Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jawapan Module Superb SBP Biologi Tingkatan 4
Uploaded by
Nasihin Bin AzmiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jawapan Module Superb SBP Biologi Tingkatan 4
Uploaded by
Nasihin Bin AzmiCopyright:
Available Formats
JAWAPAN
BAB BAB
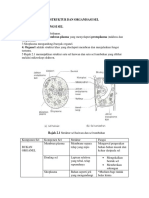
Pengenalan kepada Biologi dan Peraturan Makmal Biologi Sel dan Organisasi Sel
1 Introduction to Biology and Laboratory Rules 2 Cell Biology and Organisation
1.1 Keselamatan dan Peraturan dalam Makmal 2.1 Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Biologi Cell Structure and Function
Safety and Rules in Biology Laboratory 1 Persamaan/ Similarities:
1 • Berhati-hati semasa mengendalikan radas kaca Mempunyai nukleus, sitoplasma, membran plasma, jasad
yang panas. Golgi, mitokondrion, jalinan endoplasma dan ribosom.
Be careful when handling hot glass apparatus. Have nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus,
• Laporkan sebarang peralatan atau barang kaca mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes.
yang rosak kepada guru dengan segera.
Perbezaan/ Differences:
Report any damaged apparatus or glassware to the
teacher immediately. Sel haiwan Sel tumbuhan
• Jauhkan bahan kimia mudah terbakar daripada Animal cell Plant cell
sumber api. Tidak mempunyai Mempunyai dinding sel
Keep flammable chemicals away from fire sources. dinding sel Has cell wall
• Jangan sentuh, hidu atau rasa bahan kimia secara Does not have cell wall
langsung.
Do not touch, smell or taste chemical substances Tidak mempunyai Mempunyai kloroplas
directly. kloroplas Has chloroplast
Does not have chloroplast
1.3 Berkomunikasi dalam Biologi
Communicating in Biology Tiada vakuol/ jika ada Mempunyai vakuol
saiz kecil bersaiz besar
1 Kadar hidrolisis albumen (% minit-1) No vacuoles/ if present, they Has a large vacuole
Rate of hydrolysis of albumen (% minute-1)
are very small
Mempunyai sentriol Tidak mempunyai
1.2
Has centrioles sentriol
Does not have centrioles
1.0 ×
×
2 Sel bawang kerana bebawang hidup dalam tanah.
0.8
Pokok bawang mendapat makanan daripada organ
×
simpanannya, iaitu bebawang.
0.6
Onion cell because onions grow in the ground. Onions obtain
0.4 × food from their storage organs which are onion bulbs.
0.2 2.2 Proses Hidup Organisma Unisel
Kepekatan
albumen (%) Living Processes in Unicellular Organisms
Albumen 1(a) (i) Pseudopodium/ Pseudopodium
0 1 2 3 4 5 concentration (%) (ii) • Amoeba sp. bergerak dengan
mengunjurkan pseudopodium (kaki
2 (a) Keratan rentas, melintang palsu). Ini diikuti oleh pengaliran
Cross section, transversely sitoplasma ke bahagian pseudopodium
(b) Keratan membujur, menegak yang diunjurkan.
Longitudinal section, vertically Amoeba sp. moves by extending out its
pseudopodium (false feet). This is followed
Praktis Sumatif by the flow of cytoplasm into the extended
pseudopodium.
KERTAS 1 • Amoeba sp. bergerak ke arah makanan
dengan mengunjurkan pseudopodium
1 D 2 B 3 A 4 A untuk memerangkap zarah makanan
secara fagositosis.
J1 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
Amoeba sp. moves towards food by extending The epidermal tissue has cells with large vacuoles
its pseudopodium to trap food particles by and thin layer of cytoplasm. This tissue covers the
phagocytosis. surface of plants to protect it from injury and loss of
• Vakuol makanan bergabung dengan water.
lisosom dan makanan dihidrolisis oleh (b) • Tisu epitelium terdiri daripada satu atau lebih
enzim lisozim. lapisan sel yang melapik sesuatu permukaan
The food vacuole is combined with lysosome atau rongga badan dan melindunginya
and the food particles are hydrolysed by the daripada kecederaan dan pengontangan.
lysozyme enzyme. The epithelial tissue is made up of one or more
(b) (i) Amoeba sp. X layers of cells that cover the surface or body cavity
Amoeba sp. X and protects it from injury and drying up.
(ii) • Apabila saiz Amoeba sp. kecil, jumlah • Tisu otot terdiri daripada sel-sel otot dan
luas permukaan per isi padu selnya gentian otot yang boleh mengecut dan
adalah besar. mengendur untuk menghasilkan pergerakan.
When the size of Amoeba sp. is small, the total The muscle tissue is made up of muscle cells
surface area per cell volume is large. and muscle fibres that can contract and relax to
• Air meresap masuk ke dalam sel dengan produce movement.
cepat. 2.4 Aras Organisasi dalam Organisma Multisel
Water diffuses into the cell quickly. Levels of Organisation in Multicellular Organisms
• Kadar pengecutan vakuol mengecut yang 1 (a) P : Kloroplas/ Chloroplast
cepat membolehkan sel menyingkirkan Q : Sel mesofil palisad/ Palisade mesophyll cell
air berlebihan pada kadar yang cepat. R : Tisu floem/ Phloem tissue
The fast contraction rate of the contractile (b) P, Q, R
vacuole allows the cell to get rid of excess
(c) (i) • Mesofil palisad mengandungi banyak
water at a rapid rate.
kloroplas untuk penyerapan cahaya
(c) Semakin tinggi kepekatan larutan natrium klorida,
matahari yang maksimun.
semakin perlahan kadar pengecutan vakuol
Palisade mesophyll contain a large number of
mengecut.
chloroplasts for maximum absorption of sunlight.
The higher the concentration of sodium chloride solution,
• Cahaya matahari diperlukan oleh daun
the slower the rate of contraction of the contractile
vacuole. untuk menjalankan fotosintesis.
(d) Oleh sebab Amoeba sp. hidup dalam air tawar, air Sunlight is needed for the leaves to carry out
photosynthesis.
sentiasa meresap ke dalam sel secara osmosis dari
(ii) Tisu R: Mengangkut bahan makanan organik
persekitaran yang hipotonik.
ke seluruh bahagian tumbuhan.
Because Amoeba sp. lives in freshwater, water always
Tissue R: Transport organic food to all parts of
diffuse into the cell by osmosis from a hypotonic
the plant.
environment.
(e) Apabila racun respirasi ditambah ke dalam larutan, Sel pengawal: Mengawal pembukaan dan
repirasi sel akan terhenti. Tiada tenaga dijana untuk penutupan stoma.
pengecutan vakuol mengecut. Vakuol mengecut Guard cell: Controls the opening and closing
berhenti mengecut. of the stoma.
When respiratory poison is added to the solution, cellular Praktis Sumatif
respiration will stop. No energy is generated for the
contraction of the contractile vacuole. The contractile KERTAS 1
vacuole stops contracting. 1 D 2 A 3 D 4 A 5 A
2.3 Proses Hidup Organisma Multisel KERTAS 2
Living Processes in Multicellular Organisms Bahagian A
1 (a) • Tisu meristem ialah tisu yang mempunyai sel 1 (a) (i) Sel haiwan/ Animal cell
yang bersaiz kecil, sitoplasma yang padat dan (ii) Tiada dinding sel/ No cell wall
nukleus yang banyak. Tisu ini berfungsi untuk (iii) Proses pembezaan/ Diffrenciation process
menjalankan pembahagian sel. (b) • Tapak penjanaan tenaga melalui proses
The meristematic tissue is a tissue that has small pengoksidaan glukosa semasa respirasi sel.
cells, compact cytoplasm and many nuclei. This A site that generates energy through the glucose
tissue carries out cell division. oxidation process during cellular respiration.
• Tisu epidermis mempunyai sel yang bervakuol • Tenaga dijana dalam bentuk molekul ATP
besar dengan lapisan sitoplasma nipis. Tisu (adenosina trifosfat) untuk digunakan oleh
ini berfungsi meliputi permukaan tumbuhan sel X.
untuk melindunginya daripada kecederaan Energy released in the form of ATP (adenosine
dan kehilangan air. triphosphate) molecules to be used by cell X.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J2
(c) (i) P : Jasad Golgi The molecules diffuse from area of high
Golgi apparatus concentration of glucose from outside the cell
Q : Jalinan endoplasma kasar into the cell.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum • Mengikut cerun kepekatan.
(ii) • Sel tidak dapat merembeskan enzim/ Follow concentration gradient.
hormon. • Melalui protein pembawa.
Cell is not able to secrete enzyme/ hormone. Through carrier protein.
• Gagal memproses/ mengubah suai/ S : • Ion Na+ diangkut melalui pengangkutan
membungkus/ mengangkut bahan kimia aktif.
seperti protein/ karbohidrat/ glikoprotein. Na+ ions are transported by active transport.
Fail to process/ modify/ pack/ transport • Ion bergerak dari kawasan berkepekatan
chemicals such as protein/ carbohydrate/ rendah Na+ di luar sel ke dalam sel.
glycoprotein. The ions move from area of low concentration
• Protein gagal diubah suai menjadi enzim. of Na+ from outside cell into the cell.
Protein will not be modified to enzyme. • Melawan cerun kepekatan.
Against concentration gradient.
BAB • Melalui protein pembawa.
Pergerakan Bahan Merentasi Membran Plasma
3 Movement of Substances Across a Plasma Membrane Through carrier protein.
• Menggunakan tenaga.
3.1 Struktur Membran Plasma Using energy.
Structure of Plasma Membrane 2 (a) Pergerakan bersih molekul air dari satu larutan
1 (a) A : Protein pembawa/ Carrier protein berkepekatan bahan terlarut rendah (keupayaan air
B : Protein liang/ Channel protein tinggi) ke larutan berkepekatan bahan terlarut tinggi
C : Dwilapisan fosfolipid/ Phospholipid bilayer (keupayaan air rendah) melalui membran telap
(b) Menjadikan dwilapisan kuat, lebih fleksibel dan memilih.
kurang telap terhadap bahan larut air. A net movement of water molecules from a low solute
Make phospholipid bilayer stronger, more flexible, less concentration (high water potential) solution to a high
permeable to water soluble substances. solute concentration (low water potential) solution
(c) • Membran telap memilih through a selectively permeable membrane.
Selectively permeable membrane (b) • Jumlah molekul air di dalam tiub Visking
• Membenarkan pergerakan bebas sesetengah bertambah.
bahan merentasinya dan menghalang atau The amount of water molecules in Visking tube
mengehadkan pergerakan bahan yang lain. increase.
Only allows free movement of certain substances • Tiub akan mengembang.
across it and limit the movement of other substances. The tube will expand.
• Larutan sukrosa 30% mempunyai kepekatan
3.2 Konsep Pergerakan Bahan Merentasi Membran molekul air yang rendah.
Plasma 30% sucrose solution has a lower concentration of
Concept of Movement of Substances Across a Plasma water molecules.
Membrane • Air akan meresap masuk ke dalam tiub
1 (a) Q : Protein liang/ Channel protein Visking secara osmosis.
R : Protein pembawa/ Carrier protein Water will diffuse into the Visking tube by osmosis.
(b) Q : • Ion Ca2+ diangkut melalui resapan
berbantu.
AKTIVITI 3.1
Ca2+ ions are transported by facilitated diffusion.
• Ion meresap dari kawasan berkepekatan
Pemboleh ubah: (a) Saiz molekul/ Molecule size
tinggi Ca2+ di luar sel ke dalam sel.
Variables (b) Kehadiran molekul di dalam tiub
The ions diffuse from area of high concentration
Visking dan di dalam bikar
of Ca2+ from outside the cell into the cell.
Presence of molecules in the Visking
• Mengikut cerun kepekatan
tubing and the beaker
Follow concentration gradient
(c) Suhu persekitaran dan masa
• Melalui protein liang
rendaman
Through channel protein
Surrounding temperature and soaking time
R : • Glukosa diangkut melalui resapan
Pemerhatian: Jawapan murid/ Student's answer
berbantu.
Observation
Glucose are transported by facilitated diffusion
Perbincangan: 1 Saiz molekul kanji terlalu besar untuk
• Molekul glukosa meresap dari kawasan
merentasi liang pada membran tiub
Discussion
berkepekatan tinggi di luar sel ke dalam
Visking.
sel.
J3 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
The size of starch molecule is too large to silinder ubi kentang secara osmosis
diffuse through the pores on the membrane dan meningkatkan jisim dan panjang
of Visking tubing. silinder kentang. Sel ubi kentang
2 Molekul glukosa boleh merentasi menjadi segah.
membran tiub Visking dengan mudah (Concentration of sucrose solution is
dan masuk ke dalam larutan di dalam depend on student’s answer). Water
bikar. diffuses into potato strips by osmosis and
Glucose molecules can diffuse easily increases their masses and lengths. The
through the membrane of Visking tubing cells become turgid.
and enter the solution in the beaker. 3 (Kepekatan larutan sukrosa mengikut
3 Saiz molekul glukosa adalah kecil bagi jawapan murid). Air meresap keluar
merentasi liang pada tiub Visking. dari silinder ubi kentang secara osmosis
The size of glucose molecules are small dan mengurangkan jisim dan panjang
to pass through the pores on the Visking silinder ubi kentang. Sel ubi kentang
tubing. menjadi flasid.
Kesimpulan: Molekul kecil dapat merentasi membran (Concentration of sucrose solution is
Conclusion telap memilih manakala molekul besar depend on student’s answer). Water
tidak. Hipotesis diterima. diffuses out of potato strips by osmosis and
Only small molecules are able to diffuse through decreases their masses and lengths. The
a selectively permeable membrane while cells become flaccid.
large molecules cannot. Hypothesis is accepted. Kesimpulan: Kepekatan larutan luar sel yang isotonik
Conclusion terhadap sap sel ubi kentang ialah
3.3 Pergerakan Bahan Merentasi Membran Plasma kepekatan yang tidak mengubah jisim
dalam Organisma Hidup silinder ubi kentang. Hipotesis diterima.
Movement of Substances Across a Plasma Membrane in Concentration of the extracellular solution
Living Organisms which is isotonic to the potato cell sap is the
1 (a) • Larutan natrium klorida 4.0% adalah hipertonik concentration that does not change the mass
kepada sel. of the potato strips. Hypothesis is accepted.
4.0% sodium chloride solution is hypertonic to the cell.
3.4 Pergerakan Bahan Merentasi Membran Plasma
• Air meresap keluar daripada sel secara osmosis.
dalam Kehidupan Harian
Water diffuses out of the cell by osmosis.
Movement of Substances Across a Plasma Membrane and Its
• Sel mengalami krenasi/ Cell undergoes crenation
Application in Daily Life
(b) • Air suling adalah hipotonik kepada sel.
1 (a) • Sayur diawet atau dijerukkan menggunakan
Distilled water is hypotonic to the cell.
larutan cuka.
• Air meresap masuk ke dalam sel secara osmosis.
Vegetables can be preserved or pickled in vinegar
Water diffuses into the cell by osmosis.
solution.
• Sel mengalami hemolisis
• Larutan cuka akan meresap masuk ke dalam
Cell undergoes haemolysis
sel-sel sayur.
Vinegar solution will diffuse into the cells of the
AKTIVITI 3.2
vegetables.
• Cuka mempunyai nilai pH yang rendah,
Hipotesis: Kepekatan larutan luar sel yang isotonik
keadaan ini tidak menggalakkan pertumbuhan
Hypothesis terhadap sap sel ubi kentang ialah
mikroorganisma.
kepekatan yang tidak mengubah jisim
Vinegar has low pH value, this condition is
silinder ubi kentang. unfavourable conditions for growth of microorganism.
Concentration of the extracellular solution • Sayur yang dijerukkan dapat bertahan lama.
which is isotonic to the potato cell sap is the
Pickled vegetables can last longer.
concentration that does not change the mass of
the potato strips. (b) • Mangga dipotong kecil dan direndam dalam
Keputusan: Jawapan murid/ Student's answer larutan gula pekat.
Mango is cut into small pieces and soaked into a
Results
concentrated sugar solution.
Perbincangan: 1 Kepekatan larutan sukrosa yang
• Larutan gula pekat adalah hipertonik kepada
Discussion isotonik kepada sap sel ubi kentang
sap sel mangga dan menyebabkan air meresap
ditentukan daripada persilangan graf
keluar daripada sel mangga secara osmosis.
pada paksi-x.
The concentrated sugar solution is hypertonic to
Concentration of isotonic sucrose solution
the mango cell sap, water diffuse out of the cell by
to cell sap of potato can be determined from
osmosis.
the intersection of a graph at the x-axis.
• Sel mangga kehilangan air dan mengalami
2 (Kepekatan larutan sukrosa mengikut
plasmolisis.
jawapan murid). Air meresap ke dalam
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J4
The mango cells become dehydrated and plasmol- BAB
Komposisi Kimia dalam Sel
ysed. 4 Chemical Composition in a Cell
• Keadaan ini tidak menggalakkan pertumbuhan
mikroorganisma, mangga dapat bertahan 4.1 Air
lama. Water
This condition is unfavourable conditions for 1
growth of microorganism, mango can last longer. Sebatian
Molekul tak organik
berkutub Inorganic
SUDUT KBAT Polar molecule
compound
• Larutan garam penghidrat oral (ORS) mengandungi Air
natrium, kalium dan glukosa. Water
Oral rehydration salts (ORS) solution contains sodium,
Muatan haba
potassium and glucose. tentu tinggi Pelarut semesta
• Larutan ORS dapat mengelakkan pesakit daripada High specific Universal solvent
dehidrasi. heat capacity
ORS solution can prevent from dehydration.
• Air, natrium, kalium dan glukosa adalah unsur yang
hilang akibat cirit-birit dan muntah-muntah. 2 • Sebagai bahan mentah fotosintesis
Water, sodium, potassium and glucose are the elements that are As raw material for photosynthesis
lost due to diarrhoea and vomiting. • Mengekalkan kesegahan sel-sel tumbuhan
• Glukosa dalam ORS membolehkan penyerapan garam Maintain turgidity of plant cells
secara berkesan.
Glucose in ORS enable uptake of salts efficiently. 4.2 Karbohidrat
• Di dalam usus, glukosa, natrium dan kalium diserap Carbohydrates
secara resapan berbantu oleh protein pembawa. 1 (a) Glukosa/ Glucose
In the intestine, glucose, sodium and potassium are absorbed by (b) Fruktosa/ Fructose
carrier protein via facilitated diffusion. (c) Galaktosa/ Galactose
• Kesannya, air dapat diserap masuk semula ke dalam 2 • Glikogen dan kanji adalah molekul besar.
darah secara osmosis. Glycogen and starch are large molecules.
Consequently, water is reabsorbed into the bloodstream by • Tidak dapat meresap melalui membran plasma.
osmosis. Cannot diffuse through the plasma membrane.
• Air dan unsur lain yang hilang diganti semula. • Mereka tidak larut dalam air.
Water and the essential elements that are lost are replaced. They are insoluble in water.
• Badan terhidrat semula. • Boleh diuraikan dengan mudah dan diguna dalam
Body is dehydrated. respirasi.
Can be easily broken down and used in respiration.
