Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geo Volcanoes Projekt-2 PDF
Uploaded by
Viktória Hrašková0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesOriginal Title
GEO VOLCANOES PROJEKT-2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesGeo Volcanoes Projekt-2 PDF
Uploaded by
Viktória HraškováCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
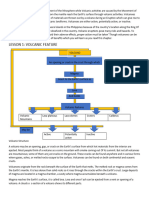
GEO VOLCANOES PROJEKT mantle, it creates magma,
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z which rises to form an explosive
gh79qt/revision/3 volcano. Hot spots are areas
on Earth where magma is hotter
than surrounding magma. It is
located over a mantle or an
● definition: A volcano is an
area under the rocky outer layer
opening in a planet or moon’s
of Earth, called the crust,
crust through which molten
rock, hot gasses, and other
● types-activity: active, dormant,
materials erupt. Volcanoes often
erupting, extinct- Active
form a hill or mountain as layers
volcanoes have a recent history
of rock and ash build up from
of eruptions; they are likely to
repeated eruptions.
erupt again. Dormant volcanoes
● where do they occur ? Volcanoes
have not erupted for a very long
are found on both land and the
time but may erupt at a future
ocean floor. When volcanoes
time. Erupting volcanoes erupt
erupt on the ocean floor, they
magma which is called lava.
often create underwater
Extinct volcanoes are not
mountains and mountain ranges
expected to erupt in the future.
as the released lava cools and
● types-structure: stratovolcanoes-
hardens. Volcanoes on the
created by eruptions and following
ocean floor become islands
effusions of lava, they are made of
when the mountains become so
layers of lava volcanic fragments
large they rise above the
of different size
surface of the ocean. Volcanoes
shield volcanoes- they produce
usually form along plate
only lava, volcanoes are not steep
boundaries, where tectonic
because the lava is very fluid when
plates are either moving
erupted, they do not explode
towards or away from one
● structure:
another:Divergent (or
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/gui
constructive) boundaries -
des/zpf9mnb/revision/2
this is where two plates move
● + - effects:
away from one another. Magma
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/gui
rises up to fill the gaps
des/zpf9mnb/revision/3
between.Convergent
● monitoring:https://www.bbc.co.uk/
boundaries - this is where two
bitesize/guides/zpf9mnb/revision/5
plates move towards one
● lava flow-
another. The oceanic crust
sinks beneath the continental
crust at a subduction zone - a SOURCES:
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/volcanoes/
point where one crustal plate https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zpf9mnb/revision/1
https://volcano.oregonstate.edu/shield-volcanoes-0
is forced beneath another. As
https://www.usgs.gov/programs/VHP/lava-flows-destroy-everything-their-path
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/pyroclastic-flow/
https://www.britannica.com/science/lahar
the oceanic crust sinks into the https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/vsc/glossary/vei.html
https://sierra.sitehost.iu.edu/papers/2013/hamdan.pdf
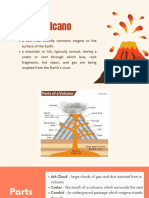
Volcanoes are openings in a planet or magma chamber- place where the
moon's crust through which molten molten rock is stored beneath the
rock, hot gasses and other materials ground.
erupt. They form a hill or mountain as main vent- channel through which
layers of rock and ash build up from magma travels to reach the Earth's
repeated eruptions. surface.
secondary vent- some magma can
They are found on ocean floors and escape through the side of the volcano,
land. They occur on plate boundaries, particularly when the main vent is
where tectonic plates are moving blocked. crater- this is found at the top
towards each (convergent boundaries) of a volcano, where the magma erupts
other or away (divergent boundaries). from.
Hotspot is a place where intense heat secondary cone- cone that builds up
in the mantle rises towards the crust. around secondary vents.
When magma reaches the surface it ash- powdery residue left after the
creates volcanoes. burning of a compound.
steam and gas- clouds which are
active- recent eruption history of pushed out of the volcano.
eruption, they are likely to erupt again. volcanic bombs- large blocks of hot
dormant- these volcanoes have not rock thrown from a volcano.
erupted in a long time but may erupt in
the future. Scientists monitor volcanoes so they
extinct- these volcanoes are expected can predict their eruption. They use
not to erupt in the future. seismometers- measures earthquakes
eruptive- volcanoes that erupt magma occurring near an eruption.
(lava). tiltmeters and GPS satellites- monitor
any changes in landscape, volcanoes
stratovolcanoes- created by eruptions tend to swell near eruption.
and following effusions of lava, they They measure temperatures-
are made of layers of lava, volcanic volcanoes become hotter when magma
fragments of different sizes. starts to rise.
shield volcanoes- they produce only VEI- volcanic explosivity index- a
lava, volcanoes are not steep because numeric scale that measures the relative
the lava is very fluid when erupted, explosivity of historic eruptions.
they do not explode. Volume of products, height of cloud
and qualitative observations are used to
determine the explosivity value.
SOURCES:
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/volcanoes/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zpf9mnb/revision/1
https://volcano.oregonstate.edu/shield-volcanoes-0
https://www.usgs.gov/programs/VHP/lava-flows-destroy-everything-their
-path
https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/pyroclastic-flow/
https://www.britannica.com/science/lahar
https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/vsc/glossary/vei.html
https://sierra.sitehost.iu.edu/papers/2013/hamdan.pdf
You might also like
- What Is A Supervolcano?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Supervolcano?api-26229229No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToVaansh DhirwaniNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDocument83 pagesVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesExam 1 AnswersAnonymous npWqNpk9vG100% (2)
- Formation and Classification of Volcanoes Based On BehaviorDocument32 pagesFormation and Classification of Volcanoes Based On BehaviorUserJoshNo ratings yet
- DRRR - Module 16Document16 pagesDRRR - Module 16Atasha ZyraNo ratings yet
- Science Q3 Week 1 2printDocument8 pagesScience Q3 Week 1 2printChelsea BialaNo ratings yet
- Geo Volcanoes Projekt-3 PDFDocument4 pagesGeo Volcanoes Projekt-3 PDFViktória HraškováNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesTadiwa MawereNo ratings yet
- SCI NOTES Q3 by Rianraingoaway PDFDocument3 pagesSCI NOTES Q3 by Rianraingoaway PDFRASCO JHERARD YSABELLENo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument17 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesChristle NgoveNo ratings yet
- CH5 VolcanismDocument8 pagesCH5 VolcanismNovie GraceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VolcanoDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Volcanoapi-266403636No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDemon bbyNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument24 pagesVolcanoesBarbara BananaNo ratings yet
- On Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orDocument5 pagesOn Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orrituNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Handouts 2Document6 pagesLesson 1 Handouts 2Keesha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Geography Note Grade 8Document7 pagesGeography Note Grade 8hasanNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleDocument18 pagesScience9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleGrace OroNo ratings yet
- Structure of A VolcanoDocument3 pagesStructure of A VolcanoIsabella persadNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Have Volcanoes?: WWW - Bgs.ac - UkDocument2 pagesWhy Do We Have Volcanoes?: WWW - Bgs.ac - UkHendrix Antonni AmanteNo ratings yet
- Science 3RD Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 3RD Quarter Reviewer-Rain Santos-No ratings yet
- Science 3rd Q RevDocument6 pagesScience 3rd Q Revethan elizaldeNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Lesson 1Document2 pagesScience Reviewer: Lesson 1AMIEL MOIRA BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (3RD Quarter)Document9 pagesScience Reviewer (3RD Quarter)Smilingchae TomatominNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument74 pagesVOLCANOESLira VelascoNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes - VulcanicityDocument12 pagesGeography Notes - VulcanicityMaster T100% (5)
- It's Getting Hot in Here: A Teacher Briefing On VolcanoesDocument5 pagesIt's Getting Hot in Here: A Teacher Briefing On VolcanoesHelen HodgsonNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument14 pagesSci ReviewerJamela Viene ValsorableNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument1 pageEarth and Life ScienceJerick E RebulaNo ratings yet
- Science DraftDocument4 pagesScience Draftmaster dilucNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument14 pagesSci ReviewerJamela Viene ValsorableNo ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer 1Document14 pagesSci Reviewer 1Jamela Viene ValsorableNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonDocument11 pagesScience 9 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbNo ratings yet
- Science-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic EruptionDocument8 pagesScience-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic Eruptionkiandizon12No ratings yet
- Week 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESDocument2 pagesWeek 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESNorraine Denice Jabalde NoricoNo ratings yet
- Geo2.5 VolcanismDocument19 pagesGeo2.5 VolcanismDanica Saraus DomughoNo ratings yet
- Geol 100 VolcanoDocument16 pagesGeol 100 VolcanoTamio, Marc Angelo100% (1)
- RANDOMDocument10 pagesRANDOMRico Albert Salting DipadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Volcanoes and Their TypesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Volcanoes and Their TypesJohn Renz CastilloNo ratings yet
- Volcano HazardsDocument17 pagesVolcano HazardsREYNON GREGORIONo ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1Document31 pagesNature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1jairolostreNo ratings yet
