Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromosomal Mutation
Uploaded by
api-668571149Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chromosomal Mutation
Uploaded by
api-668571149Copyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region V – Bicol
Schools Division Office
Camarines Norte
Eco Athletic Field, F. Pimentel Ave., camarines.norte@deped.gov.ph (054) 440-1772/(054) 440-4464
Daet, Camarines Norte DepEd Camarines Norte
CODE S10LT-IIIe-38
GRADES 1 to School Labo Science and Technology H.S. Grade Level 10 Quarter 3
12 DAILY Teacher Pierre S. Lalaqui Learning Area SCIENCE 10
LESSON PLAN Teaching Date and Time April 17-18, 2023 7:30-8:30/2:00-3:00/ 3:00-4:00
The learners demonstrate an understanding of:
1. the information stored in DNA as being used to make proteins;
A. Content Standards
2. how changes in a DNA molecule may cause changes in its product; and
3. mutations that occur in sex cells as being heritable.
The learner shall be able to write an essay on the importance of adaptation as a
B. Performance Standards
I. OBJECTIVES
mechanism for the survival of a species.
Explain how mutations may cause changes in the structure and function of a protein.
S10LT-IIIe-38
C. Learning Competencies/ At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
Objectives a. define chromosomal mutation;
b. explain chromosomal mutations and their causes;
c. identify different types of genetic disorders; and
d. create an illustration of chromosomal mutations.
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
II. CONTENT (Subject Matter/Lesson)
Chromosome Mutations
1. Teacher’s Guide pages
A. REFERENCES
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
2. Learner’s Materials pages Page 209-213
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional Materials from
Google Images, PowerPoint Presentation, Manila Paper, and Pen touch
Learning Resource portal
B. Other Learning Resources https://youtu.be/vl6Vlf2thvl (Mutations by Amoeba Sisters)
The teacher will administer the recapitulation using the paper ball game using these
questions.
1. What might happen to the DNA sequence after having a mistake in replicating
I. ELICIT
itself?
2. In what process do changes in DNA sequence occur?
3. Will this cause changes in the genes?
4. What do you call these changes?
IV. PROCEDURES
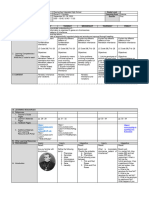
GUESS WHO
The students will identify and guess if who is/are in the picture.
II. ENGAGE
CYCLOPS MARVELS SUPER HERO
“SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams…, Valuing Aspirations…”
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region V – Bicol
Schools Division Office
Camarines Norte
Eco Athletic Field, F. Pimentel Ave., camarines.norte@deped.gov.ph (054) 440-1772/(054) 440-4464
Daet, Camarines Norte DepEd Camarines Norte
How can you describe Cyclops? What do they have in common?
Leonardo, Raphael, Donatello and Michelangelo of teenage mutant ninja turtles.
Are they real? Do they really exist?
Do you know its story? How do they become mutant ninja turtle?
The students will perform the activity in the learner materials. Page 284-287 of
Grade 10 Science LM.
In this activity the students are expected to illustrate and differentiate the kinds of
chromosomal mutations.
TRANSLOCATION
Procedure:
1. Using modeling clay, make models of two (2) chromosomes. One should have a
different color and size from the other.
2. Break one part of each of the chromosomes. Exchange the parts and attach them
to each of the other chromosomes.
DELETION
Procedure:
1. Make a model of two (2) chromatid (one of the duplicated copies of a
chromosome).
2. When done, in your second model, remove a portion of it (close to either end of
III. EXPLORE
the chromosome or within the long arm or short arm). If you choose to remove a
part within the arms, be sure to join back the bottom part.
INVERSION
Procedure:
1. Make two (2) colored chromatids.
2. In the second chromatid, break a portion (with two colors) of it.
3. Reinsert it to the chromatid in reverse manner.
Guide Questions:
Q1. How are the three chromosomal aberrations different from each other? How are
they similar?
Q2. Do you think the normal genetic content of the chromosome is affected?
Q3. Which condition results to gain of chromosome material? Loss of chromosome
material?
Q4. What are some possible effects of these chromosomal mutations?
Q5. What are the positive effects of mutations?
“SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams…, Valuing Aspirations…”
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region V – Bicol
Schools Division Office
Camarines Norte
Eco Athletic Field, F. Pimentel Ave., camarines.norte@deped.gov.ph (054) 440-1772/(054) 440-4464
Daet, Camarines Norte DepEd Camarines Norte
The teacher will choose 3 groups to present their work in the class. Then the teacher
will check and analyze the group outputs.
IV. EXPLAIN
The teacher will discuss the different effects of chromosome
mutations which can lead to variety of genetic disorders.
Genetic disorders
1. Recessive disorders
A child receives two defective genes from each parent. The carrier does not express
the disorder because it is not detectable by the dominant normal gene, it can pass
the defective gene to their children.
a. Sickle Cell Anemia – inherits two defective genes will have abnormally shaped
red blood cells and may die at an early stage.
b. Tay-Sachs disease – lack of an important chemical in the brain.
c. Phenylketonuria – can cause serious mental retardation in infants.
d. Cystic fibrosis – a disease in which some glands produce too much mucus that
clogs and damages the lungs.
2. Sex-linked Disorders
V. ELABORATE
Sex-linked disorders are more common in men because they have only one X
chromosome, so all defective genes on the chromosome will be expressed.
Shows picture of example of human genetic syndrome and students will try to
describe the appearance of each individual in the picture.
3.Human Genetic Syndrome – genetic disorders that may have few or too many
chromosomes.
a. Cri du chat – deletion of part of the short arm of chromosomes 5.
b.Down syndrome – (trisomy 21) is known as mongolism. A child receives extra
chromosomes (chromosome 21) and has a distinctive physical appearance.
c. Edward syndrome – (trisomy 18) happens when there is an extra number 18
chromosome.
d. Patau’s syndrome – (trisomy 13) caused by an extra copy of the number 13
chromosome.
e. Klinefelter’s syndrome – (XXY) a male who have this syndrome has two or more
X-chromosomes in addition to their Y-chromosomes.
“SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams…, Valuing Aspirations…”
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region V – Bicol
Schools Division Office
Camarines Norte
Eco Athletic Field, F. Pimentel Ave., camarines.norte@deped.gov.ph (054) 440-1772/(054) 440-4464
Daet, Camarines Norte DepEd Camarines Norte
f. Turner’s syndrome – has 45 chromosomes.
I. Identify what genetic disorders are being stated.
1. Deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5.
2. Has an extra chromosome 21.
3. Has 45 chromosomes.
4. It is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 13.
5. There is an extra number 18 chromosome.
II. Identify the type of chromosome mutation.
1. A portion of the chromosome is missing or deleted. Known disorders in
humans such as Cri du chat.
VI. EVALUATE
2. In one type of Down syndrome, one chromosome breaks off and attaches
to another chromosome.
3. When a portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome.
Sometimes, parts of different chromosomes switch places (reciprocal
exchange).
4. A portion of the chromosome has broken off, turned upside down and
reattached, therefore the genetic material is backward.
5. Jacobsen syndrome is a disorder caused by this type of mutation. This is
a very rare disorder. Those affected have normal intelligence or mild
mental retardation, with poor or excessive language skills.
VlI. EXTEND Watch the link provided and answer the questions provided below. (Use your
notebook in answering the questions)
https://youtu.be/vl6Vlf2thvl (Mutations by Amoeba Sisters)
1. What can you say about the video?
2. How this video contributes to your knowledge about mutation?
3. Why it is important to study mutation?
“SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams…, Valuing Aspirations…”
You might also like
- Lab Policies Differential Counting and Morphology Lab 5074Document14 pagesLab Policies Differential Counting and Morphology Lab 5074Egil SantosNo ratings yet
- Functional Ultrastructure An Atlas of Tissue Biology and PathologyDocument341 pagesFunctional Ultrastructure An Atlas of Tissue Biology and PathologyАндрей СкрынникNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - MEDICAL PARASITOLOGYDocument12 pagesLecture Notes - MEDICAL PARASITOLOGYAngelica Marzo67% (3)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartKimora BrooksNo ratings yet
- IB Biology D.3 Liver NotesDocument7 pagesIB Biology D.3 Liver NotesDilip Pandurang PattilNo ratings yet
- Gene MutationDocument5 pagesGene Mutationapi-668571149No ratings yet
- TranslationDocument5 pagesTranslationapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Sdlp-Day 1 MutationDocument6 pagesSdlp-Day 1 MutationJessica SudioNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument7 pagesBoyles Lawapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Time Date I. Objectives: Types of MutationDocument3 pagesTime Date I. Objectives: Types of MutationRod ReyesNo ratings yet
- Exemplar Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page NoDocument5 pagesExemplar Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page NoEricha Solomon100% (2)
- WEEK2Document5 pagesWEEK2Queng ElediaNo ratings yet
- Mutations 1Document5 pagesMutations 1Jhamia Cruz EstradaNo ratings yet
- WEEK3Document5 pagesWEEK3Queng ElediaNo ratings yet
- DLL Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesDLL Reproductive SystemKAnne FestijoNo ratings yet
- DLL - March 11-15, 2024Document5 pagesDLL - March 11-15, 2024Digna ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesScience 10 Lesson PlanThesairah Taule100% (1)
- BIO G10 Q3 W5 D1 RevDocument4 pagesBIO G10 Q3 W5 D1 RevGu Jun PyoNo ratings yet
- CLP in Science 10Document3 pagesCLP in Science 10bernley joy nobleza100% (1)
- WEEK4Document5 pagesWEEK4Queng ElediaNo ratings yet
- Division of Lapu-Lapu City Lesson Plan in Science 10Document3 pagesDivision of Lapu-Lapu City Lesson Plan in Science 10Khang KhangNo ratings yet
- DLL Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesDLL Reproductive SystemEdward GanggangNo ratings yet
- LP Science 8Document2 pagesLP Science 8KarenGraceKabingueNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycyle LPDocument8 pagesCell Cycyle LPRachelle CauseNo ratings yet
- DLP JM AQUINO Nov.082023Document5 pagesDLP JM AQUINO Nov.082023Teth PalenciaNo ratings yet
- DLL 5Document3 pagesDLL 5JEFFREY CUESTANo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W6Document4 pagesScience 9 Q1 W6Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W7Document5 pagesScience 9 Q1 W7Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- DLL TemplateDocument8 pagesDLL TemplateCristelle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- School: Grade Level: Teacher Learning Area: I. Objectives: Types. Biology LibretextsDocument13 pagesSchool: Grade Level: Teacher Learning Area: I. Objectives: Types. Biology LibretextsJohn Bernard RiliNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Week 5 - Feb 26 - March 1Document10 pagesQ3 - Week 5 - Feb 26 - March 1Lucky RemosNo ratings yet
- Mutation Lesson Plan-EditedDocument6 pagesMutation Lesson Plan-EditedKatherine BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: Activity Sheet, Manila Paper, Markers, Powerpoint Presentation, Laptop, TVDocument2 pagesGrade Level: Activity Sheet, Manila Paper, Markers, Powerpoint Presentation, Laptop, TVJanrex Karl Faelagmao100% (3)
- 8-Nail-Care-Tlp Week5Document12 pages8-Nail-Care-Tlp Week5Sampaguita HSNo ratings yet
- G10 5e's - Chromosomal MutationDocument5 pagesG10 5e's - Chromosomal MutationYvonne CuevasNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Chemical ChangeDocument14 pagesEvidences of Chemical ChangeJhana Kate FalculanNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 5-Viewing MaterialsDocument4 pagesENGLISH 5-Viewing Materialsverna baloloy100% (1)
- DLL Biotechnology - July 1 - 6Document3 pagesDLL Biotechnology - July 1 - 6MichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Werty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- DLL On Changes in Chromosome NumberDocument4 pagesDLL On Changes in Chromosome NumberGu Jun Pyo100% (1)
- DLL ELS Q2 Januray 4 6 2023Document5 pagesDLL ELS Q2 Januray 4 6 2023Li RaNo ratings yet
- CLASS8 - GROUP2 - Mendelian GeneticsDocument3 pagesCLASS8 - GROUP2 - Mendelian GeneticsROXANNE MONDIDONo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Barbs Castillo Paglinawan-PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mechanical EnergyDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Mechanical EnergyNorma Lyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Science 9: Southcom National High SchoolDocument3 pagesScience 9: Southcom National High SchoolJomajFalcatanDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document5 pagesWeek 3Barbs Castillo Paglinawan-PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument3 pagesNucleic AcidJenalyn PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles of An AtomDocument11 pagesSubatomic Particles of An AtomJhana Kate FalculanNo ratings yet
- DLP-4Q-Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDLP-4Q-Digestive SystemAshley Jane BenlayoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesLesson Plan: Earth and Life ScienceBorbe ClauNo ratings yet
- Cot 1Document6 pagesCot 1joshua seanNo ratings yet
- May 24 Nucleic Acid and ProteinDocument5 pagesMay 24 Nucleic Acid and Proteinhelen grace cabalagNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity For Cot 1 Copy 2Document4 pagesBiodiversity For Cot 1 Copy 2Trisha Melrose Milanes100% (1)
- DLL Q1 Week 5Document11 pagesDLL Q1 Week 5ROMEL CONDEZANo ratings yet
- Review: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesReview: I. ObjectivesshethwinNo ratings yet
- q2 Learning Plan Sci9Document20 pagesq2 Learning Plan Sci9Marielle AlystraNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4A Lesson Exemplar Using The Idea Instructional Process - ScienceDocument3 pagesPivot 4A Lesson Exemplar Using The Idea Instructional Process - Scienceericka mae tizonNo ratings yet
- DLL MutationsDocument3 pagesDLL MutationsPromiseland Christian schoolNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan AP 9 Q1 WEEK 2Document5 pagesLesson Plan AP 9 Q1 WEEK 2TOMAS III FERROLNo ratings yet
- DLP - SCI9 BiodiversityDocument7 pagesDLP - SCI9 BiodiversityYolanda CarpioNo ratings yet
- Bias Prejudice Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBias Prejudice Lesson Plangaea lou fabroNo ratings yet
- History-Of-The-Periodic Table-Dlp-Reading Mat - JOVEN PAITANDocument5 pagesHistory-Of-The-Periodic Table-Dlp-Reading Mat - JOVEN PAITANKIM ANN OPENA VILLAROSANo ratings yet
- Dna Day 3Document4 pagesDna Day 3MaricarGabitanNo ratings yet
- Oct 5 - Divergent BoundaryDocument4 pagesOct 5 - Divergent BoundaryDare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyNo ratings yet
- DLP Electric ChargeDocument13 pagesDLP Electric Chargeapi-668571149No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Behavior of GasesDocument44 pagesBehavior of Gasesapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument27 pagesBoyles Lawapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Motion DetectorsDocument28 pagesMotion Detectorsapi-668571149No ratings yet
- q4 Behavior of GasesDocument4 pagesq4 Behavior of Gasesapi-668571149No ratings yet
- MutationDocument40 pagesMutationapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Genetic DisorderDocument15 pagesGenetic Disorderapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription and Translationnora ronanNo ratings yet
- Las MutationDocument2 pagesLas Mutationapi-668571149No ratings yet
- g7 Classroom RulesDocument2 pagesg7 Classroom Rulesapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Brown Classic Plant Blank Page A4 DocumentDocument2 pagesBrown Classic Plant Blank Page A4 Documentapi-668571149No ratings yet
- School-Forms-1-7 g7Document62 pagesSchool-Forms-1-7 g7api-668289592No ratings yet
- Grade7 Tos RevisedDocument1 pageGrade7 Tos Revisedapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Black and Yellow Emergency Response Poster 1Document4 pagesBlack and Yellow Emergency Response Poster 1api-668571149No ratings yet
- Black and Yellow Emergency Response PosterDocument4 pagesBlack and Yellow Emergency Response Posterapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State Collehe HistoryDocument7 pagesCamarines Norte State Collehe Historyapi-668571149No ratings yet
- BIOCELLDocument30 pagesBIOCELLCallista Aulia ClaireneNo ratings yet
- 2 NucleusDocument19 pages2 NucleusYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- INGLES MEDICO I - TP 6 - Andrade Cavalcante, Nadyne.Document4 pagesINGLES MEDICO I - TP 6 - Andrade Cavalcante, Nadyne.Nadyne Cavalcante100% (1)
- General Biology Mod1Document104 pagesGeneral Biology Mod1mn KimNo ratings yet
- Bio101 DNAExtractionDocument3 pagesBio101 DNAExtractionGia Joy B. PardeNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument108 pagesCell Biology Lecture NotesMert PolatNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementDocument8 pagesChromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementReginaldNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesDifference Between Mitosis and Meiosiskumar_vikaNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet For Remedial StudentsDocument25 pagesBiology Worksheet For Remedial Studentsbaretoodo785No ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesBiology Projecthana fathimaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts Study Guide: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument3 pagesCell Parts Study Guide: Structure/Function Cell PartJulie V. AlegadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocument10 pagesLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarNo ratings yet
- Life Science Basics For The GEDDocument6 pagesLife Science Basics For The GEDPinn phaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Lenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Simple Mitosis QuestionsDocument2 pagesCell Division Simple Mitosis QuestionsgladdisNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio Zoology EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument264 pages12th Bio Zoology EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inAnitha SNo ratings yet
- Journey Into The World of Biology CellsDocument8 pagesJourney Into The World of Biology CellsNazar MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesChapter - 5 Fundamental Unit of LifehelloNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument28 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument15 pages1 PB PDFmimit sasmitaNo ratings yet
- 1970 - Lewontin, R. - The Units of Selection PDFDocument19 pages1970 - Lewontin, R. - The Units of Selection PDFvltg_35643No ratings yet
- Cell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesCell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisAmr NasserNo ratings yet
- BIO01 CO1 PPT - An Overview of The CellDocument60 pagesBIO01 CO1 PPT - An Overview of The CellCHRISTIAN MATTHEW DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor of Molecular GeneticsDocument24 pagesHuman Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor of Molecular GeneticsBarrak AldosaryNo ratings yet
- Plant Pathogens Principles of Plant Pathology PDFDocument376 pagesPlant Pathogens Principles of Plant Pathology PDFTECHNO buzzNo ratings yet