Praktis Sumatif
3 • Mempunyai kekuatan regangan yang tinggi/ kuat/
KERTAS 1 tegar.
High tensile strength/ strong/ tough/ rigid.
1 B 2 A 3 A 4 C
• Boleh menahan tekanan kesegahan yang tinggi.
KERTAS 2 Can withstand high turgor pressure.
Bahagian A • Mengelakkan dinding sel daripada pecah dalam
1 (a) (i) M larutan cair.
(ii) Molekul air lebih banyak dari N// molekul Prevent cell wall from bursting when in dilute solution.
sukrosa lebih rendah dari N. 4.3 Protein
More water molecules than N// sucrose molecules Proteins
are lower than N. 1 (a) karbon, hidrogen, oksigen, nitrogen
(iii) Osmosis carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
(b) (i) • Air ialah hipotonik berbanding sel sawi (b) sulfur, fosforus/ sulphur, phosphorus
Water is hypotonic than mustard green cell (c) polipeptida/ polypeptides
• Molekul air meresap masuk ke dalam sel (d) asid amino/ amino acids
Water molecules diffuse into the cell (e) kondensasi/ condensation
• secara osmosis/ by osmosis 2 • Berasa cepat letih dan lemah.
(ii)
Feeling tired and weak quickly.
• Berisiko untuk mendapat anemia.
Have risk for anaemia.
• Pertumbuhan otot dan tulang terganggu.
Muscle and bone growth is impaired.
J5 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
4.4 Lipid 2 C G
Lipids
1 (a) Mentega Minyak masak
A T
Butter Cooking oil
Mentega diperoleh Minyak masak
daripada sumber diperolehi daripada G C
haiwan sumber tumbuhan
Butter is obtained Cooking oil is obtained
from animal sources from plant sources
Pepejal pada suhu Cecair pada suhu bilik Praktis Sumatif
bilik Liquid at room
Solid at room temperature KERTAS 1
temperature 1 C 2 B 3 D 4 B 5 B
Mengandungi lemak Mengandungi lemak 6 A
tepu tak tepu KERTAS 2
Contains saturated fat Contains unsaturated fat
Bahagian A
1 (a) X: Sukrosa/ Sucrose
(b) (i)
P: Gliserol
Y: Laktosa/ Lactose
Glycerol
(b) • Z mengandungi lipid/ lemak/ minyak yang
Q: Asid lemak tinggi
Fatty acids Z contains high lipid/ fat/ oil
(ii) Proses X/ Process X.: Kondensasi/ Condensation • Lemak berlebihan akan ditukar kepada
Penerangan: P (gliserol) dan Q (asid lemak) kolesterol
digabungkan dengan penyingkiran satu Excess fat will be converted to cholesterol
molekul air. • Lemak akan terenap dalam salur darah
Explanation: P (glycerol) and Q (fatty acids) are Fat will settle in the blood vessels
combined with the removal of one water • Akan meningkatkan penyakit serangan jantung
molecule. Will increase heart attack disease
2 • Lemak haiwan terdiri daripada lemak tepu.
BAB
Pemakanan yang tinggi lemak tepu akan Metabolisme dan Enzim
menambahkan paras kolestrol LDL dalam
5 Metabolism and Enzymes
darah. 5.1 Metabolisme
Animal fats are made up of saturated fats. High intake
Metabolism
of saturated fat in daily diet will increase the level of
1
LDL cholesterol in the blood. Anabolisme Aspek Katabolisme
• Ini akan menyebabkan tekanan darah tinggi dan Anabolism Aspect Catabolism
penyakit kardiovaskular yang lain seperti strok dan Proses sintesis Proses penguraian
serangan jantung. molekul kompleks bahan yang
This will lead to high blood pressure and other daripada molekul kompleks kepada
cardiovascular diseases such as stroke and heart ringkas. bahan yang
attack. Definisi
Process of ringkas.
Definition
synthesising Process of breaking
4.5 Asid Nukleik down complex
complex molecules
Nucleic Acids from simple substances into
1 (a) DNA molecules. simple substances.
(b)
Membebaskan
Kumpulan fosfat
atau menyerap Membebaskan
Phospate group Menyerap tenaga
tenaga tenaga
Absorbs energy
Releases or Releases energy
Bes bernitrogen
absorbs energy
Nitrogenous base
Gula pentosa Penghasilan
Penguraian
Pentose sugar glukosa
glukosa semasa
(c) • DNA mengandungi kod genetik semasa
Contoh respirasi sel.
DNA contains the genetic code fotosintesis.
Examples Breakdown of
• Penting sebagai pembawa maklumat Formation of
glucose during
pewarisan glucose during
cellular respiration.
Important as a carrier of hereditary information photosynthesis.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J6
5.2 Enzim 4 (a) (i) rendah, meningkat, 10°C
Enzyme low, increases, 10°C
1 Substrat Sukrosa Laktosa Protein Lipid Kanji (ii) maksimum, 37°C
Selulosa
Substrate Sucrose Lactose Protein Lipid Starch Cellulose maximum, 37°C
(iii) mengurangkan, ternyahasli
Enzim Sukrase Laktase Protease Lipase Amilase Selulase
Enzyme Sucrase Lactase Protease Lipase Amylase Cellulase decreases, denatured
(b) (i) optimum/ optimum
2 Molekul substrat mewakili kunci dan molekul enzim (ii) 6, 8
mewakili mangga. Molekul substrat bergabung dengan (iii) cas/ charge
tapak aktif pada enzim dan membentuk kompleks enzim- (iv) memutuskan, ternyahasli/ break, denatured
substrat. Enzim memangkinkan tindak balas enzim (c) (i) bertambah/ increases
dengan substrat spesifik untuk membentuk produk yang (ii) pengehad/ limiting
kemudiannya akan meninggalkan tapak aktif. Molekul (d) (i) tinggi, enzim-substrat/ higher, enzyme-substrate
enzim kekal sama secara kimia di akhir tindak balas dan (ii) substrat/ substrate
bebas untuk bergabung dengan molekul substrat yang
lain.
EKSPERIMEN 5.1
The substrate molecule represents the key and the enzyme
molecule represent the lock. The substrate molecule binds Hipotesis: Peningkatan suhu meningkatkan kadar
to the active sites of the enzyme to form enzyme-substrate Hypothesis tindak balas enzim amilase sehingga suhu
complex. The enzyme catalyses the reaction between enzyme optimum. Kadar tindak balas enzim
and specific substrate to form product which then leave the menurun selepas suhu optimum.
active site. The enzyme molecule remain chemically the same An increase in temperature increases the reaction
at the end of the reaction and is free to bind to other substrate rate of amylase enzyme up to an optimum
molecules. temperature. The reaction rate of the enzyme
3 • Di dalam nukleus, maklumat untuk sintesis enzim decreases after the optimum temperature.
dibawa oleh DNA dalam bentuk kod. Maklumat Pemboleh ubah: (a) Suhu/ Temperature
pada DNA dikodkan ke dalam mRNA. mRNA Variables (b) Kadar tindak balas enzim amilase
dihasilkan untuk menterjemah kod-kod tersebut Reaction rate of amylase enzyme
untuk menjadi satu urutan asid amino. Keputusan/ Result: Masa untuk Kadar
In the nucleus, the information for the synthesis of enzymes hidrolisis kanji tindak
is carried by DNA in a form of codes. The information of Suhu (oC) menjadi lengkap balas
DNA is coded into mRNA. mRNA is formed to translate Temperature (minit) (min-1)
the codes into a sequence of amino acids. (oC) Time for Reaction
• mRNA meninggalkan nukleus dan melekat di starch hydrolysis rate
ribosom untuk membolehkan protein disintesis. to complete (minutes) (min-1)
Protein yang terhasil, diangkut memasuki jalinan 20 4.0 0.25
endoplasma kasar. Protein diproses dan dibungkus 30 1.5 0.67
di dalam vesikel angkutan yang akan menggenting
40 0.5 2.00
dari jasad endoplasma kasar untuk mengangkut
protein tersebut ke jasad Golgi. 50 1.5 0.67
mRNA leaves the nucleus and binds with ribosome for 60 5.0 0.20
the synthesis of protein to occur. The synthesised protein
Perbincangan: 1 Enzim amilase menghidrolisis kanji
is transported into the lumen of rough endoplasmic Discussion untuk membentuk maltosa sehingga
reticulum. The protein is processed and packaged into akhirnya membentuk glukosa.
transport vesicle which buds off from the rough endoplasmic Amylase enzyme hydrolyse starch to form
reticulum to transport the protein to Golgi apparatus. maltose and finally form glucose.
• Di jasad Golgi, protein diubah suai untuk 2 Larutan iodin digunakan untuk
membentuk enzim dan dibungkus di dalam vesikel menguji kehadiran kanji di dalam
rembesan yang akan mengangkut enzim tersebut tabung uji. Jika masih terdapat
ke membran plasma. Vesikel ini akan bergabung kanji di dalam tabung uji, larutan
dengan membran plasma untuk merembeskan iodin bertukar menjadi biru gelap.
Jika tiada kanji di dalam tabung uji,
enzim ke luar sel.
larutan iodin kekal perang.
In Golgi apparatus, the protein is modified to form enzyme The iodine solution is to test the presence of
and is packaged in secretory vesicle which transport starch in the test tube. If there is still starch
the enzymes to plasma membrane. The secretory vesicle in the test tube, the iodine solution turns
fuse with the plasma membrane to release the enzymes out dark blue. If there is no starch in the test
of the cell. tube, the iodine solution remains brown.
J7 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
3 Apabila suhu meningkat, kadar tindak formed and the reaction rate of enzyme
balas meningkat. Kadar tindak balas increases.
maksimum pada suhu optimum, 3 Campuran dalam tabung uji P
40°C. Pada suhu 60°C, enzim amilase bertukar menjadi jernih selepas 20
mula ternyahasli. minit kerana asid hidroklorik yang
When the temperature increases, the ditambah ke dalam tabung uji P
reaction rate increases. The reaction rate menyebabkan campuran menjadi
is maximum at optimum temperature, berasid. pH 2 ialah pH optimum
40°C. At 60°C, the amlyse enzyme start to untuk tindak balas enzim pepsin ke
denature. atas albumen. Albumen (protein)
dihidrolisiskan kepada polipeptida
EKSPERIMEN 5.2
dan asid amino.
The mixture in test tube P turned clear after
Hipotesis: pH 2 paling optimum bagi tindak balas 20 minutes because the hydrochloric acid
Hypothesis enzim pepsin. added to test tube P caused the mixture to
pH 2 is the most optimum for the pepsin enzyme become acidic. pH 2 is the optimal pH for
reaction. the pepsin enzyme reaction on albumen.
Pemboleh ubah: (a) pH medium tindak balas Albumin (protein) is hydrolysed into
Variables pH medium reaction polypeptides and amino acids.
(b) Kejernihan atau kekeruhan campuran 4 Campuran dalam tabung uji Q dan R
tindak balas kekal keruh selepas 20 minit kerana
The clarity or turbidity of the mixture pH medium tindak balas tidak sesuai
reaction untuk tindak balas enzim pepsin ke
Keputusan/ Result: atas albumen.
Kejernihan atau The mixture in test tubes Q and R remained
kekeruhan campuran cloudy after 20 minutes because the pH of
Tabung Clarity or turbidity reaction medium was not suitable for the
uji pH of mixture pepsin enzyme reaction on albumen.
Test tube Selepas
0 minit 5.3 Aplikasi Enzim dalam Kehidupan Harian
20 minit
0 minute Application of Enzymes in Daily Life
After 20 minutes
1 (a) → (ii)
P 2 Keruh Jernih
Cloudy Clear (b) → (v)
(c) → (i)
Q 6 Keruh Keruh (d) → (iv)
Cloudy Cloudy
(e) → (iii)
R 12 Keruh Keruh
Cloudy Cloudy Praktis Sumatif
Perbincangan: 1 Tabung uji direndam di dalam
KERTAS 1
Discussion kukus air untuk memastikan medium
tindak balas pepsin terhadap ampaian 1 A 2 C
albumen (protein) berlaku pada suhu
KERTAS 2
yang optimum, 37 oC.
Bahagian A
The test tube is soaked in water bath to
ensure that the reaction medium of pepsin 1 (a) Kompleks enzim-subsrat/ Kompleks amilase-
against the albumen suspension (protein) substrat P
occurs at the optimum temperature, 37 oC. Enzyme-substrate complex/ Amylase-substrate P complex
2 pH optimum (pH 2) memastikan (b) Enzim ekstrasel
tindak balas pepsin ke atas albumen Extracellular enzyme
berlaku dengan cekap. Lebih banyak (c) • Kerana bentuk substrat S tidak melengkapi
substrat boleh bergabung dengan bentuk tapak aktif enzim amilase.
tapak aktif enzim, lebih banyak Because the shape of substrate S does not
kompleks enzim-substrat terbentuk complement the shape of the active site of amylase
dan kadar tindak balas enzim juga enzyme.
bertambah. • Tindak balas enzim bersifat spesifik.
Optimum pH (pH 2) ensure that the The enzyme reaction is specific.
reaction of pepsin on albumen takes • Hanya enzim tertentu dapat bergabung
place efficiently. The more substrates can dengan substrat tertentu.
combine with the active site of the enzyme, Only certain enzymes can combine with certain
the more enzyme-substrate complexes are substrates.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J8
(d) • Aktiviti enzim amilase akan menjadi perlahan No identical daughter cell produced// less/ more
atau terhenti. number of chromosomes compared to the parent
Amylase enzyme activity will slow down or stop. cell
• Kerana molekul Z ialah perencat. 2 (a) Persamaan/ Similarities:
Because molecule Z is an inhibitor. • Setiap kromosom terdiri daripada dua
• Perencat berfungsi untuk memperlahankan kromatid kembar terikat pada sentromer.
atau menghentikan tindakan enzim. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids
Inhibitors work to slow down or stop the action of attached to a centromere.
enzymes. • Setiap kromosom terikat pada gentian
gelendong pada sentromer.
BAB Each chromosome attaches to the spindle fibre at a
Pembahagian Sel
6 Cell Division
centromere.
Perbezaan/ Differences:
6.1 Pembahagian Sel P Q
Cell Division
1 (a) X : Kariokinesis/ Karyokinesis Metafasa/ Metaphase Anafasa/ Anaphase
Y : Sitokinesis/ Cytokinesis
Kromatid kembar Kromatid kembar
(b) Peringkat dalam X/ kariokinesis melibatkan
tersusun di satah berpisah dan bergerak
pembahagian nukleus manakala peringkat dalam
khatulistiwa ke kutub bertentangan
Y/ sitokinesis melibatkan pembahagian sitoplasma.
Stage in X/ karyokinesis involves division of nucleus/ Sister chromatids align Sister chromatids
nuclear division while stage in Y/ cytokinesis involves at the equatorial plane separate and move to
the division of cytoplasm. opposite poles
(c) T : Kromosom/ Chromosome
(b) Kromosom
N : Kromatin/ Chromatin Chromosome
(d) Struktur T memampat, memendek dan menebal
(yang jelas di bawah mikroskop cahaya) berbanding
struktur N yang merupakan bebenang halus
(yang tidak jelas di bawah mikroskop cahaya).
Structure T condensed, become shorter and thicker
(which visible under light microscope) compared to
structure N which is thread-like structure (which invisible (c) • Teknik yang digunakan adalah tisu kultur.
under light microscope). The technique used is tissue culture.
• Hasil pengeluaran/ bilangan pokok
6.2 Kitar Sel dan Mitosis Cryptocoryne pygmaea yang banyak
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Increase the production/ to produce many
1 (a) (i) Metafasa/ Metaphase Cryptocoryne pygmaea
(ii) Setiap kromosom menyusun dirinya di satah • dalam masa yang singkat.
khatulistiwa secara rawak. in short time.
Each chromosome align at the equatorial plane • Kualiti pokok tinggi/ ciri yang terpilih
randomly. High quality of plant/ the selective characteristics
(iii) Untuk memastikan bilangan kromosom/
bahan genetik anak/ sel anak seiras/ sama 6.3 Meiosis
dengan induk// untuk mengekalkan bilangan Meiosis
kromosom yang diploid. 1 (a) Untuk pertukaran bahan genetik/ (segmen) DNA
To ensure the chromosomal number/ genetic antara dua kromatid tidak berkembar bagi pasangan
materials of offspring/ daughter cell is identical/ kromosom homolog// untuk menghasilkan variasi
same as parent cell// to maintain diploid number of To exchange genetic material/ DNA (segment) between
chromosome. two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosome// to
(b) • Perkembangan/ pertumbuhan sel terhenti produce variation
Cell development/ growth will be terminated/ stop (b) • Pindah silang berlaku// proses pertukaran
• (berakhir dengan) tiada pembahagian sel bahan genetik/ (segmen) DNA antara dua
(end up with ) no cell division kromatid tidak berkembar bagi sepasang
• (hasilkan) kromosom tidak normal kromosom homolog.
(result in) chromosome abnormalities Crossing-over occur// exchange process of genetic
• Sel anak yang tidak seiras terbentuk// sel material/ DNA (segment) between two non-sister
anak yang mengandungi bilangan kromosom chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes.
terlebih/terkurang satu kromosom berbanding • untuk menghasilkan variasi
sel induk to produce variation
J9 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• untuk hasilkan kombinasi gen yang baharu • Gamet mempunyai bilangan kromosom tidak
pada kromosom normal// gamet yang terbentuk mengandungi
to produce new combination of genes on chromosomes kurang/ lebih satu kromosom berbanding
• (organisma mempunyai) adaptasi yang lebih gamet normal// gamet mengandungi 22
baik (terhadap persekitarannya) kromosom atau 24 kromosom.
(organism have) better adaptation (to their Gamete produced contain abnormal chromosomes//
environment) gamete formed contain less/ extra one chromosome
• Mengelakkan kepupusan compared to normal gamete// gamete contain 22
Prevent extinction chromosomes or 24 chromosomes.
2 (a) (i) Metafasa I • Jika persenyawaan berlaku antara gamet
Metaphase I normal/ mengandungi 23 kromosom dan
(ii) Kromosom homolog menyusun dirinya/ gamet yang mengandungi 24 kromosom
tersusun di satah khatulistiwa secara If fertilisation occurs betwee normal gamete/
berpasangan (dan secara rawak). contain 23 chromosomes and the gamete that
Homologous chromosomes lined-up / align at contain 24 chromosomes
the equatorial plane of the cell in pair (and • zigot yang terbentuk mengandungi 47
randomly). kromosom// zigot yang terbentuk terlebih satu
(b) – Proses pindah silang berlaku. kromosom berbanding zigot normal
Crossing over occurs. the zygote produced contain 47 chromosomes// the
• Semasa profasa I zygote produced contain extra one chromosome
During prophase I compared to normal zygote
• Pertukaran bahan genetik/ segmen DNA (b)
antara dua kromatid tidak berkembar
bagi sepasang kromosom homolog.
The exchange of genetic information/ DNA
segment between two non-sister chromatids of
a pair of homologous chromosomes.
• (Penggabungan semula) menghasilkan Kromosom
kombinasi gen yang baharu. Chromosome
(The genetic recombinant) result in new gene Praktis Sumatif
combination.