- VOLCANODocument4 pagesVOLCANOTristan BucaoNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument14 pagesVolcanoLloren LianneNo ratings yet
- 10 VolcanoDocument74 pages10 Volcanostephadi0910No ratings yet
- Wiuhrq 2 IwDocument2 pagesWiuhrq 2 IwJhanna Gil BuctolanNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDocument5 pagesVolcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument2 pagesVolcanoesAntonietteSopinoCempron100% (1)
- VolcanoesDocument2 pagesVolcanoesAntonietteSopinoCempronNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument3 pagesVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsZara AhmedNo ratings yet
- Q3 Sci Rev FinalDocument10 pagesQ3 Sci Rev FinalReigne Daniella OgatisNo ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer 3Document14 pagesSci Reviewer 3Jamela Viene ValsorableNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument49 pagesVolcanoesJuan Sebastian Bohorquez RozoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes CompositeDocument29 pagesVolcanoes CompositeRudly Ann BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes 9d1d91f4Document4 pagesVolcanoes 9d1d91f4KEERTHI MANASA N R GYUA21012No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Ta3Document3 pagesScience Reviewer Ta3Alyssa LibranzaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument25 pagesVolcanoesjenjang yannieNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - Module 1 FinalDocument69 pagesVolcanoes - Module 1 FinalAngel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- I and S Volcano ReportDocument7 pagesI and S Volcano ReportJASMSJS SkskdjNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument42 pagesVolcanoesEllecarg Cenaon CruzNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes IIDocument49 pagesVolcanoes IIAsfandyar KhanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Geology 2nd Edition Reichard Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Geology 2nd Edition Reichard Test Bank Full Chapter PDFchristabeldienj30da100% (15)
- Carn & Pyle 2001 Petrology Geochem Lamongan VC PDFDocument41 pagesCarn & Pyle 2001 Petrology Geochem Lamongan VC PDFbrilianNo ratings yet
- By C. W. Smith: U.S. Geological Survey Jiddah, Saudi Arabia 1981Document29 pagesBy C. W. Smith: U.S. Geological Survey Jiddah, Saudi Arabia 1981Osman EjameNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 5 & 6 Grade 12Document54 pagesDRRR Module 5 & 6 Grade 12ayakaloveayato5509No ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes: Earth & Life Science Week 6 HandoutsDocument2 pagesEndogenic Processes: Earth & Life Science Week 6 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Volcano HazardsDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Volcano HazardsMa. Michaela Agape EstacioNo ratings yet
- Interior of The Earth NotesDocument8 pagesInterior of The Earth NotesShe ShineNo ratings yet
- Volcanology and Geothermal Energy PDFDocument1 pageVolcanology and Geothermal Energy PDFJabbok GorkaNo ratings yet
- All New LP Grade 9 (1st)Document9 pagesAll New LP Grade 9 (1st)Earn Jason CruzNo ratings yet
- Gondwana Research: H. Furnes, M. de Wit, B. RobinsDocument26 pagesGondwana Research: H. Furnes, M. de Wit, B. RobinsMárcio Antônio da SilvaNo ratings yet
- 24 Eruptive History of Mayon Volcano 1985Document19 pages24 Eruptive History of Mayon Volcano 1985Al G100% (1)
- The Petrology and Geochemistry of Gharyan Volcanic Province Of, NW LibyaDocument67 pagesThe Petrology and Geochemistry of Gharyan Volcanic Province Of, NW LibyaFrank Hoyos CubasNo ratings yet
- 03 VolkanologiDocument29 pages03 VolkanologiNicholas GrayNo ratings yet
- English Language Year 5: ReadingDocument10 pagesEnglish Language Year 5: ReadingDewi AlipNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE RocksDocument26 pagesEARTH SCIENCE RocksDAKSINo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 EditDocument6 pagesLesson 10 Edittrần hải namNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2Document24 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2Angelo DavidNo ratings yet
- Oregon Geology Vol 60Document144 pagesOregon Geology Vol 60Edwin100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Kristine BaguinatNo ratings yet
- What This Module Is About: VolcanoesDocument4 pagesWhat This Module Is About: VolcanoesGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Bicol Region, On The Large Island of Luzon in The Philippines. Cone-Shaped Wonder of A Volcano in BicolDocument4 pagesBicol Region, On The Large Island of Luzon in The Philippines. Cone-Shaped Wonder of A Volcano in Bicolahna zurcNo ratings yet
- Lake NyosDocument1 pageLake NyosAdreno CortexNo ratings yet
- The Lost City of Pompeii: Mapping ActivityDocument1 pageThe Lost City of Pompeii: Mapping ActivityHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Geography Grade 10 Term 2Document52 pagesGeography Grade 10 Term 2hghmotaunglebohangNo ratings yet
- Moore 2001 Density of Basalt Core From Hilo Drill Hole, HawaiiDocument10 pagesMoore 2001 Density of Basalt Core From Hilo Drill Hole, HawaiiAbdelmounji AmineNo ratings yet
- Volcano Sample TestDocument13 pagesVolcano Sample TestJoyArianneOrtegaAdelNo ratings yet