Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Question Bank
Uploaded by
bookaccount0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesOriginal Title
CBSE question Bank
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesCBSE Question Bank
Uploaded by
bookaccountCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
CBSE Board
Physics Question Bank
1. What is scalar? Give two examples
Ans: Physical quantity which has only magnitude, but no direction is known as scalar
Examples: distance and speed
2. What is vector? Give two examples
Ans. Physical quantity which has both magnitude and direction and also satisfying law of vector
addition is known as vector.
Examples: Displacement and velocity
3. What is unit vector?
̂ 𝑘̂ are known as unit vectors along X Y and Z axes
Ans: A vector whose magnitude is one unit. 𝑖̂, 𝑗,
4. What is a position vector
Ans: If a vector is used to represent position of point w.r.to some fixed point then that vector is
known as position vector
5. How will you find magnitude of a given vector 𝐴⃗ = 𝑥𝑖̂ + 𝑦𝑗̂ + 𝑧𝑘̂
Ans: Magnitude of 𝐴⃗ is equal to √𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 𝑧 2
6. How will you find direction of a given vector 𝐴⃗ = 𝑥𝑖̂ + 𝑦𝑗̂ + 𝑧𝑘̂
𝑥 𝑦
Ans: The angles made the vector with x axis is cos −1 ( 2 2 2) and y axis is cos−1 ( ) and
√𝑥 +𝑦 +𝑧 √𝑥 2 +𝑦 2 +𝑧 2
𝑧
z axis is cos −1( )
√𝑥 2 +𝑦 2 +𝑧 2
7. what is resolution of a vector
Ans: Expressing a vector in terms of its components is known as resolution of a vector
8. Find the components of vector 𝐴⃗, if it makes an angle θ with horizontal
Ans: The component vector along the X axis = |𝐴⃗| cosθ
The component Vector along the Y axis =|𝐴⃗| sinθ
Hence 𝐴⃗ =|𝐴⃗| cosθ 𝑖̂+|𝐴⃗| sinθ𝑗̂
9.State parallelogram law of vector addition
Ans: If two vectors acting at a point are represented as the adjacent sides of a parallelogram
drawn from a point then their resultant is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn
from the same point
10 State triangle law of vector addition
Ans : If two vectors acting at a point are represented as the sides of tringle in order then their
resultant is represented by the third side of the of the triangle taken in reverse order
11 State polygon law of vector addition
Ans : If n vectors acting at a point are represented as the sides of polygon in order then their
resultant is represented by the closing side of the polygon taken in reverse order
12. Explain about the dot product of two vectors
Ans: If product of two vectors gives a scalar then that product those vectors is named as dot
product or scalar product
𝐴⃗ . 𝐵
⃗⃗ =|𝐴⃗||𝐵
⃗⃗ | cosθ
13 Explain about cross product of two vectors
Ans: If product of two vectors gives a vector then that product those vectors is named as cross
product or vector product
𝐴⃗ 𝑋𝐵
⃗⃗ =|𝐴⃗||𝐵
⃗⃗| sinθ 𝑛̂
Here 𝑛̂ is a unit vector perpendicular to plane contain 𝐴⃗ 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐵
⃗⃗
14. Can dot product of two vectors obey commutative law
Ans: Yes, dot product of two vectors obeys commutative law
𝐴⃗ . 𝐵
⃗⃗ =𝐵
⃗⃗ . 𝐴⃗
15 Can cross product of two vectors obey commutative law
Ans: No, cross product of two vectors doesn’t obey the commutative law
𝐴⃗ 𝑋𝐵
⃗⃗ ≠ 𝐵
⃗⃗ 𝑋𝐴⃗, but 𝐴⃗ 𝑋𝐵
⃗⃗ = −(𝐵 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
⃗⃗ 𝑋𝐴)
16 Can Vector addition obeys Commutative law
Ans: Yes, vector addition obeys commutative law
𝐴⃗ + 𝐵
⃗⃗ =𝐵
⃗⃗ + 𝐴⃗
17 Can subtraction two vectors obeys commutative law
Ans No, subtraction of two vectors doesn’t obey the commutative law