• Menghasilkan variasi dalam organisma. KERTAS 1
Produce variation in organism. 1 A 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A
– Penyusunan kromosom homolog di satah
khatulistiwa secara rawak. KERTAS 2
The arrangement of homologous chromosomes at Bahagian A
the equatorial plane of the cell randomly. 1 (a) (i) Mitosis/ Mitosis
• Semasa metafasa I (ii) • Pembahagian sel bagi P berlaku dalam sel
During metaphase I soma manakala pembahagian sel bagi Q
• Menghasilkan gamet dengan kombinasi berlaku pada sel dalam organ pembiakan/
kromosom yang berbeza. testis/ gonad.
Produces gametes with different combination Cell division of P occurs in somatic cell while
of chromosomes. cell division of Q occurs in cell of reproductive
• Oleh itu, kandungan genetik dalam organ/ testis/ gonads.
setiap gamet yang dihasilkan adalah • Pembahagian sel bagi P menghasilkan
berbeza. sel-sel baharu untuk pertumbuhan/
Therefore, the genetic combination in each perkembangan otot licin manakala
gamete produced is different. pembahagian sel bagi Q menghasilkan
gamet untuk pembiakan seks.
6.4 Isu Pembahagian Sel Terhadap Kesihatan Manusia Cell division of P produce new cells for
Issues of Cell Division on Human Health growth/ development of smooth muscle tissue
1 (a) • Kromosom homolog gagal berpisah (tak while cell division of Q produce gamete for
sexual reproduction.
disjunksi) ke kutub sel bertentangan// Anafasa
(iii) Sel stem// Terapi sel stem
I tidak berlaku. Stem cell// Stem cell therapy
The homologous chromosomes fail to separate
(b) (i) • Sinaran radioaktif/ sinar-X/ sinar gama/
(nondisjunction) to the opposite poles of the cell//
sinar ultraungu
Anaphase I does not occurs.
Radioactive radiation/ X-ray/ gamma ray/
ultraviolet
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J10
• Bahan berkarsinogen/ formaldehid/benzena Potassium hydroxide (KOH) in the small
Carcinogenic substances/ formaldehyde/ tube function to absorb carbon dioxide
benzene released during respiration.
• Bahan kimia/ monosodium glutamat 3 Aras cecair berwarna di dalam tiub
Chemical substances/ monosodium glutamate kapilari B meningkat kerana belalang
(ii) • Kaedah ini menggunakan radiasi mengion menghasilkan karbon dioksida
bertenaga tinggi melalui respirasi aerob dan akan
This method uses high ionisation radiation diserap oleh KOH.
• untuk membunuh sel kanser. The level of the coloured liquid in capillary
to kill cancer cell. tube B increases because the grasshopper
• Pemberian dos tinggi ditujukan kepada released carbon dioxide through aerobic
sasaran (tumor). respiration and is absorbed by KOH.
Higher dosage is targeted to tumor area. 4 Ini menyebabkan isi padu dan
tekanan gas di dalam kelalang kurang
BAB berbanding tekanan atmosfera. Cecair
Respirasi Sel
7 Cellular Respiration berwarna ditolak masuk ke dalam
tiub kapilari.
7.1 Penghasilan Tenaga melalui Respirasi Sel This causes the volume and gas pressure
Production of Energy through Cellular Respiration in the flask become lower compared
1 tenaga/ energy to external atmospheric pressure. The
2 molekul organik/ organic molecules coloured liquid is pushed into the capillary
3 Glukosa/ Glucose tube.
4 (a) karbohidrat/ carbohydrates 5 Jarak pergerakan cecair berwarna
(b) Fotosintesis/ photosynthesis menunjukkan kuantiti oksigen yang
digunakan oleh belalang semasa
7.2 Respirasi Aerob
respirasi aerob.
Aerobic Respiration
The distance moved by coloured liquid
1 kehadiran oksigen/ present of oxygen
shows the amount of oxygen used by
2 karbon dioksida, air, tenaga/ carbon dioxide, water, energy
grasshoppers for aerobic respiration.
3 sitoplasma, mitokondrian/ cytoplasm, mitochondrion
Kesimpulan: Organisma hidup menggunakan oksigen
Conclusion dan membebaskan karbon dioksida
EKSPERIMEN 7.1 semasa respirasi aerob. Hipotesis
diterima.
Pernyataan masalah: Adakah organisma hidup menggunakan Living organisms use oxygen and release
Problem statement oksigen dan membebaskan karbon carbon dioxide during aerobic respiration.
dioksida semasa respirasi aerob? Hypothesis is accepted.
Does living organisms use oxygen and release
carbon dioxide during aerobic respiration? 7.3 Fermentasi
Hipotesis: Organisma hidup menggunakan oksigen Fermentation
Hyphothesis dan membebaskan karbon dioksida 1 (a) X : Respirasi aerob
semasa respirasi aerob. Aerobic respiration
Living organisms use oxygen and release Y : Fermentasi asid laktik
carbon dioxide during aerobic respiration.
Lactic acid fermentation
Pemerhatian:
Observation Kelalang (b) Glukosa → Asid laktik + tenaga
kon A B Glucose → Lactic acid + energy
Conical flask (c) • Dalam Y, proses penguraian glukosa berlaku
secara lengkap dengan kehadiran oksigen
Aras cecair Tidak Meningkat manakala dalam Z, proses penguraian glukosa
berwarna berubah Increase berlaku secara tidak lengkap tanpa kehadiran
Level of No change oksigen atau dalam keadaan oksigen terhad.
coloured liquid In Y, the breakdown process of glucose is completed
Perbincangan:1 Tabung uji A bertindak sebagai in the presence of oxygen while in Z, the breakdown
Discussion kawalan. process of glucose is incomplete without oxygen or
Test tube A acts as a control. in limited oxygen conditions.
2 Kalium hidroksida (KOH) di dalam • Proses dalam Y menghasilkan air manakala
tabung uji berfungsi menyerap proses dalam Z tidak menghasilkan air.
karbon dioksida yang dibebaskan Process in Y produces water while process in Z
semasa respirasi. does not produce water.
J11 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
(d) • Kadar penggunaan oksigen oleh sel otot Glucose solution is boiled to remove
melebihi kuantiti oksigen yang dibekalkan dissolved oxygen to maintain anaerobic
oleh sistem peredaran darah. condition/ ensure that the fermentation
The rate in which muscle cells uses oxygen is process is complete.
higher than the quantity of oxygen supplied by the 2 Tabung didih B bertindak sebagai
blood circulatory system. kawalan.
• Otot mengalami kekurangan oksigen atau Boiling tube B act as a control.
hutang oksigen. 3 Suhu larutan di dalam tabung didih A
Muscles are in a state of oxygen deficiency or meningkat menunjukkan fermentasi
oxygen debt. telah berlaku.
• Otot menjalankan fermentasi asid laktik. Temperature of solution in boiling tube
Muscles undergo lactic acid fermentation. A increased show that fermentation has
• Molekul glukosa diuraikan secara separa taken place.
kepada asid laktik. Praktis Sumatif
Glucose is partially broken down into lactic acid.
• Kepekatan asid laktik yang tinggi KERTAS 1
mengakibatkan kelesuan otot. 1 A 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 B
The high concentration of lactic acid causes
muscular fatigue. KERTAS 2
Bahagian B
EKSPERIMEN 7.2 1 (a) (i) Persamaan/ Similarities:
• Proses penguraian glukosa dan
Hipotesis: Yis menjalankan fermentasi untuk penukaran kepada tenaga kimia.
Hyphothesis menghasilkan karbon dioksida, etanol The breakdown process of glucose and its
dan tenaga. conversion to chemical energy.
Yeasts carry out fermentation to produce • Proses bermula di sitoplasma.
carbon dioxide, ethanol and energy. The process begins in the cytoplasm.
Pemboleh ubah: (a) Kehadiran yis • Berlaku dalam yis, bakteria, haiwan dan
Variables Present of yeast tumbuhan.
(b) Perubahan air kapur/suhu larutan Occurs in yeast, bacteria, animals and plants.
glukosa/ bau etanol • Menghasilkan tenaga kimia dalam
Changes in lime water/ temperature of bentuk ATP.
glucose solution/ ethanol smell Produces chemical energy in the form of ATP.
(c) Isi padu larutan glukosa • Proses bermula dengan glikolisis apabila
Volume of glucose solution glukosa ditukarkan kepada piruvat.
Pemerhatian: The process begins with glycolysis when
Observation glucose is converted to pyruvate.
Suhu (ºC)
Bau (ii) Perbezaan/ Differences:
Tabung Temperature (ºC) Perubahan
larutan Respirasi aerob Fermentasi
didih Awal Akhir air kapur
Smell Aerobic respiration Fermentation
Boiling eksperimen eksperimen Change
of the
tube Beginning of End of the of lime water
solution Proses penguraian Proses penguraian
the experiment experiment
glukosa secara glukosa secara
A 29 32 Jernih Berbau lengkap dengan tidak lengkap tanpa
menjadi etanol kehadiran oksigen. kehadiran oksigen
keruh Smell of The breakdown atau dalam keadaan
Clear into ethanol
process of glucose oksigen terhad.
cloudy
is completed in the The breakdown
B 29 29 Jernih Tiada presence of oxygen. process of glucose is
Clear bau incomplete without
etanol oxygen or in limited
No smell
oxygen conditions.
of ethanol
1 Larutan glukosa dididihkan untuk
Perbincangan: Berlaku dalam Berlaku dalam
Discussion menyingkirkan oksigen terlarut untuk sitoplasma dan sitoplasma.
mengekalkan keadaan anaerob/ mitokondrion. Occurs in cytoplasm.
memastikan proses fermentasi boleh Occurs in cytoplasm
berlaku. and mitochondrion.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J12
• Glikogen merupakan bekalan tenaga
Glukosa Glukosa dioksidakan
simpanan di dalam badan kita.
dioksidakan secara secara tidak lengkap
lengkap kepada kepada etanol dan
Our body stores energy in the form of glycogen.
• Simpanan glikogen ini biasanya dapat
karbon dioksida karbon dioksida atau
bertahan selama 15-20 minit untuk sesuatu
dan air. asid laktik.
aktiviti.
Glucose is oxidised Glucose is not oxidised
completely into completely into ethanol
This stored glycogen is normally enough for
15-20 minutes of activity.
carbon dioxide and and carbon dioxide or
• Selepas itu, tubuh mula memecahkan molekul
water. lactic acid.
simpanan yang lain termasuk lemak untuk
Menghasilkan air. Tidak menghasikan menghasilkan tenaga.
Produces water. air. After that, the body begins to break down other
Does not produce stored molecules, including fats, for energy.
water.
BAB
Satu molekul Satu molekul glukosa Sistem Respirasi dalam Manusia dan Haiwan
glukosa menghasilkan 8 Respiratory Systems in Humans and Animals
menghasilkan 210 kJ (fermentasi
8.1 Jenis Sistem Respirasi
2898 kJ. alkohol) atau 150 kJ
Types of Respiratory System
One molecule of (fermentasi asid
1 (a) (i) Insang/ Gills
glucose generates laktik).
(ii) • Filamen mempunyai bilangan lamela
2898 kJ of energy. One molecule of glucose
yang banyak
generates 210 kJ
Filament has many lamellae
(alcoholic fermentation)
• Lamela nipis dan mempunyai banyak
or 150 kJ (lactic acid
jaringan kapilari darah
fermentation) of energy.
Lamellae are thin and have many blood
(b) • Semasa aktiviti cergas seperti acara pecut, capillaries
oksigen yang digunakan oleh mitokondrion (b) • Semua mempunyai nisbah luas permukaan
dalam sel otot melebihi kadar oksigen yang kepada isi padu yang besar.
dibawa masuk melalui pernafasan. All have large ratio of total surface area to
During strenuous physical activities such as sprint, volume.
the rate of oxygen used by the mitochondria in • Semua mempunyai struktur respirasi yang
muscle cells is higher than the rate of oxygen taken nipis.
in through breathing.
All respiratory structures are thin.
• Apabila oksigen tidak mencukupi, • Semua struktur respirasi sentiasa lembap.
When oxygen is not enough,
All respiratory structures are moist.
• mitokondrion bertukar kepada proses • Struktur respirasi dilengkapi dengan jaringan
fermentasi asid laktik. kapilari yang banyak.
mitochondria switch to lactic acid fermentation
Respiratory structures have large network of
instead.
blood capillaries.
• Fermentasi asid laktik menghasilkan jumlah
(c) Mempunyai bilangan alveolus yang banyak untuk
tenaga yang lebih kecil berbanding dengan
menambah luas permukaan yang besar bagi
respirasi aerob.
peresapan gas respirasi.
Lactic acid fermentation produces a smaller
Large number of alveoli to increase total surface area
amount of energy compared to aerobic respiration.
for diffusion of respiratory gases.
• Fermentasi asid laktik juga menghasilkan asid
laktik yang boleh menyebabkan kekejangan
8.2 Mekanisme Pernafasan
otot.
Mechanisms of Breathing
Lactic acid fermentation also produces lactic acid,
1 (a) • Y adalah menghembus nafas.
which can cause muscles cramp.
Y is exhalation.
(c) • Senamrobik merupakan aktiviti beritma
• Otot interkosta luar mengendur manakala
dalam tempoh tertentu yang menggunakan
otot interkosta dalam mengecut.
beberapa kumpulan otot.
The external intercostal muscles relax while the
Aerobic exercise is a rhythmic activity at certain
period that involves large muscle groups. internal intercostal muscles contract.
• Senamrobik turut dikenali sebagai senaman • Sangkar rusuk digerakkan ke bawah dan ke
kardiovaskular. dalam.
It is also known as cardiovascular exercise. Ribcage move downwards and inwards.
J13 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• Otot diafragma mengendur dan diafragma eritrosit untuk membentuk asid karbonik
melengkung ke atas, berbentuk kubah. (H2CO3).
Diaphragm muscles relax and the diaphragm Carbon dioxide (CO2) released by the body cells
curves upwards to form a dome. binds with water (H2O) in the erythrocyte to form
• Isi padu rongga toraks berkurangan dan carbonic acid (H2CO3).
tekanan rongga toraks bertambah. • Enzim karbonik anhidrase dalam eritrosit
The volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and the memangkinkan tindak balas ini.
pressure of the thoracic cavity increases. The carbonic anhydrase enzyme in erythrocyte
• Udara didesak keluar dari peparu. catalyses this reaction.
Air is pushed out of the lungs. • Asid karbonik (H2CO3) kemudiannya terurai
(b) • Kepekatan oksigen dalam udara sedutan lebih kepada ion bikarbonat (HCO3−) dan ion
tinggi berbanding udara hembusan. hidrogen (H+).
The oxygen concentration in the inhaled air is Carbonic acid (H2CO3) will break down into
higher than in the exhaled air. bicarbonate ion (HCO3−) and hydrogen ion (H+).
• Kepekatan karbon dioksida dalam udara • Kemudian ion bikarbonat meresap ke dalam
sedutan lebih rendah berbanding udara plasma darah dan diangkut ke peparu.
hembusan. Then bicarbonate ion diffuses into the blood plasma
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the inhaled and is carried to the lungs.
air is lower than that of the exhaled air.
8.4 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Respirasi Manusia
(c) • Isi padu rongga toraks dan tekanan rongga Health Issues Related to the Human Respiratory System
toraks tidak berubah. 1
The volume of the thoracic cavity and the pressure (a) Asma (i)
does not change. Asthma
• Ini disebabkan otot diafragma tidak dapt
mengecut dan mengendur. (b) Emfisema (ii)
Because diaphragm muscles cannot contract and Emphysema
relax.
• Lelaki itu tidak dapat bernafas dengan normal. (c) Bronkitis kronik (iii)
The man could not breathe normally. Chronic bronchitis
2 (a) Kulit dan peparu / Skin and lungs
(b) • Semasa menarik nafas melalui lubang hidung, SUDUT KBAT
mulut dan glotis tertutup dan dasar rongga • Lapisan udara adalah nipis di puncak gunung.
mulut diturunkan. Air layer is thin at the peak of a mountain.
When inhale through the nostrils, the mouth • Tekanan separa/ kepekatan oksigen rendah.
and glottis are closed and the floor of the Low concentration of oxygen.
buccopharyngeal cavity is lowered. • Kurang oksigen dalam darah.
• Tekanan udara yang rendah dalam Less oxygen in blood.
rongga mulut menarik udara masuk • Dikesan oleh kemoreseptor periferi.
ke dalam rongga mulut melalui Detected by peripheral chemoreceptor.
lubang hidung. • Impuls dihantar ke medula oblongata.
The low air pressure in the mouth cavity draws Impulse is send to medulla oblongata.
air into the buccopharyngeal cavity through the • Impuls dihantar ke otot interkosta dan diafragma.
nostrils. Impulse is sent to intercostal muscle and diaphragm.
• Apabila glotis terbuka, lubang hidung tertutup • Kadar pengecutan dan pengenduran otot interkosta dan
dan dasar rongga mulut naik. diafragma meningkat.
When the glottis opens, the nostrils close and the Rate of contraction and relaxation of intercostal muscle and
floor of the buccopharyngeal cavity is raised. diaphragm increase.
• Tekanan udara yang meningkat menolak • Meningkatkan kadar pernafasan.
udara ke dalam peparu. Increase the rate of breathing.
The increased air pressure pushes air into the • Lebih banyak oksigen masuk ke alveolus.
lungs. More oxygen enter the alveolus.
• Kepekatan oksigen dalam darah kembali ke aras
8.3 Pertukaran Gas dalam Manusia normal.
Gaseous Exchange in Humans Concentration of oxygen in blood returns to normal.
1 (a) X: Oksigen/ Oxygen • Meningkatkan kadar denyutan jantung untuk darah
Y: Karbon dioksida/ Carbon dioxide mengangkut oksigen lebih cepat.
(b) • Karbon dioksida (CO2) yang dibebaskan oleh Increase the rate of heartbeat for blood to transport oxygen
sel badan berpadu dengan air (H2O) dalam more rapidly.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J14
Praktis Sumatif (c) • Hati tidak dapat menghasilkan hempedu.
The liver cannot produce bile.
KERTAS 1 • Keasidan kim tidak dineutralkan.
1 B 2 C 3 D 4 A Acidity of chyme is not neutralised.
• pH di duodenum tidak optimum untuk enzim
KERTAS 2 lipase/ amilase/ tripsin.
Bahagian A The pH of the duodenum is not optimal for lipase/
1 (a) X: Kapilari darah/ Blood capillary amylase/ trypsin.
Y: Alveolus/ Alveolus • Pencernaan lipid/ kanji/ peptida berkurang.
(b) • Dinding alveolus yang lembap memudahkan Decreased lipid/ starch/ peptide digestion.
gas repirasi melarut.
Alveolus wall is moist, easy for respiratory gases to 9.3 Penyerapan
dissolve. Absorption
• Dilingkari jaringan kapilari darah yang 1 (a) Tisu epitelium/ Epithelial tissue
banyak untuk mempercepatkan peresapan gas (b) • Vitamin A, D, E, K
respirasi. • Gliserol// Asid lemak/ Glycerol// Fatty acid
Large network of blood capillaries to hasten (c) Memudahkan pengangkutan hasil pencernaan.
diffusion of repiratory gases. Efficient transportation of digestive products.
• Dinding alveolus yang nipis memudahkan (d) Resapan berbantu/ Facilitated diffusion
peresapan gas.
9.4 Asimilasi
Thin alveolus wall for easier diffusion of gases.
Assimilation
(c) • Asap rokok mengandungi karbon monoksida. 1 (a) (i)
Q: Vena portal hepar
Cigarette smokes contain carbon monoxide. Hepatic portal vein
• Karbon monoksida akan bergabung T: Duktus toraks
dengan hemoglobin untuk membentuk Thoracic duct
karbosihemoglobin. (ii) Q mengangkut bahan larut air manakala T
Carbon monoxide will bind with haemoglobin to mengangkut bahan larut lipid.
form carboxyhaemoglobin Q transport water-soluble substances while T
• Menyebabkan gas oksigen kurang diangkut transport lipid-soluble substances.
ke sel badan. (b) • Proses pendeaminaan berlaku.
Will reduce the transporting of oxygen to the body The deamination process occurs.
cells. • Menukarkan asid amino yang berlebihan
• Asap rokok juga mengandungi tar yang akan menjadi urea.
membentuk lapisan pada dinding alveolus, ini Convert excessive amino acids into urea.
akan mengurangkan kecekapan pertukaran • Urea disingkirkan melalui air kencing.
gas respirasi. Urea is excreted via urine.
Cigarette smokes contain tar that will form a
layer on the wall of alveoli, reduce exchange of
9.6 Gizi Seimbang
Balanced Diet
respiratory gases.
BAB Nutrisi dan Sistem Pencernaan Manusia AKTIVITI 9.1
9 Nutrition and the Human Digestive System
Hipotesis: Jus oren mempunyai kandungan vitamin
Hyphothesis C
9.2 Pencernaan
yang paling tinggi berbanding jus limau
Digestion
nipis dan jus lobak merah.
1 (a) (i) Q: Hati/ Liver
Orange juice has the highest content of
T: Pundi hempedu/ Gall bladder
vitamin C compared to lime juice and carrot
(ii) Q: Menghasilkan hempedu/ Produce bile
juice.
T: Menyimpan hempedu/ Store bile
Pemboleh ubah: (a) Jenis jus buah dan jus sayur
(b) • pH perut adalah 1.5-2.5/ sangat berasid Variables Types of fruit and vegetable juice
pH in stomach is 1.5-2.5/ highly acidic (b) Isi padu jus buah atau jus sayur
• pH tidak optimum untuk tindak balas amilase yang diperlukan untuk melunturkan
air liur larutan DCPIP
The pH is not optimal for the salivary amylase Volume of fruit juice or vegetable juice
reaction needed to decolourise DCPIP solution
• Amilase air liur ternyahasli Keputusan: Jawapan murid/ Student's answer
Salivary amylase is denatured Result
J15 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
Perbincangan: 1 Kepekatan vitamin C dalam jus buah • Asid lemak/ gliserol diserap secara resapan
dan sayur dapat ditentukan dengan
Discussion ringkas manakala glukosa diserap secara
menggunakan larutan DCPIP. pengangkutan aktif.
Vitamin C menurunkan DCPIP dan Fatty acids/ glycerol is absorbed by simple diffusion
menyahwarnakannya. while glucose is absorbed by active transport.
The concentration of vitamin C in fruit (c) • Menyebabkan populasi bakteria dalam usus
and vegetable juices can be determined besar musnah.
by using the DCPIP solution. Vitamin C Causes the bacterial population in the large
reduces DCPIP and decolorises it. intestine to be destroyed.
2 Jika kepekatan vitamin C dalam jus • Pencernaan serat dalam usus besar tidak
buah adalah tinggi, hanya sedikit isi berlaku.
padu jus buah yang diperlukan untuk Digestion of fibre in the large intestine does not
menyahwarnakan larutan DCPIP. occur.
If the concentration of vitamin C in the • Kurang vitamin B, K/ asid folik yang
fruit juice is high, only a small volume diserap.
of fruit juice is needed to decolorise the
Lack of vitamin B, K/ folic acid absorbed.
DCPIP solution
3 Jus oren mempunyai kepekatan
vitamin C lebih tinggi berbanding BAB Pengangkutan dalam Manusia dan Haiwan
jus limau nipis dan jus lobak 10 Transport in Humans and Animals
merah. Hanya sedikit jus oren yang
diperlukan untuk menyahwarnakan 10.1 Jenis Sistem Peredaran
larutan DCPIP. Types of Circulatory System
Orange juice has a higher concentration 1 Darah mengalir di dalam salur darah dari jantung ke
of vitamin C than lime juice and carrot sel-sel badan.
juice. Only a small amount of orange Blood flows inside blood vessels from the heart to body cells.
juice is needed to decolorise the DCPIP 2 Persamaan/ Similarities:
solution.
• Kedua-duanya mempunyai darah sebagai medium
Kesimpulan: Jus oren mempunyai kandungan vitamin pengangkutan.
Conclusion C yang paling tinggi berbanding jus limau Both have blood as a transport medium.
nipis dan jus lobak merah. Hipotesis • Kedua-duanya mempunyai jantung sebagai organ
diterima. mengepam darah.
Orange juice has the highest content of vitamin
Both have a heart to pump the blood.
C compared to lime juice and carrot juice.
Hypothesis is accepted. • Darah mengalir melalui jantung 2 kali// peredaran
ganda dua.
Praktis Sumatif Blood flow through the heart twice// double circulatory
system.
KERTAS 1
Perbezaan/ Differences:
1 D 2 D 3 C 4 B 5 A
6 C
M N
KERTAS 2 Sistem peredaran Sistem peredaran
Bahagian A (tertutup) ganda dua (tertutup) ganda dua
1 (a) (i) Kelenjar liur/ Salivary gland lengkap. tidak lengkap.
(ii) • Merembeskan air liur/ Secretes saliva (Closed) complete double (Closed) incomplete
• Mengandungi enzim amilase air liur. circulatory system. double circulatory system.
Contains salivary amylase enzyme.
• Menghidrolisiskan kanji kepada maltosa. Jantung mempunyai Jantung mempunyai
Hydrolyses starch to maltose. 4 ruang// 2 atrium dan 3 ruang// 2 atrium dan
(b) • Pencernaan mentega menghasilkan asid 2 ventrikel 1 ventrikel
lemak/ gliserol manakala pencernaan roti Heart has 4 chambers// Heart has 3 chambers//
menghasilkan glukosa. 2 atria and 2 ventricles 2 atria and 1 ventricle
Digestion of butter produces fatty acid/ glycerol Darah beroksigen dan Darah beroksigen
while digestion of bread produces glucose. terdeoksigen tidak dan terdeoksigen
• Asid lemak/ gliserol diserap ke dalam lakteal bercampur di ventrikel. bercampur di ventrikel.
manakala glukosa diserap ke dalam kapilari Oxygenated and Oxygenated and
darah. deoxygenated blood are not deoxygenated blood are
Fatty acids/ glycerol is absorbed into the lacteal mixed in ventricle. mixed in ventricle.
while glucose is absorbed into the blood capillaries.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J16
10.2 Sistem Peredaran Manusia 10.5 Kumpulan Darah Manusia
Circulatory System of Humans Blood Groups of Humans
1 (e) Aorta 1 Semasa kehamilan anak pertama
(a) Arteri pulmonari Aorta During the first pregnancy,
Pulmonary artery
• Sejumlah kecil darah fetus yang mengandungi
antigen Rh
(f) Vena pulmonari
(b) Vena kava Small amount foetus blood that contains Rh antigen
Pulmonary vein
Vena cava
• meresap ke dalam/ bercampur dengan darah ibu.
(c) Atrium kanan (g) Atrium kiri diffuses into/ mixes with the mother’s blood.
Right atrium Left atrium
• Merangsang penghasilan antibodi anti-Rhesus oleh
(d) Ventrikel kanan (h) Ventrikel kiri limfosit dalam darah ibu.
Right ventricle Left ventricle Stimulates the production of anti-Rhesus antibody by
mother’s lymphocytes/ blood.
2 (a) R: Arteri/ Artery • Antibodi anti-Rhesus meresap ke dalam darah fetus.
S: Kapilari/ Capillary Anti-Rhesus antibody diffuses into foetal blood.
T: Vena/ Vein • Menyebabkan kurang penggumpalan/ hemolisis
(b) R: Mengangkut darah dari jantung ke seluruh sel darah merah fetus minor (maka anak pertama
badan. selamat)// jumlah antibodi anti-Rhesus yang
Transports blood from the heart to the whole body. dihasilkan tidak mencukupi untuk menyebabkan
T: Mengangkut darah dari seluruh badan ke penggumpalan serius dalam anak pertama.
jantung. Causing minor/ less agglutination/ haemolysis of the foetal
Transports blood from the whole body to the red blood cell (thus the first child survives)// the amount of
heart. anti-Rhesus antibody produced is not sufficient to cause
(c) Bagi menahan darah yang mengalir dalam tekanan serious agglutination in the first born.
tinggi.
Semasa kehamilan anak kedua
To hold the blood that flows in high pressure.
During the second pregnancy,
10.3 Mekanisme Denyutan Jantung • Sejumlah kecil darah fetus meresap ke dalam darah
Mechanism of Heartbeat ibu.
1 2, 1, 4, 3 Small amount of foetal blood diffuses into mother’s blood.
• Merangsang penghasilan lebih antibodi anti-
10.4 Mekanisme Pembekuan Darah Rhesus oleh limfosis dalam darah ibu.
Mechanism of Blood Clotting Stimulates more anti-Rhesus antibody to be produced by
mother’s lymphocytes/ blood.
1 • Menghentikan kehilangan darah yang banyak//
• Antibodi anti-Rhesus meresap ke dalam darah fetus.
menghalang pendarahan berterusan/ serius.
Anti-Rhesus antibody diffuses into the foetal blood.
Stop excessive loss of blood// prevent continuous/ serious
• Menyebabkan lebih penggumpalan/ hemolisis
bleeding.
sel darah merah fetus major// jumlah antibodi
• Mencegah kemasukan patogen ke dalam badan/
anti-Rhesus yang dihasilkan mencukupi untuk
sistem peredaran darah.
menyebabkan penggumpalan serius dalam anak
Prevent the entrance of pathogens into the body/ blood
kedua.
circulatory system.
Causing more/ major agglutination/ haemolysis of foetal
• Mengekalkan tekanan darah yang normal//
red blood cells// the amount of anti-Rhesus antibody
mengelakkan tekanan darah turun. produced is sufficient to cause serious agglutination in
Maintain normal blood pressure// prevent blood pressure the second born.
drops. • Fetus/ bayi baru lahir menghidap jaundis/ anemia/
2 • Penyakit yang dihidapi ialah hemofilia. kerosakan jantung/ hati/ otak.
The disease known as haemophilia. The foetus/ new born baby suffers from jaundice/ severe
• Darah sukar/ lambat membeku. anaemia/ damage heart/ liver/ brain.
The blood hard to clot// take a long time to clot.
• Kehilangan darah yang banyak berlaku. 10.6 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Peredaran Manusia
Excessive of blood loss occurs. Health Issues Related to the Human Circulatory System
• Tekanan darah semakin berkurang. 1 (a) Arteri/ Artery X: Arteri koronari/ Coronary artery
Blood pressure decrease/ drop. Fungsi: Mengangkut oksigen/ nutrien ke otot jantung.
• Kurang darah beroksigen/ oksigen/ oksihemoglobin Function: To transfer oxygen/ nutrient to the muscle of the
diangkut ke sel-sel badan/ otak. heart.
Less oxygenated blood/ oxygen/ oxyhaemoglobin (b) • Arteri koronari/ X disekat oleh kolesterol/
transported to the brain/ body cells. lemak/ trombus/ darah beku.
• Akan pengsan/ lemah Coronary artery/ X is blocked by cholesterol/ fat/
Will faint/ fatigue thrombus/ blood clot.
J17 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• Disebabkan aterosklerosis/ arteriosklerosis/ • Dari duktus toraks, ia mengalir ke vena
trombosis. subklavikel dan seterusnya memasuki sistem
Due to atherosclerosis/ arteriosclerosis/ thrombosis. peredaran darah.
• Oksigen/ nutrien yang tidak mencukupi From the thoracic duct, it flows into the subclavian
diterima oleh otot/ sel jantung. vein and then enters the blood circulatory system.
Insufficient oxygen/ nutrients received by the • Oleh itu, sistem limfa menjadi pelengkap
cardiac muscles/ cells. kepada sistem peredaran darah dalam
• Otot/ sel jantung mungkin mati mengangkut hasil pencernaan makanan.
Cardiac muscles/ cells may die. Therefore, the lymphatic system becomes
a complement to the circulatory system in
10.7 Sistem Limfa Manusia transporting the products of food digestion.
Lymphatic System of Humans • Sistem peredaran darah akan mengangkut
1 • Darah mengalir ke hujung arteriol kapilari yang hasil pencernaan lipid ke sel badan.
mempunyai diameter lebih kecil. The blood circulatory system will transport
Blood flows to arteriol end of capillaries which has smaller products of lipid digestion to body cells.
diameter. • (90%) bendalir tisu yang terbentuk akan
• Mewujudkan tekanan hidrostatik yang lebih tinggi. menyerap ke dalam kapilari darah semula.
(90%) of the tissue fluid formed will absorb into the
Create higher hydrostatic pressure.
blood capillaries again.
• Memaksa air/ bahan molekul kecil ditapis keluar
• Kira-kira 10% lagi akan meresap ke dalam
dari dinding kapilari darah.
kapilari limfa untuk membentuk bendalir
Force water/ small molecules substances filtered out of
limfa.
blood capillary wall.
About 10% more will seep into the lymphatic
• Molekul besar tidak ditapis. capillaries to form lymph fluid.
Large molecules are not filtered out. • Dari kapilari limfa, bendalir limfa akan
• Membentuk bendalir tisu yang memenuhi ruang mengalir ke salur limfa yang lebih besar
antara sel. From the lymphatic capillaries, the lymphatic fluid
Form tissue fluid which fill the intercellular space. will flow to the larger lymphatic vessels
• Kira-kira 15% bendalir tisu dalam ruang antara sel • dan akhirnya kembali ke sistem peredaran
meresap ke hujung tumpul kapilari limfa. darah
About 15% of tissue fluid in the intercellular space diffuse and finally returns to the blood circulatory system
into the blunt end of lymph capillary. • melalui duktus toraks dan duktus limfa kanan
• Untuk membentuk limfa. ke vena subklavikel.
To form lymph. through the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic
duct to the subclavian vein.
Praktis Sumatif • (Oleh itu sistem limfa merupakan pelengkap
sistem peredaran darah) untuk memastikan
KERTAS 1 kandungan darah/ isi padu/ tekanan osmosis/
1 B 2 B 3 D 4 B 5 B tekanan darah dalam salur darah sentiasa pada
aras normal.
KERTAS 2 (Thus the lymphatic system is a complement to the
Bahagian C blood circulatory system) to ensure that the blood
1 (a) • Dalam usus kecil, hasil pencernaan lipid, content/ volume/ osmotic pressure/ blood pressure
iaitu asid lemak dan gliserol in the blood vessels is always at a normal level.
In the small intestine, the products of lipid digestion (b) Persamaan/ Similarities:
that are fatty acids and glycerol • (Kedua-dua) sistem terlibat dalam
• akan menyerap masuk ke dalam lakteal di pengangkutan bahan/ glukosa/ asid amino/
vilus. sebarang contoh/ adalah sistem pengangkutan
will absorb into the lacteal of the villus. (dalam badan).
• Lakteal bercantum membentuk salur limfa (Both) systems involve in the transportation of
yang lebih besar substance/ glucose/ amino acid/ any example/ are
Lacteals join to form larger lymphatic vessels transport systems (in the body).
• dan seterusnya memasuki sistem limfa. • (Kedua-dua sistem) mempunyai salur.
and then enters the lymphatic system. (Both systems) have vessels.
• Bendalir limfa yang membawa hasil • (Kedua-dua sistem) mempunyai bendalir
pencernaan lipid seterusnya akan memasuki sebagai medium pengangkutan.
duktus toraks. (Both systems) have fluid as a medium of transport.
Lymphatic fluid that carries the products of lipid • (Kedua-dua sistem) terlibat dalam proses
digestion will then enter the thoracic duct. pertahanan badan.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J18
(Both systems) involve in body defence process. menghasilkan antibodi spesifik kepada antigen
• Vena dan saluran limfa mempunyai injap. patogen yang memasuki tubuh untuk difagositosis
Vein and lymphatic vessel have valves. oleh L.
• (Kedua-duanya) mengandungi leukosit. L carry out phagocytosis to get rid of pathogens that
(Both) contain leucocytes. enters the body while M produces specific antibodies that
Perbezaan/ Differences: match antigens of the pathogens that enter the body
to be phagocytised by L.
Sistem peredaran darah Sistem limfa
Blood circulatory system Lymphatic system
11.2 Tindakan Antibodi
Mempunyai organ/ Tidak mempunyai Actions of Antibodies
jantung mengepam organ mengepam 1 (a) N ialah mekanisme pengopsoninan. Antibodi
Has pumping organ/ heart Has no pumping organ bergabung dengan antigen sebagai petanda
Mempunyai 3 jenis salur Mempunyai 2 jenis supaya sel fagosit dapat mengenalinya bagi tujuan
darah/ mempunyai arteri, salur/ mempunyai salur memusnahkannya.
vena dan kapilari darah limfa dan kapilari N is opsonisation. Antibodies bind with the antigens and
Has 3 types of blood vessel/ Has 2 types of vessel/ act as a marker so it can be recognised by the phagocytes
has artery, vein and blood has lymphatic vessel and for elimination purpose.
capillary capillary (b) Suhu badan yang tinggi membantu meningkatkan
proses fagositosis selain merencat pertumbuhan
Tidak mempunyai nodus Mempunyai nodus
bakteria.
limfa limfa (di sepanjang
High body temperature helps to increase phagocytosis
Has no lymph nodes saluran limfa)
process and inhibit bacterial growth.
Has lymph nodes (along
lymphatic vessel)
11.3 Jenis Keimunan
Mempunyai eritrosit/ Tidak mempunyai Types of Immunity
platlet/ protein plasma eritrosit/ platlet/ 1 (a) Keimunan aktif buatan
Has erythrocyte/ platelet/ protein plasma Artificial active immunity
plasma protein Has no erythrocyte/
(b) (i) • Suntikan vaksin pertama menghasilkan
platelet/ plasma protein
antibodi pada kepekatan yang rendah di
Mengandungi limfosit Mengandungi limfosit bawah aras keimunan, maka keimunan
yang rendah yang tinggi belum dicapai.
Has low lymphocytes Has high lymphocytes The first injection of the vaccine produces
Arteri tidak mempunyai Salur limfa antibodies at low concentrations below the
level of immunity which indicate immunity has
injap mempunyai injap
not been achieved.
Artery has no valve Lymphatic vessel has
valve • Suntikan penggalak merangsang
penghasilan antibodi dengan kadar yang
lebih cepat dengan kepekatan yang lebih
BAB
Keimunan Manusia tinggi. Kepekatan antibodi dalam darah
11 Immunity in Humans melepasi aras keimunan.
Booster injection stimulates antibody production
11.1 Pertahanan Badan at a faster rate and at higher concentrations.
Body Defence The concentration of antibodies in the blood
1 (a) L: Neutrofil/ Monosit/ Sel fagosit exceeds the level of immunity.
