Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra Summary
Uploaded by
Shane RajapakshaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Summary
Uploaded by
Shane RajapakshaCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Summary
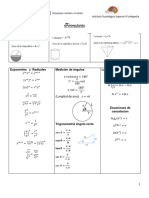
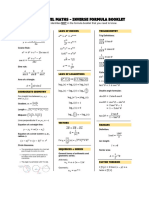
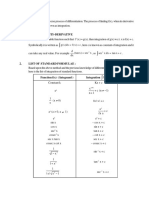
Mensuration
Area of a trapezium 1 Volume of a prism 𝐴ℎ
⎯⎯(𝑎 + 𝑏)ℎ
2
Curved Surface of a cylinder 2𝜋𝑟ℎ Volume of a cylinder 𝜋𝑟 ℎ
Area of a triangle 1 Volume of a pyramid 1
⎯⎯𝑎𝑏 sin(𝐶) ⎯⎯𝐴ℎ
2 3
Surface area of a prism 2𝐴 + 𝑃ℎ Volume of a cone 1
⎯⎯𝜋𝑟 ℎ
3
Surface area of a pyramid 1 Volume of a sphere 4
𝐴 + ⎯⎯𝑃ℎ ⎯⎯𝜋𝑟
2 3
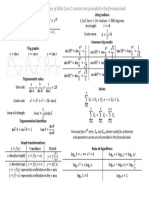
Functions
𝑓: 𝐷 → 𝑅, 𝑓(𝑥) = ⋯
Name: domain → co-domain (not range), rule
Function must be one-to-one or many-to-one (vertical line test).
Inverse functions and solving equations
The rule of the inverse can be found by swapping the 𝑥 and 𝑦 in the equation.
This can also be seen as a reflection in the line 𝑦 = 𝑥.
𝑓 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 and 𝑓 𝑓 (𝑥) = 𝑥
There may be restrictions on the inside function and there may be more solutions to consider.
Inverse function must be one-to-one and must be written as 𝑓 : 𝐷 → 𝑅, 𝑓 (𝑥) = ⋯
Function Inverse Composition to solve
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 𝑓 (𝑥) = √⎯⎯
𝑥 ⎯⎯⎯
√𝑥 = 𝑥 ⎯⎯
√𝑥 = 𝑥
⎯⎯ ⎯⎯ ⎯⎯ ⎯⎯
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 𝑓 (𝑥) = 𝑥 ⎯⎯ ⎯⎯
𝑥 =𝑥 𝑥 =𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑓 (𝑥) = log (𝑥) log (𝑒 ) = 𝑥 ( )
𝑒 =𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = sin(𝑥) 𝑓 (𝑥) = sin (𝑥) sin (sin(𝑥)) = 𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = cos(𝑥) 𝑓 (𝑥) = cos (𝑥) cos (cos(𝑥)) = 𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = tan(𝑥) 𝑓 (𝑥) = tan (𝑥) tan (tan(𝑥)) = 𝑥
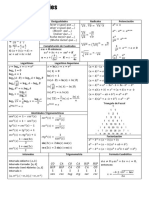
Polynomials
Remainder and factor theorems
The remainder of a polynomial 𝑃(𝑥) divided by (𝑥 − 𝑎) is equal to 𝑃(𝑎).
A polynomial 𝑃(𝑥) has a factor (𝑥 − 𝑎) if and only if 𝑃(𝑎) = 0.
Complete the square Quadratic formula Discriminant
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
𝑏 𝑏 −𝑏 ± √𝑏 − 4𝑎𝑐 Δ = 𝑏 − 4𝑎𝑐
𝑥 + 𝑏𝑥 = 𝑥 + ⎯⎯ − ⎯⎯ 𝑥 = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
2 2 2𝑎
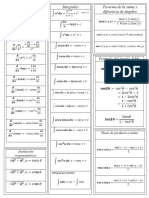
Exponential and logarithmic functions
Exponential and logarithmic functions
𝑎 ×𝑎 =𝑎 log (𝑥) + log (𝑦) = log (𝑥𝑦)
𝑎 𝑥
𝑎 ÷ 𝑎 = ⎯⎯⎯= 𝑎 log (𝑥) − log (𝑦) = log ⎯⎯
𝑎 𝑦
𝑎 =1 log (1) = 0
(𝑎 ) = 𝑎 ×
log (𝑥 ) = 𝑛 log (𝑥)
(𝑎 × 𝑏) = 𝑎 × 𝑏 𝑎 𝑎
⎯⎯ = ⎯⎯⎯
𝑏 𝑏
1 1 1
𝑎 = ⎯⎯, 𝑎 = ⎯⎯⎯ log ⎯⎯ = log (𝑥 ) = − log (𝑥)
𝑎 𝑎 𝑥
⎯⎯⎯ ⎯⎯⎯ 𝑚
𝑎⎯⎯ = √⎯⎯ 𝑎⎯⎯ = √𝑎 = √⎯⎯
⎯⎯
𝑎, 𝑎 log √𝑎 = log 𝑥 = ⎯⎯
𝑛
1 log (𝑥) = ln(𝑥)
𝑒 = lim 1 + ⎯⎯ ≈ 2.71828 …
→ 𝑛
Circular functions and trigonometry
Sine is the 𝑦 value on the unit circle. Cosine is the 𝑥 value on the unit circle.
Tangent is the length of the tangent to the 𝑥-axis. Check the sign of the gradient of the radius.
𝑂 𝐴 𝑂
sin(𝜃) = ⎯⎯ cos(𝜃) = ⎯⎯ tan(𝜃) = ⎯⎯
𝐻 𝐻 𝐴
Period of sine and cosine 2𝜋 cos (𝑥) + sin (𝑥) = 1
sin(𝜃)
Period of tangent 𝜋 𝜋 tan(𝜃) = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
sin ⎯⎯− 𝑥 = cos(𝑥) cos(𝜃)
2
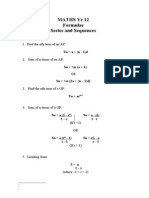
Linear simultaneous equations
Unique Solution No Solutions Infinite Solutions
Non-parallel lines Parallel lines that do not meet Parallel lines that completely
overlap each other
𝑚 ≠𝑚 𝑚 = 𝑚 , and 𝑐 ≠ 𝑐 𝑚 = 𝑚 , and 𝑐 = 𝑐
You might also like
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula Sheetapi-307595838No ratings yet
- A2 Pure Math NotesDocument7 pagesA2 Pure Math NotesSHREYA NARANGNo ratings yet
- Quick Math ReviewDocument9 pagesQuick Math ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument2 pagesAlgebrazehra batoolNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Quick ReviewDocument7 pagesMathematics Quick ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Document12 pagesFormula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Ziyang XieNo ratings yet
- C2 Essentials: Summary of AQA Core 2 Content Not Provided in The Formula BookDocument1 pageC2 Essentials: Summary of AQA Core 2 Content Not Provided in The Formula BookNyasha GweruNo ratings yet
- Functions and Graphs SummaryDocument2 pagesFunctions and Graphs SummaryLei LiNo ratings yet
- BC Calculus ReviewDocument29 pagesBC Calculus ReviewKawan EngNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Formula SpecDocument33 pagesPure Mathematics Formula SpecSubaproNo ratings yet
- Matematika - Formule Za A RazinuDocument7 pagesMatematika - Formule Za A RazinuJakov MandicNo ratings yet
- Rectangle Pyramid Area & Volume FormulasDocument3 pagesRectangle Pyramid Area & Volume FormulasFrancis AngtudNo ratings yet
- SL Maths 1 Page Formula SheetDocument1 pageSL Maths 1 Page Formula SheetpriyaNo ratings yet
- Formulario CalculoVectorialDocument2 pagesFormulario CalculoVectorialClaymohrNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo VerctorialDocument2 pagesFormulario Calculo VerctorialKEILA MERCADO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Formulário Cálculo DiferencialDocument1 pageFormulário Cálculo DiferencialmsbambirraNo ratings yet
- By: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales PotenciaciónDocument3 pagesBy: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales PotenciaciónJhon D'LozxoNo ratings yet
- Calculus CHAPTER 1Document11 pagesCalculus CHAPTER 1Kiet HoangNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Pre Calculus Formula SheetDocument1 pageGrade 11 Pre Calculus Formula SheetNantaNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 1Document9 pagesPure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 1Halal BoiNo ratings yet
- Formula ProvingDocument4 pagesFormula ProvingLew Juen HongNo ratings yet
- FormularioDocument1 pageFormularioSophia Malinalli Samperio OlveraNo ratings yet
- Formulario Corregido (Derivads e Integrales)Document7 pagesFormulario Corregido (Derivads e Integrales)juan carlos sánchezNo ratings yet
- 2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFDocument3 pages2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFMatthew SimeonNo ratings yet
- Fourier TC Vs 4Document33 pagesFourier TC Vs 4Daniel MedauraNo ratings yet
- IB Maths SL Formula Sheet 2019Document1 pageIB Maths SL Formula Sheet 2019Surya KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo Modificado Integral 2021Document2 pagesFormulario Calculo Modificado Integral 2021reneenav0No ratings yet
- Edexcel A Level Maths Inverse Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEdexcel A Level Maths Inverse Formula Sheetjanusiva1406No ratings yet
- FST Formula SheetDocument1 pageFST Formula Sheetmalvin.fedyanoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics I 12 Week 1Document4 pagesMathematics I 12 Week 1aybukealp59No ratings yet
- POWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsDocument3 pagesPOWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsLorniel GraxielNo ratings yet
- FP1 As-Level Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFP1 As-Level Formula SheetF JNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Olutions To A Quadratic Equation NtegralsDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet: Olutions To A Quadratic Equation Ntegralssamantha davidsonNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet晓春王No ratings yet
- SAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesSAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesFelipe RetamalNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formula SheetDocument1 pageGeometry Formula Sheetclara.hyun.baeNo ratings yet
- SUPER HOJA FORMULASDocument2 pagesSUPER HOJA FORMULASYUNIOR ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument2 pagesSuper HojaKyara MolinaNo ratings yet
- SUPER HOJA CHEATSHEETDocument2 pagesSUPER HOJA CHEATSHEETasdsdadNo ratings yet
- Formulario Electromagnetismo I ParcialDocument2 pagesFormulario Electromagnetismo I Parcialjhonny gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Super Hoja 1Document2 pagesSuper Hoja 1Daniel Diaz CastilloNo ratings yet
- Math For FunDocument4 pagesMath For FunFrederick MarsNo ratings yet
- Formulario de DerivadasDocument5 pagesFormulario de DerivadasMarcelo PérezNo ratings yet
- Formulario Examen Segudo HemiDocument5 pagesFormulario Examen Segudo HemiAndres CalderonNo ratings yet
- MAT 120 Calculus Analytic Geometry I Lesson 05 Derivatives Functions Series InverseDocument11 pagesMAT 120 Calculus Analytic Geometry I Lesson 05 Derivatives Functions Series InverseImranNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions (Kelompok 5)Document10 pagesTrigonometric Functions (Kelompok 5)Caesar RyantoNo ratings yet
- Formulario Cálculo Diferencial: Leyes de Los Exponentes Logaritmos Razones TrigonométricasDocument1 pageFormulario Cálculo Diferencial: Leyes de Los Exponentes Logaritmos Razones TrigonométricasJoel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Formulario EXTRADocument6 pagesFormulario EXTRALorenzo Frank ZappaNo ratings yet
- Analytic Functions of Complex VariableDocument18 pagesAnalytic Functions of Complex VariableUthman MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 2Document14 pagesPure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 2Halal BoiNo ratings yet
- Ap, Ab, Aq: 01 January 2024 20:25Document14 pagesAp, Ab, Aq: 01 January 2024 20:25SAHASRANSHU NAYAKNo ratings yet
- DerivadasDocument1 pageDerivadasKacho Rap OficialNo ratings yet
- Ma 210 Lecture 1Document8 pagesMa 210 Lecture 1James MukopaNo ratings yet
- Math FormulasDocument66 pagesMath Formulas抓愛恰No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument6 pagesTrigonometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Answer PagesDocument31 pagesAnswer PagesShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Staistics Exam G8Document8 pagesStaistics Exam G8Shane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 StatisticsDocument23 pagesGrade 7 StatisticsShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 StatisticsDocument23 pagesGrade 7 StatisticsShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument22 pagesAnswersShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Maths Revision Practice BookletDocument31 pagesYear 5 Maths Revision Practice BookletShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- War On Waste 2021 AssignmentDocument10 pagesWar On Waste 2021 AssignmentShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Line Q Ns DecimalDocument2 pagesLine Q Ns DecimalShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Multiplication and Division: Learning From HomeDocument38 pagesMultiplication and Division: Learning From HomeShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Year 6 2 BodmasDocument10 pagesYear 6 2 BodmasKhasimNo ratings yet
- Year 6 2 BodmasDocument10 pagesYear 6 2 BodmasKhasimNo ratings yet
- MASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberDocument44 pagesMASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- H Polygons Solns PDFDocument24 pagesH Polygons Solns PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- MASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberDocument44 pagesMASA Resource - Year 7 Assessment Tasks For NumberShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Whole Numbers - Burton Morewood PDFDocument44 pagesWhole Numbers - Burton Morewood PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- H Angles GBR 2011-11-29Document36 pagesH Angles GBR 2011-11-29Shane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- H No Plane Solns PDFDocument20 pagesH No Plane Solns PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Line Q Ns DecimalDocument2 pagesLine Q Ns DecimalShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Nap00031 PDFDocument61 pagesNap00031 PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Probability Level H PDFDocument16 pagesProbability Level H PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- 7 Fractions Student Booklet PDFDocument44 pages7 Fractions Student Booklet PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 19 PDFDocument17 pagesGrade 7 Exam 19 PDFShane Rajapaksha0% (1)