here 𝐴⃗ − 𝐵
⃗⃗ ≠ 𝐵
⃗⃗ − 𝐴⃗
18 if 𝐴⃗ = 3𝑖̂ + 4𝑗̂ + 5𝑘̂ and 𝐵⃗⃗ = 5𝑖̂ + 4𝑗̂ + 3𝑘̂ then find magnitude of 𝐴⃗ + 𝐵
⃗⃗
Ans: 𝐴⃗ + 𝐵⃗⃗ = 8𝑖̂ + 8𝑗̂ + 8𝑘̂
The magnitude of 𝐴⃗ + 𝐵 ⃗⃗ =8√3
19 if 𝐹⃗ = (3𝑖̂ + 4𝑗̂ + 5𝑘̂)𝑁 and 𝑠⃗ = (𝑖̂ + 𝑗̂ − 𝑘̂)𝑚 then find the work done by the force
Ans: Work(W)= 𝐹⃗ . 𝑠⃗ = 3+4-5=2 joule
20 if 𝐹⃗ = (3𝑖̂ + 4𝑗̂ + 5𝑘̂)𝑁 and 𝑟⃗ = (𝑖̂ + 𝑗̂ + 𝑘̂)𝑚 then find the torque of the force
Ans: 𝜏⃗⃗⃗ =𝑟⃗ 𝑋𝐹⃗
𝑖̂ 𝑗̂ 𝑘̂
=|1 1 1|=𝑖̂(5 − 4) -𝑗̂(5 − 3) + ̂𝐾 (4 − 3)= 𝑖̂ − 2𝑗̂ + 𝑘̂
3 4 5
21. Define distance and displacement and mention its units
Ans: Distance: The length of the path followed by a particle in between initial and final positions
Displacement: It is the shortest distance between initial and final positions always measured
along a straight line
The units of distance and displacement are meter
22. Define instantaneous velocity and Average velocity
Ans: Instantaneous Velocity: The rate of displacement is known as instantaneous velocity
Average Velocity: The displacement of particle in one second is known as average velocity
23. Define uniform velocity
Ans: If a particle covers equal displacements in equal intervals of time, then the velocity of the particle
is said to be uniform
24. Define Non uniform velocity
Ans: If a particle covers unequal displacements in equal intervals of time, then its velocity is non
uniform
25. Define uniform acceleration
Ans: If particle possesses equal changes in velocities in equal intervals of time, then the acceleration of
the particle is said to be uniform
26. Define Non uniform acceleration
Ans: If particle possesses unequal changes in velocities in equal intervals of time or equal changes in
velocities in unequal intervals of time then acceleration of the particle is minimum
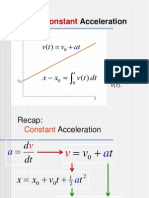
27 Mention the equations of motion in case of a particle is moving with uniform acceleration
Ans :If a particle has initial velocity u and travelling along a straight line with uniform acceleration a
and covers a distance s in t seconds, then
(i) v= u +a t
1
(II) s=ut+2 𝑎𝑡 2
(III) v2-u2=2as
1
(IV) sn=u+a(n- 2)
Here sn is the displacement in the n th second
28. Mention equations motion in case of a particle is dropped freely from the top of a tower of height h
Ans: In case of freely falling body u=0, a=-g and s=-h
(i) v=-gt
1
(ii) h=2 𝑔𝑡 2
(iii) v=√2𝑔ℎ
1
(iv) sn=-g(n- 2)
29. Mention the equations of motion in case of a particle projected vertically up
Ans: In case of a particle projected vertically upward a=-g
(i) v= u -g t
1
(II) s=ut-2 𝑔𝑡 2
(III) v2-u2=-2gs
1
(IV) sn=u-g(n- 2)
30. If air friction is taken into account, then, in time of ascent and time of descent, which will be
greater
Ans: If air friction is taken into account, then time of descent is greater than time of ascent
31. What is projectile
Ans: Any object thrown into the air and moves under gravity is known as projectile
32 what is the trajectory equation when a particle is thrown with a velocity u at an angle θ with
horizontal
𝑔𝑥 2
Ans: y= 𝑥 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 − 2𝑢2 𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝜃
Here x is horizontal displacement and y is vertical displacement
33 Define the terms (a) Time of flight(b) Range
Ans: Time of flight(T): time spent by the projectile in air is known as time of flight
2𝑢 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
T= 𝑔
Range: The maximum horizontal displacement during the time of flight is known as range
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃
R= 𝑔
34. If two stones A and B are projected from the same point on the ground with same speed but
different angles θ and (90-θ) and RA and RB are the ranges covered by them respectively, then
compare them
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃
Ans: RA= and
𝑔
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2(90−𝜃) 𝑢2 sin (180−2𝜃) 𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃
RB= = =
𝑔 𝑔 𝑔
Hence RA and RB are equal
35. What is the velocity of the projectile at maximum height when it is projected with an initial
velocity u at an angle θ with horizontal
Ans: The velocity of the projectile at the maximum height is u cosθ
36. Derive the equation for the maximum height reached by a projectile when it is projected from the
ground with a velocity u at an angle θ with horizontal
Ans:
The component of velocity of the projectile in the vertical direction at origin (uy)= u sinθ
The component of velocity of the projectile at the highest point in the vertical direction(vy) =
The component of acceleration of the projectile in the vertical direction(ay)= -g
The displacement of the projectile in the vertical direction(s) = H
Using the third equation of motion
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃
Vy2-uy2=2ays =≫ 0-u2sin2θ=-2gH =≫ H= 2𝑔
37. Obtain the relation between range and maximum height of a projectile, when the a particle is
projected from the ground with an initial velocity u at an angle θ with horizontal
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃
Ans: R= -----(1) and
𝑔
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃
H= -----(2)
2𝑔
Taking the ratio of equations (1) and (2) We will get R=4H cotθ
38. Obtain the trajectory equation when a particle is projected horizontally from the top of a tower of
H
Ans: Here ux=u and ax=0
and uy=o and ay=-g
let the projectile takes t seconds to reach a point (x, -y)
The horizontal displacement of the projectile (X)=u t -----(1)
𝑔𝑡 2
The vertical displacement of the projectile (-y)=- ---(2)
2
𝑋
substituting t=𝑢 value in the second equation we will get
𝑔𝑥 2
Y=
2𝑢2
39. A stone is projected with an initial velocity 20√2 m/s at an angel 450 with horizontal. Find (a) time
of flight (b) Range and (c) max. height
Ans :
2𝑢 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 2(20√2) 1
(a) T= = =4 second
𝑔 10 √2
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃 800
(b) R= = = 80m
𝑔 10
𝑢2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃 800 1
(c) H= = 20 = 20m
2𝑔 2
40. A stone is projected horizontally from the top of a tower with an initial velocity 10 m/s from the
top of the tower of height 20 m.
Find(a) time taken by stone to reach the ground (b) Horizontal distance covered by the stone (c)
velocity of the just before reaching the
Ans:
2𝐻
(a) T= √ 𝑔 =2 seconds
(b) X = ut = 20m
(c) Velocity of the stone just before reaching the ground =√𝑣𝑥2 + 𝑣𝑦2 = √𝑢2 + (𝑔𝑡)2 =10√5 m/s
41. Define radial acceleration
Ans: when a particle is moving along the circumference circle with constant speed due to continuous
change in direction of motion there exists an acceleration known as centripetal acceleration
42. Explain about uniform circular motion
Ans: If a particle moves along the circumference of a circle with constant speed or constant angular
velocity then the motion of a particle is said to be uniform circular motion
43. Explain about non uniform circular motion
Ans: If a particle moves along the circumference of a circle with variable speed or variable angular
velocity then the motion of a particle is said to be uniform circular motion
44. What are the uses of dimensional formulae
Ans: (a) To check the correctness of given equation
(b) To convert one system of units into other system
(c) To derive an equation connecting different physical quantities
45. What are the limitations of dimensional formulae
46 Mention dimensional formulae of (a) Universal gas constant (b) universal gravitational constant
(c) Planck’s constant (d) Stefan’s constant
47 Define the terms (i) Absolute error (ii) Accuracy (iii) precision.
48 Distinguish between Systematic errors and random errors.
49. How the random error changes with the increase in number of observations
50. If y=xn. then find relative and percentage error in calculating y
You might also like
- 4.motion in A PlaneDocument17 pages4.motion in A Planerchandra2473No ratings yet
- Focus Area Questions-1Document53 pagesFocus Area Questions-1AswithNo ratings yet
- 01ParticleProblems PDFDocument10 pages01ParticleProblems PDFBarbaraNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two or Three DimensionsDocument58 pagesMotion in Two or Three DimensionsMarc Howard Detera PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document37 pagesLecture 12Sarah Rachel100% (1)
- COLLEGE PHYSICS - Projectile MotionDocument7 pagesCOLLEGE PHYSICS - Projectile MotionAllen TorogonNo ratings yet
- +1 Phy Imp Questions 2023Document30 pages+1 Phy Imp Questions 2023athi887766No ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionDocument26 pagesMotion in Two DimensionKnowledgeIsTruePowerNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Rectilinear Motion and Its ApplicationDocument15 pagesDerivation of Rectilinear Motion and Its Applicationcontactmahtab78667% (3)
- Very Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesVery Short Answer Type QuestionsAlok ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectilesDocument12 pagesMaths Projectilesමේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- Today's Objectives: In-Class Activities:: Motion of A ProjectileDocument22 pagesToday's Objectives: In-Class Activities:: Motion of A ProjectileclinthopkinsNo ratings yet
- 2 +Kinematics+of+particles+-+Part+IIDocument43 pages2 +Kinematics+of+particles+-+Part+IIBEYZA ÇAVUŞOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Motion in Two or Three DimensionsDocument26 pagesLecture 2 Motion in Two or Three Dimensionsa5759761No ratings yet
- Motion in A PlaneDocument27 pagesMotion in A PlaneMichael KiddNo ratings yet
- Study Material Motion in A PlaneDocument10 pagesStudy Material Motion in A PlanexkryxxzNo ratings yet
- BC 9A Note PagesDocument5 pagesBC 9A Note PagesCarson ReskeNo ratings yet
- Physics CH 4Document32 pagesPhysics CH 4aasifNo ratings yet
- 6.7 Introduction Dynamics in Three Dimensions A. General PrinciplesDocument12 pages6.7 Introduction Dynamics in Three Dimensions A. General PrincipleselvyNo ratings yet
- 2d Kinematics Projectile MotionnotesDocument4 pages2d Kinematics Projectile MotionnotesMahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Understanding Differentiation: Bridge CourseDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Differentiation: Bridge CourseAZTECIANO SORCERERNo ratings yet
- Isu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotionDocument22 pagesIsu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotioneysNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument15 pagesMotion in A Straight LineJyothiNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimensionDocument13 pagesMotion in One DimensionMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Physic Lab. I Manual MMDocument33 pagesPhysic Lab. I Manual MMhzkel2312No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument13 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentCvm GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class XI: Physics Chapter 3: Motion in Plane Chapter Notes Key LearningsDocument7 pagesClass XI: Physics Chapter 3: Motion in Plane Chapter Notes Key Learningsध्रुव पांडेयNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-15Document59 pagesChapter 12-15Abdulaziz FarhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics Lecture 3Document30 pagesEngineering Dynamics Lecture 3Anokha LadlaNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument10 pagesVector18008 K M ABDULLAH MAHMUD ZIADNo ratings yet
- Revise Physics in 1days PDFDocument141 pagesRevise Physics in 1days PDFAkshat PandeyNo ratings yet
- Vyg FJutwx ZD Ov IV7 AfwnDocument84 pagesVyg FJutwx ZD Ov IV7 AfwnAllyson DianeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Curvilinear MotionDocument43 pagesDynamics - Curvilinear Motionawethaf9876No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3 - Curvilinear Motion - Projectile - StudentversionDocument17 pagesChapter 2.3 - Curvilinear Motion - Projectile - StudentversionAmirulHanif AlyahyaNo ratings yet
- Y11 Physics 2022 Model Paper Answer KeyDocument71 pagesY11 Physics 2022 Model Paper Answer KeyMadhan chakravarthyNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes 02 KinematicsDocument13 pages11 Physics Notes 02 KinematicsPirated VirusNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - +1 Focus Area Notes All Chapters Seema TRDocument99 pagesHSSRPTR - +1 Focus Area Notes All Chapters Seema TRAswithNo ratings yet
- Waves and Oscillations SummaryDocument35 pagesWaves and Oscillations Summarykinusfrank92No ratings yet
- PH 103 Fall 2008:, Third Week: Scalars and VectorsDocument9 pagesPH 103 Fall 2008:, Third Week: Scalars and VectorsAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Iit-Physics - Set - IDocument50 pagesKinematics: Iit-Physics - Set - IHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Short Answer PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Short Answer PDFAmar SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch4. Motion in Plance (Vector) 2 (AK)Document19 pagesCh4. Motion in Plance (Vector) 2 (AK)20 Mohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Week3 PDFDocument39 pagesWeek3 PDFOverHorizon shameNo ratings yet
- Math Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesMath Investigatory ProjectKavinn100% (1)
- Motion in Plane NotesDocument9 pagesMotion in Plane NotesK S SayyedNo ratings yet
- Dynamics CompanionDocument191 pagesDynamics CompanionMahendra AbesingheNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram Law of VectorsDocument7 pagesParallelogram Law of VectorsdeezNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee StudyDocument955 pagesIit Jee StudyGarlapati Srinivasa Rao88% (17)
- Kinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyDocument18 pagesKinematics Using Vector Analysis: Standard CompetencyYasheive saadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Objectives: Projectile Motion: - Solve Problems Involving The Motion of A Projectile in 2DDocument28 pagesLecture 7 Objectives: Projectile Motion: - Solve Problems Involving The Motion of A Projectile in 2DExceed DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Notes 4Document15 pagesMechanics Notes 4niteshNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Question Bank-AllDocument53 pagesHSSRPTR - +1 Physics Focus Area Question Bank-AllAswithNo ratings yet
- 03 KinematicsDocument33 pages03 Kinematicssurya_kotniNo ratings yet
- Class11 - Physics - Motion in A Plane - SolutionsDocument14 pagesClass11 - Physics - Motion in A Plane - Solutionsajmerkaur947No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Kinematics CurveDocument30 pagesTopic 3 - Kinematics CurveBoodjieh So ImbaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension: Physics NotesDocument17 pagesMotion in One Dimension: Physics NotesEs ENo ratings yet
- Vector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsFrom EverandVector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- AnomaliesDocument7 pagesAnomaliesbookaccountNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- Nerve & MuscleDocument82 pagesNerve & MusclebookaccountNo ratings yet
- GitDocument57 pagesGitbookaccountNo ratings yet
- Involute Spur GearsDocument109 pagesInvolute Spur GearsBORNASCHNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 3 - Q3 - W5Document8 pagesDLL - Math 3 - Q3 - W5Ah KiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Reviewer Analytic GeometryDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Exam Reviewer Analytic GeometryMj LeeNo ratings yet
- SLHT Math9 Q3 Wk6Document8 pagesSLHT Math9 Q3 Wk6Erica BecariNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument23 pagesMensurationAditiNo ratings yet
- ULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureDocument14 pagesULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureCHARLIE AMOGUIS JRNo ratings yet
- All About TrigonometryDocument13 pagesAll About TrigonometryAhmad100% (1)
- Three Dimensional Geometry - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument22 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGocakes and bakes pvtNo ratings yet
- January Silver AnswersDocument31 pagesJanuary Silver AnswersNagajyothi KodaliNo ratings yet
- Suresh Thread 1Document21 pagesSuresh Thread 1anshuldceNo ratings yet
- Geometry Lesson ReadingDocument82 pagesGeometry Lesson ReadingGerard NugasNo ratings yet
- 2.2a Congruency of Triangles - 0Document28 pages2.2a Congruency of Triangles - 0pamela ocampoNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument11 pagesVectorsLyndon ChenNo ratings yet
- 01 Congruent TrianglesDocument7 pages01 Congruent TrianglesBilawal ZiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: Answer The QuestionsDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume: Answer The QuestionssaiNo ratings yet
- CTQ Nimcet 2022: Straight Line IDocument3 pagesCTQ Nimcet 2022: Straight Line INetwork BusyNo ratings yet
- Math 10 - Q2 - Week 3 - Module 3 - Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles - For ReproductionDocument21 pagesMath 10 - Q2 - Week 3 - Module 3 - Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles - For ReproductionMichelle IrisNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10.geometryDocument4 pagesGRADE 10.geometrySnenhlanhla MonaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Class 10 Term 2 Full ExamDocument9 pagesSolutions Class 10 Term 2 Full ExamPriyankAhujaNo ratings yet
- CS6100: Topics in Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Delaunay Triangulation John AugustineDocument25 pagesCS6100: Topics in Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Delaunay Triangulation John AugustineSentinel BergNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document17 pagesCH 04Raf.Z100% (2)
- Ss2 Technical Drawing ExamDocument3 pagesSs2 Technical Drawing ExamTriplejayart100% (1)
- Olymon 2001Document73 pagesOlymon 2001viterickNo ratings yet
- T-Ratio (Compound Angles)Document10 pagesT-Ratio (Compound Angles)TUSHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- ACT 30 Math Questions 1Document11 pagesACT 30 Math Questions 1mruthyunjayamNo ratings yet
- DevelopementDocument85 pagesDevelopementGagandeep Singh MaviNo ratings yet
- Erwin Kreyszig - Advanced Engineering Mathematics 10th Edition (Chapter 13) AnswersDocument3 pagesErwin Kreyszig - Advanced Engineering Mathematics 10th Edition (Chapter 13) AnswersShah RiyanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 3: General InstructionsDocument20 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Sample Paper 3: General InstructionsSHREYA AKHADENo ratings yet
- Geo t7 1Document15 pagesGeo t7 1api-261379705No ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pagesEngineering GraphicsAby AbrahamNo ratings yet