Neutrophil/ Monocyte/ Phagocyte • Patogen dapat dimusnahkan dengan
M: Limfosit/ Lymphocyte pantas sekiranya berlaku jangkitan pada
(b) • Kulit tebal untuk ditembusi bakteria. masa akan datang.
Skin is too thick to for bacteria penetration. Pathogens can be destroyed quickly if another
• Mikroorganisma sukar hidup kerana event of infection occurs in the future.
penanggalan sel kulit mati, minyak dan asid (ii) • Minna akan mendapat penyakit/ kesan
pada sebum mengelakkan pertumbuhan jangkitan X.
bakteria. Minna will get the disease/ effects of infection X.
Shedding of dead skin cell prevent microorganisms • Aras kepekatan antibodi adalah di bawah
growth, oil and acid in sebum prevent bacterial growth. aras keimunan.
• Lisozim dalam peluh memusnahkan dinding The level of antibody concentration is below
sel bakteria. the level of immunity.
Lysozyme in sweat break down the cell wall of • Minna masih belum dilindungi
bacteria. sepenuhnya dari jangkitan X.
(c) L menjalankan fagositosis untuk menyingkirkan Minna still not fully protected from infection
patogen yang memasuki tubuh manakala M X.
J19 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
(c) • Walaupun aras kepekatan antibodi X telah In order to produce protection (immunity) naturally
mencapai aras keimunan tetapi masih tidak against certain diseases, a child needs to be infected with
akan melindungi Minna dari jangkitan Y the bacteria or virus and fully recover from the infection.
kerana sifat antibodi adalah spesifik. • Dalam proses tersebut, kanak-kanak berisiko
Although the concentration level of antibody X untuk mengalami komplikasi jangkitan yang boleh
has reached the level of immunity but still will not mengancam nyawa.
protect Minna from infection Y because the nature In the process, children are at risk for life-threatening
of the antibody is specific. complications of infection.
• Aras kepekatan antibodi Y masih di bawah • Vaksin, sama ada yang berunsurkan bakteria
aras keimunan. Minna masih belum dilindungi atau virus yang telah dimatikan atau dilemahkan
sepenuhnya dari jangkitan Y. Dos penggalak memberi perlindungan setaraf dengan perlindungan
untuk vaksin Y diperlukan untuk merangsang (keimunan) semula jadi hasil daripada jangkitan
penghasilan antibodi Y. tanpa perlu melalui risiko komplikasi jangkitan.
The concentration level of antibody Y is below the Vaccines, whether bacterial or viral that have been killed
level of immunity. Minna is still not fully protected or weaken provide protection equivalent to the natural
from infection Y. A booster dose for vaccine Y is protection (immunity) resulting from infection, without
required to stimulate the production of antibody Y. having to go through the risk of infection complications.
2 (a) • Cik Sim telah dijangkiti dengan Hepatitis • Vaksin menggunakan tindak balas semula jadi
A dan B kerana antigen dikesan dalam tubuh terhadap jangkitan untuk merangsang sistem
darahnya. Aras kepekatan antibodi Cik Sim keimunan.
terhadap Hepatitis A dan B adalah rendah/ di Vaccines use the body's natural response to infection to
bawah aras keimunan, maka Cik Sim tidak stimulate the immune system.
dilindungi dari jangkitan Hepatitis A dan B. • Maka, sekiranya seseorang terdedah kepada
Ms. Sim was infected with Hepatitis A and B patogen tertentu pada masa hadapan, sistem
because the antigens were detected in her blood. keimunan individu tersebut akan ‘mengenali’
Ms. Sim's antibody concentration level against patogen tersebut dan menghasilkan tindak balas
Hepatitis A and B is low/ below the level of yang berkesan bagi menyekat jangkitan tersebut
immunity, so Ms. Sim is not protected from atau mengurangkan gejalanya.
Hepatitis A and B infection. So if a person is exposed to a particular pathogen in the
• Encik Joo telah dijangkiti dengan Hepatitis A future, the individual's immune system will 'recognise' the
dan B kerana antigen dikesan dalam darahnya. pathogen and produce an effective response to block the
Aras kepekatan antibodi Encik Joo terhadap infection or reduce the severity of symptoms.
Hepatitis A dan B adalah tinggi/ melebihi aras
keimunan, maka sistem pertahanan Encik Joo 11.4 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Keimunan Manusia
sedang melawan jangkitan dan akan beransur Health Issues Related to Human Immunity
pulih. 1 HIV memusnahkan sel limfosit yang menghasilkan
Mr Joo was infected with Hepatitis A and B because antibodi hingga menyebabkan sistem pertahanan badan
the antigens were detected in his blood. Mr. Joo's lumpuh. Sebarang bakteria termasuk bakteria komensal
antibody concentration level against Hepatitis boleh menjadi jangkitan oportunistik kerana sistem
A and B is high/ above the level of immunity, so pertahanan tidak lagi berfungsi.
Mr. Joo's defence system is fighting the infection HIV destroys lymphocyte cells that produce antibodies to
and will gradually recover. paralyze the body's immune system. Any bacteria including
• Encik Park bebas dari jangkitan Hepatitis A commensal bacteria can become opportunistic infections
dan B kerana tiada antigen Hepatitis A dan B because the immune system is no longer functioning.
dikesan. Aras kepekatan antibodi Encik Park
terhadap Hepatitis A dan B adalah rendah/ di SUDUT KBAT
bawah aras keimunan, maka Encik Park tidak
dilindungi dari jangkitan Hepatitis A dan B. S1 − Apabila ramai orang tidak divaksinasi, semua berpotensi
Mr Park was free of Hepatitis A and B infections untuk dijangkiti dan menjadi hos/ pembawa. Kehadiran
because no Hepatitis A and B antigens were beberapa orang yang dijangkiti dalam komuniti yang
detected. Mr Park's antibody concentration level tidak divaksin menyebabkan penyakit tersebar dengan
against Hepatitis A and B is low/ below the level cepat.
of immunity, so Mr Park is not protected from When many people are not vaccinated, all have the
Hepatitis A and B infection. potential to become infected and become hosts/ carriers.
(b) Encik Park/ Mr Park The presence of several infected people in unvaccinated
3 • Bagi menghasilkan perlindungan (keimunan) secara communities caused the disease to spread rapidly.
semula jadi terhadap penyakit tertentu, seorang S2 − Jika sebahagian kecil sahaja individu dalam komuniti
kanak-kanak perlu dijangkiti oleh bakteria atau virus divaksinasi, jangkitan masih boleh berlaku dan
tersebut dan sembuh sepenuhnya dari jangkitan itu. tersebar kepada setiap individu yang belum divaksin
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J20
kerana masih ramai berpotensi untuk dijangkiti. as body has already been introduced to the bacteria
If only a small fraction of individuals in the community are through natural infection.
vaccinated, infections can still occur and spread to every • Pesakit perlu pulih daripadanya untuk mencapai
unvaccinated individual because there are still many potential keimunan.
individual to be infected. The patient need to be recover from it to achieve
S3 − Apabila lebih ramai individu dalam komuniti immunity.
telah divaksinasi, kehadiran pembawa tidak akan (b) • Keimunan yang diperolehi melalui suntikan
menyebabkan penyebaran jangkitan yang berleluasa. vaksin tifoid merupakan keimunan aktif buatan
Individu yang telah divaksin telah mencapai keimunan. manakala keimunan yang diperolehi melalui
Sekiranya terjangkiti, patogen dapat dimusnahkan suntikan antiserum ialah keimunan pasif buatan.
dengan cepat kerana vaksinasi menjadikan penghasilan Immunity acquired through typhoid vaccine injection
antibodi lebih cepat pada kepekatan yang tinggi. is artificial active immunity while immunity acquired
through antiserum injection is artificial passive
Keimunan berkelompok dicapai apabila rantaian
immunity.
penularan putus apabila kurang/ tiada individu dalam
• Limfosit berperanan menghasilkan antibodi
komuniti yang boleh dijangkiti.
dalam keimunan yang diperolehi melalui
When more individuals in the community have been vaccinated,
suntikan vaksin tifoid manakala keimunan
the presence of carriers will not lead to the widespread
yang diperolehi melalui suntikan antiserum
of infection. Individuals who have been vaccinated have
membekalkan antibodi dari sumber luar tanpa
achieved immunity. If infected, pathogens can be destroyed
melibatkan fungsi limfosit.
quickly because vaccination makes antibody production
Lymphocytes play a role in producing antibodies in
faster at higher concentrations. Cluster immunity is achieved
immunity acquired through typhoid vaccine injection
when the chain of transmission breaks when there are few/ no while immunity acquired through antiserum injection
individuals in the community who can be infected. supplies antibodies from external sources without
involving lymphocyte function.
Praktis Sumatif
• Oleh kerana suntikan vaksin tifoid diberikan
KERTAS 1 sebelum individu dijangkiti, maka keimunan
yang diberikan adalah bersifat jangka panjang
1 C 2 D 3 B 4 D 5 A berbanding suntikan antiserum yang diberikan
KERTAS 2 selepas berlaku jangkitan yang memberikan
keimunan jangka pendek.
Bahagian B
Since the injection of typhoid vaccine is given before
1 (a) • Pembawa bakteria adalah mereka yang tidak
the individual is infected then the immunity given is
lagi mempunyai simptom dan disalah anggap long term in nature as compared to the antiserum
sebagai 'sembuh'. injection given after the occurrence of infection
Bacteria carriers are those who no longer have which gives short term immunity.
symptoms and are mistaken for 'cured'. • Suntikan vaksin tifoid berfungsi untuk
• Seseorang boleh menjadi pembawa jika mereka mencegah penyakit berbeza dengan suntikan
tidak mendapat rawatan yang tepat untuk antiserum yang bertindak sebagai rawatan
membunuh bakteria di dalam badan mereka. kepada jangkitan yang berlaku.
A person can be a carrier if they do not get the proper Typhoid vaccine injections work to prevent disease
treatment to kill the bacteria in their body. in contrast to antiserum injections which act as a
• Suntikan vaksin akan mengaktifkan limfosit treatment to the infections that occur.
untuk menghasilkan antibodi spesifik yang (c) • Kedua-dua jenis keimunan berfungsi untuk
akan membunuh bakteria 'tersembunyi' dalam melindungi tubuh tetapi berbeza dari segi
badan dan mewujudkan keimunan. kegunaannya.
Vaccine injection will activate the lymphocyte to The two types of immunity work to protect the body
produce specific antibody that will eliminate the but differ in terms of their uses.
‘hidden’ bacteria in the body and provide immunity. • (Keimunan aktif) badan mampu menghasilkan
• Vaksin tifoid tidak akan merawat jangkitan antibodi apabila dirangsang oleh kehadiran
aktif yang telah berkembang di dalam badan. antigen sama ada melalui suntikan vaksin atau
Typhoid vaccine will not treat an active infection that jangkitan semula jadi.
has already developed in the body. (Active immunity) the body is able to produce
• Ini kerana vaksin tifoid yang mengandungi antibodies when stimulated by the presence of
bakteria yang mati/ lemah/ dilemahkan tidak antigens either through vaccine injections or natural
akan mengaktifkan limfosit kerana badan infections.
telah diperkenalkan kepada bakteria melalui • Tetapi penghasilan antibodi mengambil masa
jangkitan semula jadi. malah bagi kes jangkitan semula jadi, pesakit
Typhoid vaccine that contains killed/ weak/ perlu sembuh sepenuhnya untuk memperoleh
attenuated bacteria will not activate the lymphocyte keimunan.
J21 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
But the production of antibodies takes time even 2 Jenis tindakan/ Type of action:
for the case of a natural infection, the patient needs • Tindakan terkawal/ Voluntary action
to be completely cured to acquire immunity. • Berlaku dengan kesedaran
• (Keimunan pasif) suntikan antiserum atau Occurs under consciousness
penyusuan susu ibu membekalkan antibodi
Laluan penghantaran maklumat:
yang terus boleh digunakan oleh badan untuk
Pathway of information transmission:
menghapuskan bakteria yang menjangkiti
• Rangsangan daripada bunga.
dengan segera.
Stimulation from the flowers.
(Passive immunity) antiserum injections or
breastfeeding supplies antibodies that can directly be
• Merangsang fotoreseptor di dalam retina mata
used by the body to eliminate the infecting bacteria untuk menjana impuls.
immediately. Stimulate the photoreceptors in the eyes retina to
• Ini menjimatkan masa kerana dalam kes generate impulse.
kecemasan seperti disengat atau dipatuk • Impuls dihantar melalui neuron deria ke neuron
haiwan berbisa, antibodi segera diperlukan geganti di dalam otak.
untuk meneutralkan toksin (bisa haiwan) bagi Impulse is transmitted through sensory neurone to relay
neurone in the brain.
menyelamatkan nyawa.
This saves time because in case of an emergency
• Proses interpretasi/ integrasi berlaku di dalam otak.
such as being stung or bitten by a poisonous Interpretation/ integration occurs in the brain.
animal, antibodies are immediately needed to • Impuls dijana dan dihantar melalui neuron geganti
neutralise the toxin (animal poison) to save lives. ke neuron motor.
• Sekiranya suntikan vaksin diberikan supaya Impulse is generated and transmitted through relay
limfosit menghasilkan antibodi secara semula neurone to motor neurone.
jadi, dikhuatiri mangsa/ pesakit tidak dapat • Neuron motor menghantar impuls ke efektor, iaitu
diselamatkan. otot rangka di lengan.
If a vaccine injection is given to allow lymphocytes Motor neurone transmits impulse to effector which is
to produce antibodies naturally, it is feared that skeletal muscles in the arm.
the victim/ patient will not be able to be saved. • Untuk bergerak balas iaitu, memetik bunga.
(d) Penyebab/ Cause: Respond by picking the flowers.
SLE merupakan penyakit autoimun yang mana
sel pertahanan menyerang sel badan sendiri 12.2 Sistem Saraf
manakala AIDS berpunca dari jangkitan Nervous System
HIV 1 (a) R: Serebrum/ Cerebrum
SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the body's Q: Serebelum/ Cerebellum
defence cells attack the body's own cells while AIDS is (b) • Ia adalah bahagian otak yang terbesar.
caused by HIV infection. It is the largest part of the brain.
• Ia mempunyai permukaan yang berlipat.
Kesan/ Effects: It has a deeply folded surface.
Sel pertahanan pesakit SLE menyebabkan (c) • T ialah hipotalamus.
kerosakan pada organ tertentu pesakit manakala T is hypothalamus.
pada pesakit AIDS sel pertahanan badan • Ia adalah pusat koordinasi sistem saraf
dilumpuhkan oleh virus menyebabkan badan autonomi.
terdedah kepada jangkitan sekunder/ oportunistik It is the coordination centre of the autonomic
yang boleh menyebabkan kematian. nervous system.
The immune cells of SLE patients cause damage to • Ia mengawal rembesan beberapa jenis
certain organs of the patient while in AIDS patients the hormon kelenjar pituitari.
body's defence cells are paralysed by the virus causing It control the secretion of a few types of pituitary
the body to become vulnerable to secondary/opportunistic gland hormones.
infections that can lead to death. • Ia terlibat dengan homeostasis dan sistem
endokrin.
BAB Koordinasi dan Gerak Balas dalam Manusia It is coordinating homeostasis and the endocrine
12 Coordination and Response in Humans system.
12.3 Neuron dan Sinaps
12.1 Koordinasi dan Gerak Balas
Neurones and Synapse
Coordination and Response
1 (a) • P ialah neuron deria.
1 (a) Nosireseptor
P is a sensory neurone.
Nocireceptor
• Neuron deria menghantar impuls saraf dari
(b) Untuk melindungi diri daripada bahaya.
organ deria/ reseptor kepada sistem saraf
To protect herself from danger.
pusat.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J22
A sensory neurone transmit nerve impulses from Perbezaan/ Differences:
sensory organs/ receptors to the central nervous
system. X Y
• Q ialah neuron motor. Tindakan refleks/ luar Tindakan terkawal
Q is a motor neurone. Voluntary action
kawal
• Neuron motor menghantar impuls saraf dari Reflex/ involuntary action
sistem saraf pusat kepada efektor.
A motor neurone transmit nerve impulses from the Tindakan berlaku tanpa Tindakan berlaku dalam
central nervous system to effectors. kesedaran/ secara kesedaran/ mengikut
• R ialah neuron geganti. automatik/ tidak mengikut kehendak sendiri
R is a relay neurone. kehendak sendiri Action occurs with
Action occurs without consciousness/ follow own
• Neuron geganti membawa impuls saraf dari
consciousness/ automatically/ will
neuron deria ke neuron motor.
not follow own will
Relay neurone send nerve impulses from sensory
neurone to motor neurone. Melibatkan sistem saraf Melibatkan sistem saraf
(b) • Apabila seseorang melihat seekor anjing autonomi soma
yang sangat garang. Involves the autonomic Involves somatic nervous
When a person sees a fierce dog. nervous system system
• Neuron deria menghantar impuls daripada Dikawal oleh saraf Dikawal oleh korteks
mata kepada sistem saraf pusat. tunjang serebrum
The sensory neurone transmit the impulses from Controlled by spinal cord Controlled by cerebral cortex
the eyes to the central nervous system.
• Otak mentafsirkan impuls (situasi bahaya) 12.5 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Saraf Manusia
dan hipotalamus diaktifkan. Health Issues Related to the Human Nervous System
The brain interprets the impulses (dangerous 1 • Dadah melambatkan penghantaran impuls di
situation) and hypothalamus is activated. sinaps.
• Impuls saraf dihantar melalui neuron motor Drug delay the transmission of impulse at the synapse.
ke otot dan kelenjar adrenal. • Dengan menghalang penghantaran
Nerve impulses are sent via the motor neurone to neurotransmiter.
muscles and adrenal gland. Inhibit the transmission of neurotransmitter.
• Kelenjar adrenal akan merembeskan • Akibatnya, otak tidak dapat menerima atau
hormon adrenalina. menghantar impuls ke efektor.
Adrenal gland will secretes adrenaline hormone. As a result, the brain cannot receive or send impulses to
• Adrenalina akan meningkatkan degupan the effector.
jantung, kadar pernafasan, tekanan darah, • Dan ini melambatkan gerak balas.
aras glukosa dalam darah dan kadar And this slow down the response.
metabolisme.
Adrenaline will increase heartbeat rate, breathing 12.6 Sistem Endokrin
rate, blood pressure, blood glucose level and The Endocrine System
metabolism rate. 1 (a) • Kalenjar B ialah pankreas.
• Jantung akan mengepam lebih banyak Gland B is pancrease.
oksigen dan glukosa ke otak dan otot • Apabila aras glukosa dalam darah meningkat.
rangka. When blood glucose level increase.
Heart will pump more oxygen and glucose to the • Pankreas akan merembeskan hormon insulin.
brain and skeletal muscles. Pancrease will secretes insulin hormone.
• Ini akan menyebabkan individu mempunyai • Insulin akan menukarkan glukosa yang
tenaga yang cukup untuk lari laju atau berlebihan kepada glikogen.
berlawan. Insulin will convert excess glucose into glycogen.
It will cause the individual to get enough energy • Glikogen akan disimpan di hati.
to run quickly or fight. Glycogen will be stored in liver.
• Apabila aras glukosa dalam darah menurun.
12.4 Tindakan Terkawal dan Tindakan Luar Kawal When blood glucose level decrease.
Voluntary and Involuntary Actions • Pankreas akan merembeskan hormon
1 Persamaan/ Similarity: glukagon.
• Kedua-dua tindakan melibatkan rangsangan/ Pancrease will secretes glucagon hormone.
impuls/ neuron/ otot rangka (efektor). • Glukagon akan menukarkan glikogen kepada
Both actions involve stimulation/ impulse/ neurone/ glukosa.
skeletal muscles (effector). Glucagon will convert glycogen into glucose.
J23 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
(b) • Kalenjar C ialah kalenjar tiroid yang BAB Homeostasis dan Sistem Urinari Manusia
merembeskan hormon tiroksina. 13 Homeostasis and the Human Urinary System
Gland C is thyroid gland that secretes thyroxine
hormone.
13.1 Homeostasis
• Hormon tiroksina yang berlebihan boleh Homeostasis
menyebabkan hipertiroidisme. 1 (a) Kelenjar peluh
Excessive of thyroxine hormone may cause Sweat gland
hyperthyroidism. (b) • Kelenjar peluh tidak terangsang.
• Hipertiroidisme menyebabkan seseorag Sweat gland is not stimulated.
individu mengalami pembengkakan pada • Berpeluh tidak berlaku.
kelenjar tiroid, kadar degupan jantung Sweating does not happen.
meningkat. (c) • Bulu roma tidak akan condong/ tegak.
Hyperthyroidism can cause individual to suffer No hair will lower/ stand erect.
swelling of the thyroid gland and higher heart • Lapisan udara yang nipis tidak terperangkap.
rate. No thin layer of air is trapped.
• Hormon tiroksina yang rendah boleh • Haba dapat dibebaskan dengan cepat.
menyebabkan hipotiroidisme. Heat can be released quickly.
Insufficient of thyroxine hormone may cause (d) • Suhu badan meningkat.
hypothyroidism. Body temperature increase.
• Hipotiroidisme menyebabkan seseorang • Arteriol di dalam kulit mengembang/
individu mengalami kadar degupan jantung pemvasodilatan.
dan kadar metabolisme rendah. Arterioles in the skin dilate/ vasodilation.
Hypothyroidism can cause lower heart rate and • Lebih banyak darah mengalir ke permukaan
lower metabolic rate. kulit.
Allow more blood to flow to the skin surface.
Praktis Sumatif • Lebih banyak haba dapat disingkirkan.
More heat is removed.
KERTAS 1 2 (a) S: Glukagon/ Glucagon
1 D 2 A 3 C 4 B 5 D T: Insulin/ Insulin
(b) Selepas makan
After taking a meal
KERTAS 2
(c) (i) • Sel Langerhans lebih terangsang untuk
Bahagian A
mengeluarkan lebih banyak insulin.
1 (a) S: Otak Langerhans cells more stimulated to secrete
Brain more insulin.
T: Saraf tunjang • Lebih banyak penukaran glukosa
Spinal cord
berlebihan menjadi glikogen.
(b) Tindakan terkawal: 1, 2, 4 More conversion of excess glucose into
Voluntary action:
glycogen.
Tindakan refleks: 5, 3, 4 • Glukosa yang berlebihan akan
Reflex action:
menyebabkan diabetes melitus.
(c) • Kawasan deria P memproses maklumat. Excessive glucose will cause diabetes mellitus.
The sensory areas of P process information.
• Berasa dahaga/ letih/ lelah/ mengalami
• dan kawasan motor P menghantar impuls penurunan berat badan.
melalui R kepada otot kaki. Thirsty/ tired/ fatigued/ suffers weight loss.
and the motor areas of P send impulses via R to the
(ii) • Suntikan insulin.
leg muscles.
Insulin injections.
• untuk mengecutkan otot dan menaikkan kaki • Pil yang menurunkan kadar gula dalam
untuk berjalan. darah.
to contract the muscles and raise the legs to walk.
Pills that lower blood sugar levels.
• Pada masa yang sama, Q memproses • Diet yang betul/ diet rendah gula.
maklumat daripada otot, sendi, tendon dan Proper diet/ low sugar diet.
telinga.
At the same time, Q processes information from the 13.2 Sistem Urinari
muscles, joints, tendons and ears. Urinary System
• untuk menyeimbangkan badan semasa 1 (a) P: Ultraturasan/ Ultrafiltration
berjalan. Q: Penyerapan semula/ Reabsorption
to balance the body while walking. R: Perembesan/ Secretion
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J24
(b) • Diameter arteriol aferen lebih besar daripada • Kelenjar pituitari kurang dirangsang. Jadi,
diameter arteriol eferen. kurang ADH dirembes.
Diameter of the afferent arteriole is larger than the The pituitary gland is less stimulated. So, less ADH
diameter of the efferent arteriole. is secreted.
• Darah yang memasuki glomerulus bertekanan • Tubul berlingkar distal dan duktus pengumpul
hidrostatik tinggi. menjadi kurang telap terhadap air.
Blood entering the glomerulus is under high Distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
hydrostatic pressure. become less permeable to water.
• Bendalir meresap melalui dinding kapilari • Kurang air diserap semula.
glomerulus ke dalam rongga kapsul Less water is reabsorbed.
Bowman. • Air kencing banyak dihasilkan.
Fluid enters through the capillary wall of the More urine produced.
glomerulus into the cavity of Bowman's capsule. • Tekanan osmosis darah kembali normal.
• Hasil turasan glomerulus sama seperti plasma Blood osmotic pressure back to normal.
darah tetapi tidak mengandungi sel darah (b) • Tekanan osmosis darah akan menjadi tinggi.
merah, platlet dan protein plasma. The osmotic pressure of blood will be high.
Glomerular filtrate has the same composition as • Tubul ginjal akan menjadi lebih telap kepada
blood plasma but does not contain red blood cells, air.
platelets and plasma proteins. The kidney tubules will become more permeable to
water.
• dipanggil hasil turasan glomerulus.
• Lebih banyak ADH akan dirembeskan
known as glomerular filtrate.
More ADH will be secreted.
(c)
Hasil turasan • Air kencing yang dihasilkan akan menjadi
Bahan Air kencing
glomerulus pekat.
Substances Urine
Glomerular filtrate The urine produced will be concentrated.
Eritrosit
Erythrocyte 13.3 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Urinari
Health Issues Related to the Urinary System
Air
3 3 1 (a) Batu karang/ Kidney stone
Water
(b) Guna pancaran laser untuk memecahkan batu
Ion natrium karang itu.
Sodium ion
3
Use a laser beam to break the kidney stone.
Urea (c) • Kepekatan bendalir dialisis bersifat isotonik
Urea
3 3 berbanding kepekatan darah.
The concentration of dialysis fluid is isotonic
Glukosa
3 compared to the concentration of blood.
Glucose
• Tiub dialisis bersifat separa telap.
Protein The dialysis tube is semi-permeable.
Protein • Kepekatan urea dalam darah lebih tinggi
(d) • Penyerapan semula asid amino tidak berlaku/ daripada kepekatan urea dalam cecair dialisis.
kurang efisien. The concentration of urea in the blood is higher
Reabsorption of amino acid does not occur/ less than the concentration of urea in the dialysis fluid.
efficient. • Urea meresap masuk ke dalam bendalir
• Asid amino tidak diserap semula (dalam dialisis.
kapilari darah) melalui pengangkutan aktif. Urea diffuse into the dialysis fluid.
Acid amino does not reabsorbed by active transport. • Mengikut kecerunan kepekatan.
• Dikeluarkan di air kencing. According to the concentration gradient.
Excreted by urine. SUDUT KBAT
2 (a) • Kelenjar R ialah kelenjar pituitari.
• Di P, apabila aras glukosa dalam darah meningkat/
Gland R is pituitary gland.
melebihi aras normal
• Individu Y, tekanan osmosis darah menurun
At P, when the blood glucose level is high/ above normal range
ke bawah julat normal.
• sel beta (β) pada kelompok sel Langerhans di pankreas
Individual Y, blood osmotic pressure drops below
beta (β) cells in the Langerhans cell group at pancreas
the normal range.
• merembeskan insulin ke dalam darah.
• Osmoreseptor di dalam hipotalamus kurang
secretes insulin into the blood.
dirangsang.
• Di hati,
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus are less
stimulated. In the liver,
J25 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• insulin menukarkan glukosa berlebihan Proses metabolisme
the insulin converts excess glucose Metabolic processes
• kepada glikogen • Otot rangka tidak dirangsang.
to glycogen The skeletal muscle are not stimulated.
• disimpan di hati dan sel otot • Menggigil tidak berlaku
stored in liver and muscle cells Shivering are not occur
• penggunaan glukosa untuk respirasi sel meningkat • Kelenjar adrenal kurang dirangsang
increased uptake of glucose for cellular respiration The adrenal glands are less stimulated
• pertukaran glukosa berlebihan kepada lipid • Adrenalina kurang dirembeskan
conversion of excess glucose to lipids Less adrenaline secreted
• menurunkan aras glukosa yang tinggi ke aras normal • Kelenjar tiroid kurang dirangsang
lowers high glucose levels to normal range The thyroid glands are less stimulated
• Tiroksina kurang dirembeskan
Praktis Sumatif Less thyroxine secreted
KERTAS 1 • Kadar metabolisme rendah
The metabolic rate is low
1 C 2 D 3 C 4 D 5 C (c) • Perlu/ Necessary
6 B • (apabila demam) suhu badan meningkat.
KERTAS 2 (when fever) body temperature rises.
• Arteriol di dalam kulit mengembang/
Bahagian C
pemvasodilatan.
1 (a) • Arteriol mencerut/ pemvasocerutan.
Arterioles in the skin expand/ vasodilate.
Arteriole constrict/ vasoconstriction
• Kurang darah mengalir ke permukaan kulit. • Lebih banyak darah mengalir ke permukaan
Less blood flows to the surface of the skin. kulit.
• Kurang haba hilang ke persekitaran luar (secara More blood flows to the surface of the skin.
radiasi). • Kepingan gel lembut menyerap haba.
Less heat is lost to the external environment (by Soft gel sheets absorb heat.
radiation). • Kepingan gel adalah sejuk.
• Mencapai suhu badan normal/ 37°C. Soft gel sheets are cold.
Achieve normal body temperature/ 37°C. • Haba keluar dari badan lebih cepat.
(b) Tindakan fizikal/ Physical action Heat leaves the body faster.
• Termoreseptor di hipotalamus dan
termoreseptor haba di kulit BAB Sokongan dan Pergerakan dalam Manusia dan
Haiwan
Thermoreceptor in the hypothalamus and 14 Support and Movement in Humans and Animals
thermoreceptors in the skin
• mengesan kenaikan suhu badan. 14.1 Jenis Rangka
detect the increase temperature in body. Types of Skeleton
• Pemvasodilatan berlaku 1 (a) Rangka luar/ Exoskeleton
Vasodilation occur (b) Rangka dalam/ Endoskeleton
• Otot licin di sekitar arteriol aferen mengendur. (c) Rangka hidrostatik/ Hydrostatic skeleton
The smooth muscle around afferent arterioles relax. 2 (a) 3
• Meningkatkan jumlah darah yang mengalir (b) 3
melalui kulit.
Increase the amount of blood flowing through the skin. 14.2 Sistem Otot Rangka Manusia
• Meningkatkan jumlah haba yang hilang melalui Musculoskeletal System of Humans
darah secara sinaran. 1 (a)
Increase the amount of heat radiated lost via the blood.
• Kelenjar peluh merembeskan lebih banyak Rawan
peluh ke permukaan kulit. Cartilage
The sweat glands secrete more sweat onto the surface of
the skin. Membran sinovia
• Otot erektor pada kulit mengendur. Synovial membrane
Erector muscles in the skin relax.
• Merendahkan/ menurunkan rambut/ rambut
mendatar. (b) • Sebagai pelincir
Lowering the skin hairs/ hairs flatten on the skin. Serves as lubricant
• Udara panas tidak/ kurang terperangkap pada • Mengurangkan geseran antara tulang-tulang
kulit Reduces the friction between end of bones
Hot air is not/ less trapped against the skin (c) Sutur/ Sutur
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J26
(d) 2 • Pergerakan ikan ke hadapan menjadi perlahan.
Sendi lesung Sendi engsel
Forward movement of the fish slows down.
Ball-and-socket joint Hinge joint
• Otot miotom yang cedera tidak dapat mengecut.
Membenarkan putaran Membenarkan The injured myotom muscle cannot contract.
dalam semua arah pergerakan tulang • Ekor ikan akan mengibas dengan perlahan
Allows rotational dalam satu satah The tail of the fish will whipped slowly
movement in all Allows movement of • Otot miotom di sebelah kiri mengendur
directions bones in one plane The myotom muscle on the left side relaxes
Contoh: Contoh: • Gelombang pengenduran dan pengecutan akan
Alternating waves of contraction and relaxation along
Sendi bahu/ sendi Sendi lutut/ sendi siku
myotome will
punggung Example: Knee joint/
elbow joint • menyebabkan pergerakan bahagian badan dari sisi
Example: Shoulder joint/
hip joint
ke sisi perlahan
cause the body to move side to side slowly
• Penolakan air ke belakang dan ke sisi perlahan
14.3 Mekanisme Pergerakan dan Gerak Alih Pushing of water backwards and sideways are slow
Movement and Locomotion
1 Persamaan/ Similarity: 14.4 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Otot Rangka
• Kedua-dua organisma mempunyai otot berantagonis Manusia
Both organisms have antagonistic muscles Health Issues Related to the Human Musculoskeletal
• membenarkan koordinasi pergerakan badan. System
to allow coordination of body movements. 1 (a) • Pusat graviti badannya beralih.
The centre of her body's gravity is shifting.
Perbezaan/ Differences:
• Turus vertebra menjadi senget.
• Cacing tanah mempunyai rangka hidrostatik
The vertebral column becomes tilted.
manakala belalang mempunyai rangka luar.
• Berat badan jatuh pada kaki hadapan.
Earthworm has hydrostatic skeleton but grasshopper has
Body weight falls onto the fore foot.
exoskeleton
• Dalam cacing tanah, daya pengecutan digunakan • Meningkatkan sejumlah tekanan pada kaki
untuk mengisi rongga berisi cecair tetapi dalam hadapan.
belalang, otot melekat pada permukaan dalam Increase amount of pressure on the fore foot.
rangka luar. • Menyebabkan dia menyesuaikan seluruh
In earthworm, the force of contraction is applied to a fluid- berat badan untuk menjadi seimbang.
filled cavity (coelom) but in grasshopper, muscles attached Causing her to adjust the rest of the body to be
to the interior surface of exoskeleton. balanced.
• Cacing tanah mempunyai otor membujur dan otot • Kecederaan tisu-tisu lembut, sendi dan
lingkar tetapi belalang mempunyai otot fleksor dan tulang.
ekstensor. Injured soft tissues structures, joints and bones.
Earthworm has longitudinal and muscular muscles but • Tekanan berlebihan diletakkan pada lutut.
grasshopper has flexor and extensor muscles. Excessive pressure placed on knees.
• Otot cacing tanah menghasilkan gelombang • Dari masa ke masa otot betis kekejangan.
peristalsis sepanjang badan tetapi otot belalang From time to time calf muscle cramp and bulge.
menyebabkan pembengkokan dan meluruskan (b) • Untuk meningkatkan suhu badan/otot
kaki. To increase temperature of body and muscle
Earthworm muscle produce peristaltic waves along • Membolehkan penggunaan tenaga yang lebih
the body but grasshopper muscles cause bending and efisien
straightening of the legs. Enabling more efficient use of energy
• Cacing tanah mempunyai keta tetapi belalang • Pengoksidaan glukosa lebih cekap
mempunyai sepasang kaki belakang yang panjang More efficient of glucose oxidation
dan kuat. • Meningkatkan peredaran darah/ meningkatkan
Earthworm has chaetae but grasshopper has a pair of degupan jantung/ membekalkan oksigen
long and strong hind legs. dengan lebih cekap
• Keta digunakan oleh cacing tanah untuk Increase blood circulation /increase heartbeat/
mencengkam tanah tetapi kaki belakang belalang supply of oxygen faster
diadaptasi untuk melompat. • Mengelakkan kecederaan dan kekejangan
Chatae is used to anchor the ground for earthworm but otot
hind legs are adapted for hopping for grasshopper. Prevent injuries and muscle cramp
J27 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
Praktis Sumatif 15.2 Gametogenesis Manusia
Gametogenesis in Human
KERTAS 1 1 (a) K : Sperma/ Sperm
1 B 2 C 3 A 4 D 5 D L : Ovum // Oosit sekunder
6 C 7 A Ovum // Secondary oocyte
(b) K : Testis/ Testes
KERTAS 2 L : Ovari/ Ovary
Bahagian A 2 (a) oosit sekunder, ovari/ secondary oocyte, ovaries
1 (a) X: Otot lingkar/ Circular muscle (b) Sel germa primordium/ Primordial germ cells
Y: Otot membujur/ Longitudinal muscle (c) oosit primer/ primary oocyte
(b) • Otot membujur di posterior mengecut dan otot (d) primer, sekunder/ Primary, secondary
lingkar mengendur. (e) hormon peluteinan (LH), estrogen
The posterior longitudinal muscle contracts and the luteinizing hormone (LH), oestrogen
circular muscle relaxes. 3 (a) Spermatogonium/ Spermatogonium
• Cacing tanah menjadi lebih pendek dan tebal. (b) Spermatosid primer/ Primary spermatocyte
Earthworm becomes thicker and shorter. (c) Spermatosid sekunder/ Secondary spermatocyte
• Otot lingkar di anterior mengecut dan otot (d) Spermatid/ Spermatid
membujur mengendur. (e) Sperma/ Sperm
The circular muscle at the anterior contracts and (f) Mitosis berulang/ Repeated mitosis
longitudinal muscle relaxes. (g) Meiosis I
• Cacing tanah menjadi lebih panjang dan (h) Meiosis II
kurus. (i) Pembezaan/ Differentiation
Earthworm becomes longer and thinner.
(c) (i) • Tenaga disimpan dalam tendon yang 15.3 Kitar Haid
(kenyal) pada otot fleksor dan ekstensor. Menstrual Cycle
Energy is stored in the tendon (elactic) in the 1 • Hormon X adalah hormon perangsang folikel.
flexor and extensor muscles. Hormone X is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
• Digunakan untuk menghasilkan suatu daya • Merangsang perkembangan folikel primer menjadi
menolak belalang ke atas dan ke hadapan. folikel sekunder/ folikel Graaf.
Used to produce a force to push the grasshopper Stimulates development of primary follicle to secondary
up and forward. follicle/ Graafian follicle.
(ii) • Apabila otot ekstensor tidak boleh • Merangsang oosit primer menjalani meiosis I//
mengecut. merangsang oosit sekunder menjalani meiosis
When extensor muscles cannot contract. II.
• Kaki belakang tidak boleh diluruskan. Stimulates primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I//
The hind legs cannot be straightened. stimulates secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis II.