- Grade 7 Exam 18 PDFDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Exam 18 PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- 2695 21852150 NZL H Polygons NZL PDFDocument36 pages2695 21852150 NZL H Polygons NZL PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 12 PDFDocument13 pagesGrade 7 Exam 12 PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 7 PDFDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Exam 7 PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 19 PDFDocument17 pagesGrade 7 Exam 19 PDFShane Rajapaksha0% (1)
- H Converting Units Solns PDFDocument16 pagesH Converting Units Solns PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 21 PDFDocument16 pagesGrade 7 Exam 21 PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Exam 15 PDFDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Exam 15 PDFShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Introduction To Mellin Transforms Part - 01Document5 pagesIntroduction To Mellin Transforms Part - 01Shivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Tutorial ProblemsDocument3 pagesUnit 4 Tutorial Problemsaman bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Case 1 Excel Data Ebtm 350Document5 pagesCase 1 Excel Data Ebtm 350api-530290270No ratings yet
- 3.Problems on Expansion of Sinnθ and Cosnθ in Terms of Sinnθ AndcosnθDocument2 pages3.Problems on Expansion of Sinnθ and Cosnθ in Terms of Sinnθ AndcosnθShubham100% (1)
- Trignometric IdentitiesDocument4 pagesTrignometric IdentitiesMuhammadNo ratings yet
- List of Functions in Python Math ModuleDocument3 pagesList of Functions in Python Math ModuleBhasutkar MaheshNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument3 pagesAlgebra FormulasJALS100% (1)
- Fourier (Nirali)Document11 pagesFourier (Nirali)Bhavesh Rajput100% (1)
- FHMM1014 Topic 1 Numbers and Sets StudentDocument125 pagesFHMM1014 Topic 1 Numbers and Sets StudentPok Zheng HanNo ratings yet
- Math 9C Final Practice 3 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 9C Final Practice 3 With SolutionsArthy SangarNo ratings yet
- Proving Identities and Other ApplicationsDocument13 pagesProving Identities and Other ApplicationsJonnifer QuirosNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IntegralsDocument14 pagesTrigonometric IntegralsStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PARI GPDocument52 pagesTutorial PARI GPEmmanurevaNo ratings yet
- Trig IdentitiesDocument8 pagesTrig IdentitiesZeck Aviel Alcantara100% (1)
- MSC Syll Math-UohDocument49 pagesMSC Syll Math-Uohrcpuram01No ratings yet
- Formulasheetalgebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormulasheetalgebra 2 Trigapi-265200443No ratings yet
- 19-Indefinite Integral-01 - TheoryDocument23 pages19-Indefinite Integral-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 11th Maths TrignometryDocument8 pages11th Maths TrignometryAdesh GadageNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Complex Kind: Week 5Document15 pagesAnalysis of A Complex Kind: Week 5rabiaNo ratings yet
- 433 8.5 Application of Laplace Transforms To Partial Differential EquationsDocument16 pages433 8.5 Application of Laplace Transforms To Partial Differential EquationsHyun Deog YooNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in General MathematicsClarisse MeiNo ratings yet
- Milne Thomson - Calculus of Finite DifferencesDocument590 pagesMilne Thomson - Calculus of Finite DifferencesmtichyscribdNo ratings yet
- Sum SeriesDocument2 pagesSum SeriesUnique ArkNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument8 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaGargi SarkarNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series 1.1-1.89: Preface VIIDocument3 pagesSequence and Series 1.1-1.89: Preface VIIHamid HamidoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document1 pageAssignment 3Harish VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Additional Complex Number Problems 2 PDFDocument2 pagesAdditional Complex Number Problems 2 PDFtiwihNo ratings yet
- Negative secant and tangent between 90 and 180 degreesDocument7 pagesNegative secant and tangent between 90 and 180 degreesKevin Christian Plata100% (1)
- Complex Number IIDocument18 pagesComplex Number IIAadarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument30 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet