – 5xdownloaded
+ 6y + 45 by
= 0100000839416317 from CourseHero.com on 05-21-2022
24. 09:48:04
ExpressGMTy3 =-05:00
4x2 in its polar form.
CERTCDAVAO: 0932 328 8053
https://www.coursehero.com/file/74612470/8analytic-geometry-2-OCpdf/
CERTCDAVAO ANALYTIC GEOMETRY 2
A. r = 4cot2θcscθ C. r = 4cotθcsc2θ 15. Find the equation of the locus of a point which moves so that
B. r = 4cot2θcsc2θ D. r = 4cotθcscθ its distance from (1,-7) is always 5.
A. x2+y2-2x+14y+25=0 *
B. x2+y2-2x-14y+25=0
3
25. Transform the rectangular equation x2 y2 4x2 y2 into its C. x2+y2 +2x+14y+25=0
equivalent polar form. D. x2+y2-2x+14y+16=0
A. r = 2cosθ C. r = sin2θ
B. r = 2sinθ D. r = cos2θ 16. Find the eccentricity of the hyperbola whose transverse and
conjugate axes are equal in length.
26. Determine the coordinates of the vertex of the curve A. 1.414* B. 1.732 C. 1.707 D. 1.333
4
r . 17. Find the eccentricity of a hyperbola having distance between
1 cos
foci equal to 18 and the distance between directrices equal to
A. (2, 0) C. (0, 2) 2.
B. (−2, 0) D. (0, −2) A. 2 B. 3* C. 2.8 D. 3.7
TAKE HOME EXAM 18. Find the length of the tangent from point (7,8) to the circle
x2 +y2-9=0.
1. An ellipse has its center at (0,0) with its axis horizontal. The A. 10.2* B. 14.7 C. 11.3 D. 13.6
distance between the vertices is 8 and its eccentricity is 0.5.
Compute the length of the longest focal radius from point (2,3) 19. A hut has a parabolic cross-section whose height is 30 m. and
on the curve. whose base is 60 m. wide. If a ceiling 40 m. wide is to be
A. 3 B. 5 * C. 4 D. 6 placed inside the hut, how high will it be above the base?
A. 16.67 m * C. 14.47 m
2. What is the new equation of the line 5x+4y+3=0 if the origin is B. 15.48 m D. 19.85 m
translated to the point (1,2)?
A. 4x’+3y’+16=0 C. 5x’-4y’-16=0 20. An ellipse has an eccentricity of 1/3. Compute the distance
B. 5x’+4y’+16=0 * D. 6x’+6y’-16=0 between directrices if the distance between foci is 4.
A. 18 B. 36* C. 32 D. 38
3. What conic section is described by the equation
r 6 /(4 3cos ) ? 21. A parabola having its axis along the x-axis passes through (-
A. circle C. hyperbola 3,6). Compute the length of the latus rectum if the vertex is at
B. ellipse * D. parabola the origin.
A. 4 B. 8 C. 6 D. 12 *
4. A locus of a point on a circle which rolls on the outside of a
fixed circle without slipping is called: 22. Find the equation of the circle tangent to the y-axis and the
A. hypocycloid C. epicycloids * center is at (5,3).
B. cycloid D. astroid A. (x+5)2+(y-3)2 =25 C. (x-5)2+(y-3)2 =25*
B. (x-5)2+(y+3)2 =25 D. (x-5)2+(y-3)2 =50
5. What conic section is 2x2-8xy+4x=12?
A. parabola C. hyperbola * 23. How far is the center of the circle x2+y2-10x-24y+25=0 from
B. ellipse D. circle the line y=-2.
A. 10 B. 14 * C. 12 D. 16
6. An ellipse has length of semi-major axis of 500 and a semi-
minor axis of 300. Compute the second eccentricity of the 24. Determine the area bounded by the curve x2 +y2-6y=0.
ellipse. A. 27.28 sq. units C. 28.27 sq. units *
A. 1.112 C. 3.112 B. 72.28 sq. units D. 18.27 sq. units
B. 2.331 D. 1.333 *
25. Find the area bounded by the curve 9x2 + 25y2 + 18x – 100y
2
7. A curve has an equation of x =Cy+d. The length of the latus = 116.
rectum is 4 and the vertex is at (0,2). Compute the value of C A. 15* C. 20
and d. B. 24 D. 31
A. 4, -8 * B. 6, -2 C. 2, -5 D. 3, -7
26. Determine the length of the latus rectum of the curve r cos 2 θ
8. An arc in the form of a parabola is 60 m across the bottom. – 4 cos θ = 16 sin θ.
The highest point is 16 m above the horizontal base. What is A. 8 C. 16*
the length of the beam placed horizontally across the arc 3 m B 12 D. 6
below the top.
A. 19.36 C. 25.98 * 27. Change the equation (x2 + y2)3 = 4x2y2 to polar coordinates.
B. 24.86 D. 27.34 A. r = Sin 2θ*
B. r = 2 Sin θ
9. The focus of the parabola y2 =4x is at: C. r = 2 Cos 2θ
A. (4,0)* B. (1,0) C. (0,4) D. (0,1) D. r = Cos 2θ
10. Find the shortest distance from (3,8) to the curve x2 +y2 +4x- 28. How far from the x-axis is the focus (F) of the hyperbola x2 –
6y=12. 2y2 + 4x + 4y + 4 = 0.
A. 1.21 B. 2.07 * C. 4.09 D. 3.73 A. 2.14 C. 2.73
B. 2.51 D. 2.36*
11. A circle has its center on the line 2y=3x and tangent to the x-
axis at (4,0). Find its radius. 29. Find the eccentricity of a hyperbola whose transverse and
A. 6 * B. 7 C. 5 D. 8 conjugate axes are equal in length.
A. 0.82 C. 1.52
12. Determine the length of the line joining the intersections of the B. 1.41* D. 1.73
equation x2 +y2=48 and x2=-8y.
A. 10.57 C. 12.18 30. Find the equation of the asymptotes for a hyperbola: (y – 5)2
B. 11.31* D. 12.38 – (x + 5)2 = 36.
A. y – 5 = ±(x + 5)* C. y – 4 = ±(x – 4)
13. A locus of a point whose difference of the distances from two B. y = ± x D. y – 5 = ±(x – 5)
fixed points is constant.
A. ellipse
B. parabola
C. hyperbola*
D. circle
“You get what you work for not what
you wish for.” - Anonymous
14. The difference of the distances of a moving point from (1,0)
and (-1,0) is 1. Find the equation of its locus.
A. 4x2-12y2 =3 C. 12x2-4y2 =3 *
2 was2 downloaded by 100000839416317
This study source
B. 3x -4y =12 D. 4x2-9y2=3 from CourseHero.com on 05-21-2022 09:48:04 GMT -05:00
CERTCDAVAO: 0932 328 8053
https://www.coursehero.com/file/74612470/8analytic-geometry-2-OCpdf/
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Analytic GeomDocument4 pagesAnalytic GeomPhil Irish DumalayangNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 4 2018 PDFDocument43 pagesPractice Exam No. 4 2018 PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Rme April 2019 Exam 5 Key PDFDocument8 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 5 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Rme April 2019 Exam 4 Key PDFDocument8 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 4 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 5 2018 PDFDocument13 pagesPractice Exam No. 5 2018 PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Pec Answers 101 To 200Document7 pagesPec Answers 101 To 200Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Pec Answers 601 To 700Document5 pagesPec Answers 601 To 700Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Conic Section DPPDocument63 pagesConic Section DPPRahul Jain87% (23)
- Rme Quick View Part 8Document11 pagesRme Quick View Part 8Jevan Calaque0% (1)
- Rme April 2019 Exam 2 Key PDFDocument7 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 2 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Solicar Engineering Review Center and ServicesDocument7 pagesSolicar Engineering Review Center and ServicesJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Solicar Engineering Review Center and ServicesDocument7 pagesSolicar Engineering Review Center and ServicesJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 3 2018 PDFDocument29 pagesPractice Exam No. 3 2018 PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Rme April 2019 Exam 7 Key PDFDocument8 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 7 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Notes - Analytic Geometry 1 PDFDocument1 pageNotes - Analytic Geometry 1 PDFmitchrldnNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 2 2018 PDFDocument23 pagesPractice Exam No. 2 2018 PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Circle: X H (H, K)Document4 pagesConic Sections Circle: X H (H, K)JadeChristynLeonorNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 - RME APRIL 2023Document5 pagesPreboard 2 - RME APRIL 2023Jevan Calaque0% (1)
- Mthn14e Lec 2Document26 pagesMthn14e Lec 2Aly BueserNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test NewDocument4 pagesAchievement Test NewKelly Cheng100% (1)
- Algorithmic Sketchbook-W3 - Nicola LeongDocument71 pagesAlgorithmic Sketchbook-W3 - Nicola LeongMARIONUNEZTELLONo ratings yet
- Ometry 2Document5 pagesOmetry 2Gladwin BuquironNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 2Document4 pagesIntegral Calculus 2Paulynne Jhee BedicoNo ratings yet
- Ma1512 Cheatsheet Summary Differential Equations For EngineeringDocument4 pagesMa1512 Cheatsheet Summary Differential Equations For EngineeringDennis SorianoNo ratings yet
- Slope Formulas: Slope of Two Given Points Slope of The Given AngleDocument4 pagesSlope Formulas: Slope of Two Given Points Slope of The Given AngleClarence PortoNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document14 pagesGroup 4alethuaNo ratings yet
- Parabola: Definitions of Various Important TermsDocument11 pagesParabola: Definitions of Various Important Termsno nameNo ratings yet
- A Two-Spiral Flat Coil For Detecting N NQR Signals: G. V. Mozzhukhin, A. V. Efremov, A. V. Bodnya, and V. V. FedotovDocument6 pagesA Two-Spiral Flat Coil For Detecting N NQR Signals: G. V. Mozzhukhin, A. V. Efremov, A. V. Bodnya, and V. V. FedotovCatanescu Alexandru-LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- The Straight LineDocument1 pageThe Straight LineFATIN NOORNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Graphs of Linear Equations and InequalitiesDocument22 pagesCh12 Graphs of Linear Equations and InequalitiesVera DuNo ratings yet
- Conic Section FormulaeDocument7 pagesConic Section FormulaeRomik100% (1)
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument6 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Maths - Parabola UnacadDocument72 pagesMaths - Parabola UnacadKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Comb W Book-2Parab Ellip HypDocument18 pagesComb W Book-2Parab Ellip Hypuser 12No ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument13 pagesParabolaAtapolLeetrakulNo ratings yet
- 03 Electrostatics (Concept 16 To 20)Document10 pages03 Electrostatics (Concept 16 To 20)lakshya rautelaNo ratings yet
- Mathsfull BookDocument3 pagesMathsfull Bookpunjabcollegekwl5800No ratings yet
- 01 Parabola1 Jeemain - GuruDocument29 pages01 Parabola1 Jeemain - GuruMugi ChintuNo ratings yet
- 7 ParabolaDocument36 pages7 ParabolaCasCade 104No ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument8 pagesDifferential EquationVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1Document10 pagesCaie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1ARMANI ROYNo ratings yet
- MFC - Formulário 2015Document18 pagesMFC - Formulário 2015MartimAlentejoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - HyperbolaDocument9 pagesGroup 2 - HyperbolaMicko RenomeronNo ratings yet
- (Eduwaves360) CONIC 12th (2018C) EDocument101 pages(Eduwaves360) CONIC 12th (2018C) EAlbertNo ratings yet
- QM Formula Sheets by JahanzaibDocument6 pagesQM Formula Sheets by JahanzaibBasit MehrNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetsDocument5 pagesFormula SheetsAayesha NoorNo ratings yet
- 36 INTEGRATION FULL PART 2 of 5 PDFDocument20 pages36 INTEGRATION FULL PART 2 of 5 PDFrappycatNo ratings yet
- Notes Pre Calculus 1Document1 pageNotes Pre Calculus 1Sydrey Jada-ongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Part2) - 992Document5 pagesChapter 2 (Part2) - 992Subhan, MScNo ratings yet
- MOD 2 - Conic SectionsDocument42 pagesMOD 2 - Conic SectionsVirender DassNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Notes 3Document3 pagesPre Calculus Notes 3Lex LabadoNo ratings yet
- Division of Line SegmentDocument2 pagesDivision of Line Segmentprince ian cruzNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Hyperbola - ReportDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Hyperbola - ReportMicko RenomeronNo ratings yet
- A. Defenisi: Z Diff. IntgDocument8 pagesA. Defenisi: Z Diff. IntgNathanNo ratings yet
- Stiffness Matrix ReportDocument21 pagesStiffness Matrix ReportSubodh KumarNo ratings yet
- C Symmetry - BCLDocument4 pagesC Symmetry - BCLstosicdusanNo ratings yet
- Checklist c2Document3 pagesChecklist c2Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- Doubtnut Today: Baap of All Formula ListsDocument3 pagesDoubtnut Today: Baap of All Formula ListsJoydeep SarkarNo ratings yet
- Areas and Definite IntegralsDocument20 pagesAreas and Definite IntegralsMichael OpenaNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Properties 9th GradeDocument4 pagesFormulas and Properties 9th Gradedgjdf hgjhdgNo ratings yet
- IGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideDocument7 pagesIGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideNITAKSH jain NJNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geom 1-3Document4 pagesAnalytic Geom 1-3Noriele Theresa Berja RamosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDocument12 pagesMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2Edmar TabinasNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFRimar LiguanNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2Ronna Mae De AsisNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulas PDFDocument1 pageMathematics Formulas PDFStevenAronNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2Ashley TalayNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2Jaypee BucatcatNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document1 pageMath 2Alan Manuel-GuyNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFRJNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFChloe OlazoNo ratings yet
- 7bea3804 Ea3e 5b8Document2 pages7bea3804 Ea3e 5b8HeLio 007No ratings yet
- Algebra PDFDocument12 pagesAlgebra PDFPaul Christian BondocNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Revision Notes Conic SectionsDocument37 pagesClass 11 Maths Revision Notes Conic SectionsVarnika Arumugam NNo ratings yet
- AS Mathematics - Practice Paper - Differentiation (Part 2) MSDocument7 pagesAS Mathematics - Practice Paper - Differentiation (Part 2) MSShayekhNo ratings yet
- 9-Engineering Data AnalysisDocument4 pages9-Engineering Data AnalysisJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- 7solid Geometry OC PDFDocument5 pages7solid Geometry OC PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 1 2018Document27 pagesPractice Exam No. 1 2018kali bangon100% (1)
- Rme April 2019 Exam 3 Key PDFDocument7 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 3 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Pec Answers 401 To 500Document11 pagesPec Answers 401 To 500Edward Roy “Ying” AyingNo ratings yet
- Tech 501 To 600Document3 pagesTech 501 To 600Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Probability PDFDocument7 pagesProbability PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Rme April 2019 Exam 1 Key PDFDocument7 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 1 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Multiple Choice Questions inDocument19 pagesThermodynamics: Multiple Choice Questions inJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Pec Answers 301 To 400Document7 pagesPec Answers 301 To 400Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Tech 401 To 500Document4 pagesTech 401 To 500Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Tech 101 To 200Document4 pagesTech 101 To 200Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Tech 301 To 400Document4 pagesTech 301 To 400Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Three Times Only The Subjects in Which He Has Obtained The Grade Below 50%Document5 pagesThree Times Only The Subjects in Which He Has Obtained The Grade Below 50%Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Tech 201 To 300Document4 pagesTech 201 To 300Jevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Circles IIDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Circles IIsims363No ratings yet
- Development of SurfacesDocument40 pagesDevelopment of Surfaceskamal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 1 MathsDocument5 pagesClass 1 MathsDharam SekhonNo ratings yet
- Eng GraphicsDocument25 pagesEng GraphicsDavis AllanNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument26 pagesPolygonCross VandoeuvreNo ratings yet
- Transformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementDocument23 pagesTransformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementmangimanNo ratings yet
- Circle 7 DPP 78Document1 pageCircle 7 DPP 78Ashwani SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Circles Answer KeyDocument1 pageCH 10 Circles Answer KeyAlexie Mangalo100% (1)
- Trial Kelantan SPM 2012 MathsDocument58 pagesTrial Kelantan SPM 2012 MathsSiah Woan ChiouNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument34 pagesMensurationRajkumar MajjiNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Converse Pythagorean Theorem and Word ProblemsDocument7 pagesDay 2 - Converse Pythagorean Theorem and Word Problemsapi-253195113No ratings yet
- Geometry Curriculum MapDocument12 pagesGeometry Curriculum MapFosheeMNo ratings yet
- Tangent To ConicsDocument3 pagesTangent To ConicsNilesh Kumar Chauhan100% (1)
- Chords, Arcs, and Central and Inscribed AngleDocument14 pagesChords, Arcs, and Central and Inscribed AngleAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Surface Normals and Tangent PlanesDocument17 pagesSurface Normals and Tangent Planesjupe01No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Deductive GeometryDocument44 pagesChapter 4: Deductive GeometryEric MooiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesAerl XuanNo ratings yet
- PDF Unit Plan Packet 10 PolygonsDocument9 pagesPDF Unit Plan Packet 10 PolygonsLuna LedezmaNo ratings yet
- Geo t7 1Document15 pagesGeo t7 1api-261379705No ratings yet
- Plane Geometry Part 2Document14 pagesPlane Geometry Part 2Maria Lourven AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Quadrics - Linear Algebra, Analytic Geometry, Differential GeometryDocument8 pagesQuadrics - Linear Algebra, Analytic Geometry, Differential GeometrycecilchifticaNo ratings yet
- Stanley Rabinowitz GeometriDocument12 pagesStanley Rabinowitz Geometrinicolas dionisio ordonez barrueta100% (3)
- TriangleDocument85 pagesTriangleSunilKumarNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10velavanNo ratings yet
- 4 T1 MatSciSocial EMDocument160 pages4 T1 MatSciSocial EMMohan RajNo ratings yet
- AQA Foundation Answers PDFDocument48 pagesAQA Foundation Answers PDFSindi DallashiNo ratings yet