• Tiada daya untuk melompat. • Merangsang sel-sel folikel menjalani mitosis.
No uplift force is produced. Stimulate follicle cells undergo mitosis.
• Merangsang sel-sel folikel merembeskan hormon
BAB Pembiakan Seks, Perkembangan dan estrogen.
Pertumbuhan dalam Manusia dan Haiwan
15 Sexual Reproduction, Development and
Stimulates follicle cells to secrete oestrogen hormone.
Growth in Humans and Animals
2 (a) korpus luteum/ corpus luteum
(b) korpus luteum, plasenta/ corpus luteum, placenta
15.1 Sistem Pembiakan Manusia (c) FSH, LH/ FSH, LH
Reproductive System of Humans (d) keguguran/ miscarriage
1 (a)
(iii) Tiub Falopio
Fallopian tube 15.4 Perkembangan Fetus Manusia
(i) Ovari
Ovary
Development of a Human Foetus
(iv) Faraj 1 • Tisu parut adalah tisu (endotelium/ otot licin) yang
(ii) Uterus
Uterus Vagina rosak/ tidak berfungsi.
Scar tissue is (endothelium/ smooth muscle) tissue that is
(b) (iii) Vesikel simen damaged/ not function.
Seminal vesicle • Tiada silia pada tisu parut.
(i) Duktus sperma (iv) Kelenjar prostat No cilia on scar tissue.
Sperm duct Prostat gland • Tiada pengecutan otot licin// tiada peristalsis
(ii) Testis
berlaku.
Testis (v) Zakar No contraction of smooth muscle tissue// no peristalsis
Penis
occurs.
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J28
• Pergerakan embrio/ blastosista perlahan/ tidak
Kedua-dua kembar Kedua-dua kembar
berlaku.
berkongsi satu plasenta. mempunyai plasenta
Embryo/ blastocyst movement is slow/ does not occurs.
Both twins share one masing-masing.
• Embrio/ blastosista tidak sampai ke (ruang)
placenta. Both twins have their
uterus.
own placenta.
The embryo/ blastocyst does not reach to uterine
(cavity). Kedua-dua kembar Kedua-dua kembar
• Blastosista tidak menempel pada dinding mempunyai jantina yang mempunyai jantina
endometrium// Blastosista menempel pada tiub sama. yang sama atau
Falopio/ tisu parut. Both twins have the same berlainan.
Blastocyst does not attach to the endometrial wall// gender. Both twins have the same
Blastocyst attached to the Fallopian tube/ scar tissue. or different gender.
• Kehamilan ektopik/ luar rahim berlaku.
Ectopic pregnancy occurs. 15.6 Isu Kesihatan Berkaitan Sistem Pembiakan Manusia
2 • Melindungi fetus daripada bahan yang berbahaya Health Issues Related to the Human Reproductive System
seperti toksin dan bakteria. 1 Kebaikan/ Advantages:
Protect foetus from harmful substances such as toxins • Membantu pasangan suami isteri yang mandul
and bacteria. untuk mendapatkan zuriat.
• Menghalang salur darah fetus yang halus daripada Helping barren couples to get descendant.
pecah akibat tekanan darah ibu yang tinggi. • Membantu keluarga merancang bilangan anak bagi
Prevent the delicate blood vessels of foetus from breaking menjamin kesihatan dan mengelakkan masalah
due to mother’s high blood pressure. kewangan.
Helping families to plan the number of children to ensure
15.5 Pembentukan Kembar health and avoid financial problems.
Formation of Twins
1 Persamaan/ Similarity: Keburukan/ Disadvantages:
• Kedua-dua embrio terbentuk hasil daripada • Meningkatkan risiko kelahiran berganda
persenyawaan. disebabkan banyak embrio dimasukkan ke dalam
Both embryos formed from fertilisation. uterus.
• Kedua-duanya berkembang dalam uterus. Increases the risk of multiple births due to multiple
Both growing in uterus. embryos inserted into the uterus.
• Kedua-duanya mempunyai tali pusat. • Risiko kehamilan luar rahim// embrio melekat
Both have umbilical cord. dalam tiub Falopio/ ruang abdomen.
• Kedua-dua darahnya tidak bercampur dengan Risk of pregnancy outside the uterus// embryos attached
darah ibu. to the Fallopian tubes/ abdominal spaces.
Both their bloods do not mix with their mother's blood. • Kos pembiayaan perubatan yang tinggi.
High medical financing costs.
Perbezaan/ Differences:
• Kesan sampingan ubat kesuburan// pendarahan
Kembar A Kembar B berlebihan.
Twins A Twins B Side effects of fertility medicines// excessive bleeding.
Kembar seiras Kembar tidak seiras Praktis Sumatif
Identical twins Fraternal/ Non-identical
twins KERTAS 1
Satu ovum disenyawakan Dua ovum 1 D 2 C 3 B 4 A 5 B
oleh satu sperma disenyawakan oleh KERTAS 2
membentuk satu zigot. dua sperma berasingan Bahagian A
One ovum fertilised by one membentuk dua zigot. 1(a) (i) Kelenjar pituitari/ Pituitary gland
sperm to form one zygote. Two ova are fertilised by
(ii) Korpus luteum/ Corpus luteum
two separate sperms to
(b) • FSH merangsang perkembangan sel-sel folikel
form two zygotes.
di dalam ovari.
Kedua-dua kembar Kedua-dua kembar FSH stimulates the development of follicle cells in the
mempunyai kandungan tidak mempunyai ovary.
genetik yang sama. kandungan genetik • Pertambahan sel-sel folikel meningkatkan
Both twins have the same yang sama. perembesan hormon estrogen.
genetic content. Both twins do not have The increase number of follicle cells will increase the
the same genetic content. secretion of oestrogen.
J29 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• Aras estrogen yang tinggi merangsang (c) • Sel mengalami mutasi
perembesan hormon LH oleh kelenjar pituitari. Cell will mutate
High level of oestrogen stimulates the secretion of LH • Maklumat pewarisan dalam DNA mengalami
by pituitary gland. perubahan
• Hormon LH merangsang ovulasi. Hereditary information in DNA undergoes changes
LH triggers ovulation. • Penghasilan protein akan terganggu
(c) • Folikel Graaf berkembang menjadi korpus luteum. Protein production will be disrupted
Graafian follicle developed into corpus luteum. • Sel mengalami keadaan yang tidak normal
• Korpus luteum merembeskan hormon Cell experiences abnormal conditions
progesteron. 3 (a) (i) X : Glikoprotein
Corpus luteum secrete progesterone. Glycoprotein
• Progesteron mengekalkan ketebalan endometrium. Y : Dwilapisan fosfolipid
Progesterone maintains the thickness of the endometrium. Phospholipid bilayer
• Untuk penempelan embrio sekiranya persenyawaan (ii) • Molekul bersaiz kecil
berlaku. Small size molecule
For implantation of embryo if fertilisation occurs. • Molekul tidak berkutub
Nonpolar molecule
Penilaian Akhir Tahun (b) • Sap sel tumbuhan adalah hipotonik terhadap
larutan sukrosa 20 %
KERTAS 1 Plant cell sap is hypotonic to 20 % sucrose solution
1 C 2 B 3 C 4 C 5 D • Molekul air dari sap sel tumbuhan meresap
6 D 7 D 8 D 9 D 10 C keluar secara osmosis
11 C 12 C 13 B 14 B 15 B Water molecules from plant cell sap diffuse out by
16 A 17 D 18 C 19 B 20 C osmosis
21 D 22 D 23 C 24 C 25 A • Vakuol menjadi kecil dan membran plasma
26 B 27 D 28 A 29 D 30 A tertarik daripada dinding sel
31 D 32 C 33 B 34 B 35 D The vacuole becomes small and the plasma membrane
36 A 37 B 38 D 39 C 40 D is pulled away from the cell wall
• Sel mengalami plasmolisis
The cell undergoes plasmolysis
KERTAS 2
4 (a) (i)
P : Meiosis
Bahagian A Q : Mitosis
1 (a) (i) Mitokondrion (ii) Membina sel baharu bagi menggantikan sel
Mitochondrion
yang rosak/ mati
(ii) Menjana tenaga
Produce new cell to replace damaged/ dead
Generates energy
cell
(b) Sel otot/ sel hati/ sel sperma/ sel neuron
(b) (i) Sindrom Down
Muscle cell/ liver cell/ sperm cell/ neurone cell
Down syndrome
(c) • Tenaga ATP tidak dapat dijana
(ii) • Gentian gelendong gagal berfungsi
Energy in the form of ATP cannot be generated
semasa anafasa I atau anafasa II
• Sel otot tidak dapat mengecut/ sel hati tidak
Spindle fibres fail to function during anaphase
dapat melakukan proses pendeaminaan/ sel
I and anaphase II
sperma tidak dapat berenang ke arah ovum/ sel
• Kromosom homolog gagal berpisah atau
neuron tidak dapat menghantar impuls
tak disjunksi berlaku
Muscle cell cannot contract/ liver cell cannot do the
Homologous chromosomes fail to separate or
deamination/ sperm cell cannot swim towards the
ovum/neurone cell cannot transmit the impulse nondisjunction occur
2 (a) (i) Asid deoksiribonukleik (DNA) • Sel gamet yang terhasil mempunyai
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) bilangan kromosom yang tidak normal
(ii) Menyimpan maklumat pewarisan dalam (22/24)
organisma hidup Gamete cells with abnormal number of
Store genetic information of living organism chromosomes (22/24) formed
(b) • Protein dihasilkan oleh ribosom • Sel gamet yang bersenyawa akan
Proteins are produced by ribosomes menghasilkan zigot tidak normal yang
• Maklumat pewarisan pada DNA akan mempunyai bilangan 47 kromosom
ditranskripkan oleh RNA A fertilised gamete cell will produce an
Hereditary information on DNA will be transcribed abnormal zygote having a number of 47
by RNA chromosomes
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J30
5 (a) (i) • Mengangkut hasil pencernaan lipid • Pesakit emfisema akan mengalami masalah
seperti vitamin A, D, E, K, asid lemak pernafasan, batuk yang berterusan dan
dan gliserol penghasilan mukus yang banyak
Transport lipid digestive products such Emphysema patient will face shortness of breath,
as vitamins A, D, E, K, fatty acids and long coughing and increased production of
glycerol mucus
• Nodus limfa menghasilkan limfosit 7 (a) (i) Ampaian yang mengandungi patogen yang
untuk sistem pertahanan badan mati atau dilemahkan dan disuntik ke dalam
Lymph nodes produce lymphocytes for the badan untuk mengaktifkan limfosit untuk
body defence system menghasilkan antibodi
(ii) • Kedua-duanya mengandungi sel darah A suspension which contains dead or weakened
putih dan antibodi pathogen and is injected into the body to activate
Both contain white blood cells and antibodies the lymphocytes to produce antibodies
• Di dalam arteri, terdapat komposisi (ii) • Vaksin yang disuntik ke dalam badan
darah yang lengkap (platlet, eritrosit dan akan merangsang limfosit
protein plasma) tetapi di dalam salur Vaccine injected into the body will stimulate
limfa hanya terdapat leukosit lymphocytes
In the arteries, there is complete composition • Sistem pertahanan badan akan
of blood (platelets, erythrocytes and plasma menghasilkan antibodi yang spesifik dan
proteins) but in the lymphatic vessels there is maklumatnya akan disimpan
only leukocytes The body defence system will produce
• Di dalam arteri, kandungan oksigen specific antibodies and its information is
dalam darah adalah tinggi tetapi di dalam stored
salur limfa kandungan oksigen adalah • Sekiranya berlaku jangkitan dari
rendah patogen yang sama, antibodi akan
In the arteries, the oxygen content in the bertindak untuk menghalang tindakan
blood is high but in the lymphatic vessels the patogen
oxygen content is low If the infection from the same pathogen
(b) (i) Injap/ Valves occurs, antibodies will act to block the action
(ii) • Nodus limfa akan membengkak dan of the pathogen
menjadi lebih aktif (iii) • Sistem pertahanan badan berjaya
The lymph node will swell and become more membina sedikit antibodi
active The body defence system manages to build up
• Lebih banyak limfosit akan dihasilkan a small amount of antibodies
More lymphocytes will be produced • Jumlah antibodi yang sedikit tidak
6(a) (i) Diafragma/ Diaphragm melepasi aras keimunan
(ii) • Struktur Z akan mengendur semasa The small amount of antibodies does not
menghembus nafas exceed the level of immunity
During exhalation, structure Z will relax (b) (i) • Individu X memperolehi keimunan
• Ia akan melengkung ke atas aktif buatan manakala individu Y
It will curve upwards memperolehi keimunan pasif buatan
(b) • Struktur respirasi adalah lembap bagi Individual X acquires artificial active
memudahkan resapan gas immunity while individual Y acquires
The respiratory structure is moist to help gases artificial passive immunity
diffusion • Individu X memperolehi keimunan yang
• Lapisan sel yang melapisi struktur respirasi kekal dalam tempoh yang lama manakala
adalah nipis bagi meningkatkan resapan gas individu Y memperolehi keimunan yang
The cells lining of the respiratory structure is thin to sementara
increase gases diffusion Individual X acquires an immunity that lasts
• Struktur respirasi mempunyai luas permukaan for a long period of time while individual Y
yang besar untuk meningkatkan kadar acquires a temporary immunity
pertukaran gas (ii) • Individu X boleh dijangkiti oleh penyakit
The respiratory structure has large surface area to kerana antibodi yang dihasilkan belum
increase gases exchange rate mencapai aras keimunan
(c) • Pundi udara di dalam peparu rosak, pertukaran Individual X can be infected by disease
gas kurang berlaku because the antibodies produced have not yet
The air sacs of lung are damaged, less gas exchange reached the level of immunity
occurs
J31 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• Individu Y terus mengalami penyakit • Individu A juga mengalami masalah makan
tersebut kerana antibodinya sudah dalam kuantiti yang banyak tanpa kawalan
menurun Individual A also has trouble eating in large
Individual Y continues to suffer from quantities without control
the disease because his antibodies have • Individu A akan rasa bersalah dan akan
decreased memuntahkan balik makanan tersebut atau
8 (a) (i) Ultraturasan mengambil laksatif
Ultrafiltration Individual A will feel guilty and will vomit out the
(ii) Terdapat protein plasma dan sel darah merah food or take a laxative
di dalam hasil turasan glomerulus • Keadaan ini menyebabkan berat badan
There are plasma proteins and red blood cells sentiasa berubah-ubah, mengalami kekurangan
in the glomerular filtrate nutrisi
(iii) • Di Y, proses rembesan berlaku This condition causes the weight to fluctuate
manakala di Z, proses penyerapan constantly, suffering from nutritional deficiencies
semula berlaku • Individu A mengalami ketidakseimbangan ion
At Y, the process of secretion occurs while at dan mineral dalam darah
Z the process of reabsorption occurs Individual A experiences an imbalance of ions and
minerals in the blood
• Di Y, bahan toksik dan dadah dirembes
kembali ke dalam tubul manakala di • Kerosakan pada perut dan usus juga boleh
Z, air, glukosa dan asid amino diserap berlaku
Damage to the stomach and intestines can also
semula ke dalam salur darah.
occur
At Y, toxic substances and drugs are secreted
back into the tubule whereas at Z, water, Individu/ Individual B
glucose and amino acid are reabsorbed into • Individu B mengalami kegemukan atau obesiti
the blood vessel. Individual B is overweight or obese
(b) • Proses rembesan/ Secretion process • Pengambilan makanan yang diproses,
• Bahan buangan toksik yang berlebihan bergoreng dan berkalori tinggi dalam tempoh
dirembeskan secara pengangkutan aktif yang lama telah menyebabkan individu B
Excessive toxic wastes are secreted by active mengalami obesiti
transport Consumption of processed, fried and high-calorie
(c) Persamaan/ Similarity: foods over a long period of time has caused individual
Kedua-dua proses pengosmokawalaturan berlaku B to become obese.
di ginjal • Obesiti akan menyebabkan individu B terdedah
Both osmoregulation processes occur in kidney kepada penyakit kardiovaskular, kencing
manis, kerosakan organ (hati dan ginjal)
Perbezaan/ Differences: Obesity will make individual B vulnerable to
• Ravi mengalami tekanan osmosis darah yang cardiovascular disease, diabetes, organs damage
meningkat manakala Amin mengalami tekanan (liver and kidney)
osmosis darah yang menurun • Pergerakan dan aktiviti yang boleh dijalankan
Ravi experiences increased blood osmotic pressure oleh individu B akan terganggu
while Amin experiences decreased blood osmotic The movements and activities that can be performed
pressure by individual B will be disrupted
• Hormon ADH pada Ravi dirembeskan dengan • Komplikasi sendi dan tulang kerana
banyak, manakala hormon ADH kurang peningkatan berat badan
dirembeskan pada Amin Complications of joints and bones due to weight
ADH hormone in Ravi is highly secreted while ADH gain
hormone is less secreted in Amin • Masalah pernafasan seperti asma serta masalah
tidur
Bahagian B Respiratory problems such as asthma and sleep
9 Individu/ Individual A problems
(a) • Masalah kesihatan yang dialami ialah bulimia • Kesan psikologi seperti kemurungan dan
nervosa kurang keyakinan diri
The health problem experienced is bulimia nervosa Psychological effects such as depression and lack of
• Bulimia adalah gangguan mental terhadap self-confidence
pesakit yang ingin mengekalkan berat badan (b) Pesakit/ Patient X
yang normal • Pesakit X yang tidak mempunyai pundi
Bulimia is a mental disorder of patients who want to hempedu akan mengalami pelepasan hempedu
maintain a normal weight yang tidak teratur
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J32
Patient X who does not have a gallbladder will 10 (a) (i) • Bonggol sinaps/ hujung akson
experience irregular release of bile mempunyai banyak mitokondrion dan
• Makanan yang mempunyai kandungan lemak vesikel sinaps
dan protein yang tinggi tidak dapat dicernakan The synaptic knob/ axon terminal has many
dengan baik mitochondria and synaptic vesicles
Foods that are high in fat and protein cannot be • Vesikel sinaps mengandungi
digested properly. neurotransmiter
• Pesakit perlu mengelakkan makanan yang Synaptic vesicles contain neurotransmitters
tinggi lemak, makanan yang diproses, makanan • Impuls saraf yang sampai ke bonggol
seperti daging merah, organ dalaman haiwan, sinaps akan merangsang vesikel sinaps
kek dan pastri serta lain-lain bergerak ke membran plasma
Patient should avoid foods high in fat, processed Nerve impulses reaching the synaptic knob
foods, food such as red meat, internal organs of will stimulate synaptic vesicles to move to the
animals, cakes and pastries and others plasma membrane
• Pesakit digalakkan mengambil protein kurang • Vesikel sinaps bertaut dengan
lemak seperti ikan, ayam, tempe dan tauhu membran plasma dan membebaskan
bagi menggantikan daging merah neutrotransmiter ke dalam sinaps
Patients are encouraged to consume low-fat protein The synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasma
such as fish, chicken, tempeh and tofu to replace red membrane and release neurotransmitters into
meat the synapse
• Pesakit juga perlu menukar cara memasak • Dendrit akan dirangsang untuk menerima
secara menggoreng kepada cara merebus, neurotransmiter
mengukus dan membakar Dendrites will be stimulated to receive
Patients also need to change the way of cooking by neurotransmitters
frying to the way of boiling, steaming and baking • Impuls saraf baharu dicetuskan di dendrit
• Pesakit dinasihatkan mengambil sumber serat dan diangkut ke bonggol sinaps neuron
untuk membantu pencernaan seperti buah- New nerve impulses are triggered in the
buahan dan sayur-sayuran dendrites and they are transmitted to the
Patients are advised to take fibre sources to aid synaptic knob of the neurone
digestion such as fruits and vegetables • Mitokondrion membekalkan tenaga untuk
Pesakit/ Patient Y impuls merentasi sinaps
• Pesakit mengalami masalah insulin tidak dapat Mitochondria supply energy for impulses across
dirembes dengan normal the synapses
Patient has problem with insulin not being secreted (ii) • Alkohol mengandungi etanol yang
normally melambatkan gerak balas saraf terhadap
• Gula yang berlebihan tidak dapat ditukarkan rangsangan
kepada glikogen Alcohol contains ethanol which slows down the
Excess sugar cannot be converted to glycogen nerves response to stimuli
• Pesakit perlu mengelakkan pengambilan • Etanol menghalang neurotransmiter
karbohidrat yang berlebihan seperti nasi, mi, merentasi sinaps
pasta, roti, kek dan pastri Ethanol inhibits neurotransmitters across the
Patient should avoid excessive intake of synapse
carbohydrates such as rice, noodles, pasta, bread, • Proses penghantaran impuls di neuron
cakes and pastries menjadi lambat
• Pesakit juga perlu mengurangkan pengambilan The process of impulses transmission in
lemak neurones become slow
Patient should also reduce fats intake • Ia mengganggu proses integrasi maklumat/
• Pesakit perlu mengambil makanan dengan menerima dan menterjemah impuls saraf
kerap dalam hidangan yang kecil bagi di otak
menstabilkan tahap gula dalam darah It disrupts the process of integrating
Patient need to take food regularly in small portion to information/ receiving and translating nerve
stabilise blood sugar level impulses in the brain
• Pesakit dinasihatkan mengambil sumber serat • Gerak balas dan koordinasi otot akan
untuk membantu pencernaan seperti buah- terganggu dan menyebabkan lambat
buahan dan sayur-sayuran bertindak
Patient is advised to take fibre sources to aid digestion Muscle reactions and coordination will be
such as fruits and vegetables disrupted and cause slow action
J33 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
• Penggunaan alkohol menyebabkan Bahagian C
pemandu tidak dapat memandu dengan 11 (a) (i) • Folikel mula berkembang dan menjadi
selamat, reaksi yang perlahan, penglihatan matang di dalam ovari
yang kabur dan pendengaran yang kurang The follicles begin to grow and mature in the
jelas ovaries
Alcohol used causes drivers to be unable to • Haid berlaku kerana penguraian
drive safely, slow reactions, blurred vision and endometrium di dalam uterus
impaired hearing Menstruation occurs due to the breakdown of
(b) • Budak lelaki itu nampak dua ekor anjing sedang the endometrium in the uterus
berlari ke arahnya • Pembaikpulihan dan penebalan
The boy saw two dogs running towards him endometrium berlaku selepas haid
• Dia juga mendengar anjing tersebut menyalak Repair and thickening of the endometrium
He also heard the dogs barking occurs after menstruation
• Keadaan/ maklumat ini telah dihantar ke (ii) Fasa ovulasi/ Ovulation phase
hipotalamus • Folikel yang matang akan merembeskan
This condition/ information has been sent to the hormon estrogen
hypothalamus Mature follicles will secrete oestrogen
• Hipotalamus merangsang kelenjar adrenal • Hormon estrogen berfungsi untuk
untuk merembeskan hormon adrenalina ke membaik pulih dan menebalkan
dalam darah endometrium
The hypothalamus stimulated the adrenal glands to The oestrogen works to repair and thicken the
secrete adrenaline into the blood endometrium
• Hormon adrenalina merangsang penguraian • Kepekatan hormon estrogen yang tinggi
glikogen di dalam hati dan otot kepada merangsang kelenjar pituitari untuk
glukosa. merembeskan hormon perangsang folikel
Adrenaline stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in (FSH) dan hormon peluteinan (LH)
the liver and muscles into glucose. High concentration of the oestrogen stimulate
the pituitary gland to secrete follicle-
• Keadaan ini meningkatkan aras glukosa dalam
stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing
darah untuk dibekalkan kepada sel badan untuk
hormone (LH)
proses respirasi aerob
• Aras LH yang tinggi akan merangsang
This condition increases the level of glucose in the
ovulasi berlaku (pada hari ke-14)
blood to be supplied to the body cells for aerobic
High LH level will stimulate ovulation to occur
respiration (on the 14th day)
• Hormon adrenalina juga meningkatkan • LH juga merangsang pembentukan korpus
kadar pertukaran gas untuk meningkatkan luteum
pengambilan oksigen ke dalam badan LH also stimulates the formation of the corpus
Adrenaline also increases the rate of gas exchange luteum
to increase the uptake of oxygen into the
body
Fasa luteum/ Luteal phase
• Hormon adrenalina juga meningkatkan • Selepas ovulasi, folikel Graaf akan
denyutan jantung untuk membekalkan lebih membentuk korpus luteum
After ovulation, Graafian follicle will form the
oksigen dan glukosa kepada otak, jantung dan
corpus luteum
otot.
Adrenaline also increases the heartbeat to supply
• Korpus luteum menghasilkan estrogen dan
more oxygen and glucose to the brain, heart and
progesteron
The corpus luteum produce oestrogen and
muscles.
progesterone
• Kandungan oksigen dan glukosa yang tinggi
akan meningkatkan kadar metabolisme dalam • Penebalan dan perkembangan salur darah
badan di endometrium disebabkan oleh hormon
High oxygen and glucose content will increase the
progesteron dan estrogen
Thickening and development of endometrial
rate of metabolism in the body
blood vessels are caused by the progesterone
• Lebih banyak tenaga dihasilkan untuk bergerak
and oestrogen
balas sama ada budak lelaki tersebut ingin
• Sekiranya persenyawaan berlaku, korpus
melawan atau melarikan diri
luteum dikekalkan dan progesteron serta
More energy is produced to counteract whether the
sedikit estrogen terus dihasilkan untuk
boy wants to fight or run away
penebalan endometrium
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J34
If fertilisation occurs, the corpus luteum Prevent blood clots from occurring if the foetal
is maintained and progesterone and some blood group and mother blood group are
oestrogen continue to be produced for different in turn causing foetal blood capillaries
endometrial thickening.
to become blocked and death.
• Sekiranya tiada persenyawaan, korpus • Mengelakkan tekanan darah ibu yang
luteum merosot tinggi merosakkan salur darah dan organ
If there is no fertilisation, the corpus luteum
fetus yang masih kecil
degenerates
Avoiding high maternal blood pressure damages
• Progesteron dan estrogen yang
the foetal blood vessels and organs that are still
berkurangan menyebabkan endometrium
small
mengurai (haid) serta FSH dan LH
• Mengelakkan kemasukan bakteria
dirembeskan oleh kelenjar pituitari
dengan mudah ke dalam salur darah
Decreased progesterone and oestrogen cause the
fetus yang menyebabkan jangkitan dan
endometrium to break down (menstruation) and
FSH and LH to be secreted by the pituitary gland kematian
(b) Fungsi tali pusat/ Umbilical cord functions Prevents the easy entry of bacteria into the
• Mengangkut bahan keperluan seperti bloodstream of the foetus that cause infection
nutrien dan oksigen dari plasenta kepada and death
fetus bagi memastikan sel-sel fetus dapat (c) • Rawatan yang boleh digunakan adalah
berkembang dengan baik persenyawaan in vitro (IVF)
Transport essential substances such as The treatment that can be used is in vitro
nutrients and oxygen from the placenta to fertilisation (IVF)
the foetus to ensure that foetal cells can grow • Ovari akan dirangsang (dengan menyuntik
well hormon) untuk mematangkan lebih
• Mengangkut keluar bahan kumuh/ banyak telur/ ovum
bernitrogen dan gas karbon dioksida The ovaries will be stimulated (by injecting
yang dihasilkan oleh sel-sel fetus bagi hormones) to mature a dozen or more eggs/ ova
memastikan bahan buangan ini tidak • Telur/ ovum yang matang dikumpulkan
menjadi toksik dan mengganggu dan disenyawakan oleh sel sperma di
perkembangan fetus makmal
Removes waste/ nitrogenous waste and carbon The mature eggs/ ova are collected and
dioxide produced by foetal cells to ensure that fertilised by the sperm cells in a laboratory
these wastes do not become toxic and interfere • Embrio-embrio yang sihat akan
with foetal development dipindahkan ke dalam uterus
The healthy embryos will be transferred to the
Sistem peredaran darah ibu tidak uterus
bersambung dengan sistem peredaran • Semasa rawatan, penggunaan hormon
darah fetus membantu proses IVF
The mother blood circulatory system is not During the treatment, the used of hormone
connected to the foetal blood circulatory system helped the IVF process
• Mengelakkan penggumpalan darah • Selepas dua mingºgu prosedur IVF,
berlaku sekiranya kumpulan darah fetus ujian kehamilan akan dijadualkan untuk
dan kumulan darah ibu berbeza seterusnya mengesahkan kehamilan
menyebabkan kapilari darah fetus After two weeks of IVF procedure, the
tersumbat dan kematian pregnancy test will be scheduled
J35 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
CATATAN
© Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P) J36
You might also like
- 2.3 Proses Hidup Organisma MultiselDocument74 pages2.3 Proses Hidup Organisma Multiselwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Kegunaan Unsur Peralihan Dalam Pelbagai IndustriDocument1 pageKegunaan Unsur Peralihan Dalam Pelbagai Industriengene ehnypenNo ratings yet
- Magnetosfera Bumi KepentingannyaDocument6 pagesMagnetosfera Bumi Kepentingannya泇棋陈100% (1)
- Fizik Kertas 2 Ting 4 Pertengahan Tahun 2012 TerengganuDocument35 pagesFizik Kertas 2 Ting 4 Pertengahan Tahun 2012 TerengganuSiew Çhung Fxyne100% (2)
- Nota & Latihan Sejarah KSSM Tingkatan 4 Bab 2.4 - WeAcademia (2021)Document3 pagesNota & Latihan Sejarah KSSM Tingkatan 4 Bab 2.4 - WeAcademia (2021)syahbesah100% (1)
- 2.1 Sel Dan FungsinyaDocument33 pages2.1 Sel Dan FungsinyaTANG TIONG MIN MoeNo ratings yet
- E Jawapan Percubaan pt3 2019Document9 pagesE Jawapan Percubaan pt3 2019Yang Jin RongNo ratings yet
- Amali 2.1Document5 pagesAmali 2.1IzzatAnwariNo ratings yet
- Skema Bahagian CDocument11 pagesSkema Bahagian CEyla Adele II100% (1)
- Folio Sains Aisyah Bab 5Document8 pagesFolio Sains Aisyah Bab 5Tsun Tsun100% (3)
- Peristiwa Novel Jendela Menghadap JalanDocument28 pagesPeristiwa Novel Jendela Menghadap JalanNOR KALBI BT. MAHFODZ MoeNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Esei Bab 2Document2 pagesJawapan Esei Bab 2NIK AIDA MASTURA BINTI NIK ABDUL MAJIDNo ratings yet
- Nilai TanggungjawabDocument2 pagesNilai TanggungjawabVincent ChongNo ratings yet
- T3 Novel Isi&huraianDocument1 pageT3 Novel Isi&huraianKiki LauNo ratings yet
- Skema Gerak Gempur Sejarah JPNDocument21 pagesSkema Gerak Gempur Sejarah JPNshadoworacleNo ratings yet
- Atom Ion MolekulDocument14 pagesAtom Ion MolekulSyier MohdNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Kereaktifan LogamDocument10 pagesBab 4 Kereaktifan LogamNur Amal Zainul AbidinNo ratings yet
- T3 SN Modul Nilam Bab 7Document18 pagesT3 SN Modul Nilam Bab 7Saridah Mohamad0% (1)
- Mengekalkan Bahan Supaya Tetap Panas Dan SejukDocument2 pagesMengekalkan Bahan Supaya Tetap Panas Dan SejukYusnizar Mohd YunusNo ratings yet
- Bank DarahDocument4 pagesBank DarahAmirul Haqimie100% (5)
- E-Buku Bab 10 Penerokaan Angkasa Lepas - Space ExplorationDocument9 pagesE-Buku Bab 10 Penerokaan Angkasa Lepas - Space ExplorationAina FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Latar Tempat-ChotDocument1 pageLatar Tempat-Chotzuryn100% (1)
- 5 6100433532759310917Document6 pages5 6100433532759310917Devina SangkarNo ratings yet
- JAWAPANDocument6 pagesJAWAPANSagigal Gil0% (1)
- Sains T3Document14 pagesSains T3sclau7878% (9)
- Novel Jendela Menghadap JalanDocument34 pagesNovel Jendela Menghadap JalanLokman Lis50% (2)
- Bahagian C SkemaDocument11 pagesBahagian C SkemaZam BisuNo ratings yet
- Sipnosis Bab 19 - 21Document2 pagesSipnosis Bab 19 - 21NUR AFIQ ZUHAIRI BIN NORASIKIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Fizik f.4Document20 pagesFizik f.4Eeyqa Zynuddin0% (1)
- Bab 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4Document15 pagesBab 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4Idaayu AkNo ratings yet
- Whole Book Answers PDFDocument178 pagesWhole Book Answers PDFHaavinesh Ganesh100% (1)
- RUMUSANDocument2 pagesRUMUSANSITI FATIMAH BINTI JAMALUDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- RBT Folio t3Document27 pagesRBT Folio t3Kian Hoong LimNo ratings yet
- PT3 Kertas 1Document24 pagesPT3 Kertas 1Nurul SyudNo ratings yet
- Sejarah 2Document6 pagesSejarah 2Ahmad Nazri100% (2)
- 2022 Johor - Muar Add - Maths K2 JawapanDocument9 pages2022 Johor - Muar Add - Maths K2 JawapanSheila YongNo ratings yet
- Skema Modul Bab 4 Ting 3Document16 pagesSkema Modul Bab 4 Ting 3azilah_abd@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Zakat Emas Dan PengiraannyaDocument9 pagesZakat Emas Dan PengiraannyaMiss VioletNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF3 06 B4Document14 pages05 - SPSF3 06 B4Sin Ling Wong100% (2)
- Nota Lengkap Novel Silir DaksinaDocument18 pagesNota Lengkap Novel Silir DaksinaANIMAH BINTI ASSIHNo ratings yet
- Bab 7 - Tenaga Dan KuasaDocument10 pagesBab 7 - Tenaga Dan KuasaMOHD.ASWAD BIN ABDUL RAHIM Moe100% (2)
- Fizik SPM 2008 Paper 3 + SkemaDocument19 pagesFizik SPM 2008 Paper 3 + SkemaSUHAINA BINTI SAMSUDIN -50% (2)
- JawapanDocument8 pagesJawapanNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Folio Kimia Bab 5Document14 pagesFolio Kimia Bab 5Farhana UmairahNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Kimia SPM 2022Document12 pagesJawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Kimia SPM 2022MUHAMMAD HAZRIQ BIN ARIS JABATAN SAINS100% (1)
- Bab 7..... Sej F4Document4 pagesBab 7..... Sej F4Noorhashila Abdul Hamid100% (2)
- Kerja Khusus Sejarah Tingkatan 3 2019 NUR IRDHINADocument5 pagesKerja Khusus Sejarah Tingkatan 3 2019 NUR IRDHINAanalizaNo ratings yet
- SOALANDocument7 pagesSOALANVERONICA A/P FRANCIS MoeNo ratings yet
- PRAKTIS FIZIK BAB 4 Ting 4Document8 pagesPRAKTIS FIZIK BAB 4 Ting 4KHAIRINA NAZIHAH BINTI KAMARUL RIZAM Moe100% (1)
- Jawapan Praktis Topikal Platinum SPM Biologi Tingk 230617 134420Document23 pagesJawapan Praktis Topikal Platinum SPM Biologi Tingk 230617 134420ijanNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab Reportamsyar0% (1)
- Latihan Sejarah Bab 5 2 JulyDocument5 pagesLatihan Sejarah Bab 5 2 JulyNur NazirahNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan BM K1 Modul Oasis '21Document65 pagesSkema Jawapan BM K1 Modul Oasis '21Cikgu MaiNo ratings yet
- ASS BM Langkah2 Memajukan SukanDocument1 pageASS BM Langkah2 Memajukan SukanFaizul HishamNo ratings yet
- 9.3 AloiDocument12 pages9.3 AloiismalindaNo ratings yet
- Bab 2-1Document8 pagesBab 2-1Illyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 T4 Edisi Murid (Struktur Sel & Organisasi)Document16 pagesBab 2 T4 Edisi Murid (Struktur Sel & Organisasi)castellNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) Struktur SelDocument20 pages2.1 (A) Struktur Selamalina rohaizanNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Cell Organization Biologi Sel Dan Organisasi SelDocument21 pagesCell Biology and Cell Organization Biologi Sel Dan Organisasi SelPriya DarshiniNo ratings yet
- Biologi Bab 2Document12 pagesBiologi Bab 2NADIRA BINTI ISMAIL MoeNo ratings yet
- Conquerl Sains Dwi Tg2 2023 B7 4thDocument16 pagesConquerl Sains Dwi Tg2 2023 B7 4thNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Tingkatan 4 2023Document22 pagesRPT Sains Tingkatan 4 2023Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Conquer Sains TKT 1-Bab 2Document13 pagesConquer Sains TKT 1-Bab 2Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Tahunan 2018 Pihak Berkuasa Pembangunan Tenaga Lestari MalaysiaDocument138 pagesLaporan Tahunan 2018 Pihak Berkuasa Pembangunan Tenaga Lestari MalaysiaNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Inisiatif MESTECC 2020 Kuasai. Laksana. Ungguli Own It. Do It. Ace ItDocument31 pagesInisiatif MESTECC 2020 Kuasai. Laksana. Ungguli Own It. Do It. Ace ItNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Sample Poster Sains Untuk KesihatanDocument11 pagesSample Poster Sains Untuk KesihatanNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Jom-Teka-Silang-Kata-Bab-6-Tenaga-Nuklear-Kbsm-Tingkatan-4 (DUA)Document1 pageJom-Teka-Silang-Kata-Bab-6-Tenaga-Nuklear-Kbsm-Tingkatan-4 (DUA)Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Panitia Sains (Keberhasilan 2020)Document7 pagesPanitia Sains (Keberhasilan 2020)Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- PDPR 5PA (Laporan)Document2 pagesPDPR 5PA (Laporan)Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Slaid Tugas P - Makmal PDFDocument16 pagesSlaid Tugas P - Makmal PDFNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Borang Keceriaan Dan KebersihanDocument9 pagesBorang Keceriaan Dan KebersihanNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Kajian KesDocument17 pagesKajian KesNasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- Reka Bentuk Kajian BBM3413Document18 pagesReka Bentuk Kajian BBM3413Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet