Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recognize Locate Evaluate Communicate
Uploaded by
Rayvie MendejaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recognize Locate Evaluate Communicate
Uploaded by
Rayvie MendejaCopyright:
Available Formats
ARELLANO UNIVERSITY REVIEWER #2
Jose Rizal High School TOPIC: MEDIA LITERACY, INFORMATION LITERACY AND
Gov. W. Pascual Ave., Malabon City TECHNOLOGY LITERACY.
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
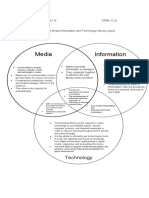
Literacy
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY
1st SEMESTER SY: 2021-2022 • Is the ability to identify, understand, interpret, create,
communicate and compute, using printed and written
REVIEWER #1 materials associated with varying contexts.
TOPIC: COMMUNICATION, MEDIA AND INFORMATION
Communication Media Literacy
• Is the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, and create
• is the act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or media in a variety of forms. It aims to empower you by
behaviors to express or exchange information, or to providing the knowledge and skills necessary to
express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone engage with both traditional and new technologies.
else.
• Communication is a process by which information is Characteristics of a Media Literate Person:
exchanged from sender to receiver through a common ACCESS ANALYZE OR CREATE
system of symbols, signs or behavior resulting in EVALUATE
interpretations of meaning on both ends.
To access means means having the To create means
the ability to ability to think being able to use
Media
recognize the critically about the media tools to
media needed accuracy, produce media
• refers to various means of communication, maybe and its availability credibility or content.
classified into traditional media and new media. for your use. evidence of bias in
• This Media are communication outlets or tools that are the context
used to store and deliver information. presented in
various media.
Information
Information Literacy
• refers to the message conveyed by a sender to its
recipient. • It is the ability to recognize when information is needed,
• Information is defined as knowledge or facts learned about and to locate, evaluate, and effectively communicate
a certain subject, situation or event. information in its various formats.
Characteristics of an Information Literate Person:
Types of communication RECOGNIZE LOCATE EVALUATE COMMUNICATE
1. Verbal
2. Nonverbal To recognize to locate To evaluate To communicate
3. Written means having means means means having the
4. Visual the ability to having the having the ability to share
identify ability to find ability to information
information reliable assess effectively.
MISINFORMATION DISINFORMATION when needed sources of whether the
This is information that is This Information is false and and to use it information information is
false but not created with the deliberately created to harm efficiently or locate true or fake.
intention of causing harm. a person, a social them when
group, an organization or a needed.
country.
Technology Literacy
It is the ability of an individual either working independently or
with others, to use technological tools responsibly,
appropriately, and effectively.
Characteristics of a Technology Literate Person:
SKILLFUL KNOWLEDGEABLE ENGAGE
In using of By knowing the basic By having the
digital tools principles in ability to
computing devices. responsibly
engage in
online
activities.
• Large electronic computers- i.e. EDSAC (1949) and
UNIVAC 1 (1951)
ARELLANO UNIVERSITY
Jose Rizal High School • Mainframe computers – i.e. IBM 704 (1960)
Gov. W. Pascual Ave., Malabon City • Personal computers – i.e. Hewlett-Packard 9100A
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT (1968), Apple 1 (1976)
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY
1st SEMESTER SY: 2021-2022 Information Age (1900s-2000s)
The Internet paved the way for faster communication and the
REVIEWER #3 creation of the social network. People advanced the use of
TOPIC: THE EVOLUTION OF TRADITIONAL TO NEW microelectronics with the invention of personal computers,
MEDIA mobile devices, and wearable technology. Moreover,
The Evolution of Traditional to New Media voice, image, sound, and data are digitalized. We are now living
The evolution of traditional to new media depict the records of in the information age. Examples:
the past on the progress of media technology. The development
of media helps people communicate and disseminate • Web browsers: Mosaic (1993), Internet Explorer
information in the fastest and efficient way. (1995)
• Blogs: Blogspot (1999), LiveJournal (1999),
Pre-Industrial Age (Before 1700s) WordPress (2003)
People discovered fire, developed paper from plants, and • Social networks: Friendster (2002), Multiply (2003),
forged weapons and tools with stone, bronze, copper, and iron. Facebook (2004)
Examples: • Microblogs: Twitter (2006), Tumblr (2007)
• Video: YouTube (2005)
• Papyrus in Egypt (25000 BC) • Augmented Reality / Virtual Reality
• Clay tablets in Mesopotamia (2400 BC) • Video chat: Skype (2003), Google Hangouts (2013)
• Cave paintings (35,000 BC) • Search Engines: Google (1996), Yahoo (1995)
• Acta Diurna in Rome (130 BC) • Portable computers- laptops (1980), netbooks (2008),
• Dibao in China (2nd Century) tablets (1993)
• Codex in the Mayan region (5th Century) • Smartphones
• Printing press using wood blocks (220 AD) • Wearable technology
• Cloud and Big Data
Industrial Age (1760s-1930s)
People used the power of steam, developed machine tools, REVIEWER #4
established iron production, and the manufacturing of various
TOPIC: TYPES OF MEDIA
products (including books through the printing press).
Examples: Media – are communication outlets or tools that are used to
store and deliver information. Also, the main means of mass
• Printing press for mass production (19th century)
• Newspaper- The London Gazette (1665) communications regarded collectively.
• Typewriter (1800)
Types of Media
• Telephone (1876)
• Motion picture photography/projection (1890) 1. Print Media involves the usage of a physical medium such
• Commercial motion pictures (1913) as paper and is printed and distributed by a publishing
• Motion picture with sound (1926)
company. Ex. Newspapers, magazines, books and
• Telegraph
pamphlets.
• Punch cards
2. Broadcast Media transmits information immediately to the
widest possible audience. Ex. Television, radio, speaker
Electronic Age (1930s-1980s)
and telephone.
The invention of the transistor ushered in the electronic age.
People harnessed the power of transistors that led to the 3. New Media is the type of media that uses the newest means
transistor radio, electronic circuits, and the early computers. In of communication, digital technology. Internet is the main
this age, long distance communication became more
gateway for accessing such type of media and information.
efficient. Examples:
Ex. Blogs, online articles and social media.
• Transistor Radio
• Television (1941)
REVIEWER #6
ARELLANO UNIVERSITY TOPIC: MEDIA AND INFORMATION LANGUAGES
Jose Rizal High School In Media and Information Languages the information is
Gov. W. Pascual Ave., Malabon City
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT distributed not only in the format of words or phrases. But also,
the information can be delivered through the presence of
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY
1st SEMESTER SY: 2021-2022 symbols, codes, pictures or videos.
REVIEWER #5
TOPIC: MEDIA AND INFORMATION SOURCES Language - is the method of human communication, either
spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structures
Media and Information Sources and conventional way.
Information can be access anywhere as long as there is
Media Language - are codes, convention, formats, symbols
communication. But these sources can present information
differently. and narrative structures that indicate the meaning of media
3 Main Sources of Information messages to an audience.
1. Indigenous knowledge – Local and indigenous knowledge refers
Media Codes – is a system of signs that when put together
to the understandings, skills and philosophies developed by
societies with long histories of interaction with their natural creates a meaning.
surroundings. For rural and indigenous people, local knowledge
3 Types of Media Codes
informs decision-making about fundamental aspects of day-to-
day life. -UNESCO 1. Symbolic codes - Shows what is beneath the surfaces
Main Characteristics of indigenous knowledge are the following of what we see. It includes the setting, mise en scene,
• Oral tradition of communication acting and color.
• Store information in memories
• Information exchange is face-to-face 2. Written codes – are the formal written language used
• Information is contained within the border of the in a media product. written codes include font style and
community font size, captions, choice of words and emphasis of
2. Library – a building or a room containing collections of books, words.
periodicals, and sometimes films and recorded music for people
3. Technical codes are all the ways in which equipment
to read, borrow, or refer to.
is used to tell the story in a media it includes camera
The following are some of the reading materials that are available in
work, audio or sound, lighting and editing.
your school library;
• Books – which contains in depth explanation about a
certain topic. Also we have
Media Conventions – refers to a standard or norm that acts as
• Scholarly journals – which information are updated and
highly specific for scholars and researchers. rule governing behavior and are generally established and
• Magazines – a broad summaries of issues for general accepted ways of doing something.
audiences.
• Newspaper –are updated national and regional information 3 types of conventions
for a general audience published daily.
1. Form conventions – certain ways we expect types of
3. The Internet – Is a network of networks that consists of millions
of private, public, academic, business and government networks, media’s codes to be arranged. In films, there should be
of local to global scope, that are linked by a broad array of a title at the beginning and credits at the end.
electronic and optical networking technologies. Newspapers have a masthead, headline, and different
sections.
RAVAT
5 things that we need to consider to determine that the 2. Story conventions – are common narrative structures
information is credible. and understandings that are common in story telling
1. Check the Reliability media product.
2. Know the Accuracy
3. Genre Conventions - are common use of tropes,
3. Value of the source
characters, settings or themes in a particular type of
4. Authority of the Source
5. Timeliness medium. Genre conventions are closely linked with
audience expectations. It can be formal or thematic
You might also like
- Building trust: How to establish empathic relations when designing with peopleFrom EverandBuilding trust: How to establish empathic relations when designing with peopleNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: COM-CON CHECK Comparison ContrastDocument1 pageActivity 3: COM-CON CHECK Comparison ContrastKeunNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Media LiteracyDocument8 pagesWeek 3 Media LiteracyGrace BullequeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Media LiteracyDocument8 pagesWeek 3 Media LiteracyGrace BullequeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (1) - Introduction To MILDocument20 pagesLesson 1 (1) - Introduction To MILchristina burlazaNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument3 pagesMil ReviewerTravis AmadoNo ratings yet
- Blue and Yellow Introduction To Media and Information Literacy PresentationDocument12 pagesBlue and Yellow Introduction To Media and Information Literacy PresentationMAY GALESNo ratings yet
- Medinfolit 1Document7 pagesMedinfolit 1JASIS JULIA NOELYN V.No ratings yet
- MIL - Lesson 1Document3 pagesMIL - Lesson 1Kim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument2 pagesComparisonMissy Artica100% (10)
- PT2 JironDocument2 pagesPT2 JironJennefer Gudao AranillaNo ratings yet
- Mill L LLLLL LLLLLDocument2 pagesMill L LLLLL LLLLLjhonernie.official.onceNo ratings yet
- PaprintngapremwahDocument1 pagePaprintngapremwahLanz LawrenceNo ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer v1 For Grade 12Document8 pagesMIL Reviewer v1 For Grade 12Kienstel GigantoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mil PDFDocument17 pagesReviewer in Mil PDFJulius Cesar CuderaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument2 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyKarylle Joy TerezoNo ratings yet
- Fake or NOT?: Literacy: LiteracyDocument14 pagesFake or NOT?: Literacy: LiteracymariancantalNo ratings yet
- Mil Week 2Document15 pagesMil Week 2Shiela FernandoNo ratings yet
- Triple Venn Diagram MilDocument1 pageTriple Venn Diagram MilSteven PascualNo ratings yet
- MINLIT1-Kurien - ESGUERRA, Angelene3 PDFDocument1 pageMINLIT1-Kurien - ESGUERRA, Angelene3 PDFAngelene EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Media and Information LiteracyDocument20 pagesIntroduction of Media and Information LiteracyJay JayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1christian renz gallardoNo ratings yet
- MIL Lesson 1 4 PPT 1 3Document18 pagesMIL Lesson 1 4 PPT 1 3Jake MalabananNo ratings yet
- Media Information LiteracyDocument13 pagesMedia Information LiteracyEunice DaquiuagNo ratings yet
- (1stSem1stQtr2ndWeek) Lesson1 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument13 pages(1stSem1stQtr2ndWeek) Lesson1 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyMARVIN GUIANGNo ratings yet
- MIL Prelims DEDocument6 pagesMIL Prelims DEKenken GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram - Act#3: QuestionsDocument2 pagesVenn Diagram - Act#3: QuestionsHannah Marie Gatpolintan100% (2)
- 3Q L1 Introduction To Media Literacy 1Document1 page3Q L1 Introduction To Media Literacy 1shanehfernandez18No ratings yet
- Mercado, Aubrey M. (ABM205-KOTLER) MIL Activity #2Document1 pageMercado, Aubrey M. (ABM205-KOTLER) MIL Activity #2Roma MalasarteNo ratings yet
- Intro To MIL and Evolution of MediaDocument36 pagesIntro To MIL and Evolution of MediaririNo ratings yet
- SHS MIL Week 2 - CHRISTINA NAMOC - FINALDocument9 pagesSHS MIL Week 2 - CHRISTINA NAMOC - FINALmary joy aquinoNo ratings yet
- Q1 W2 Media Literacy Information Literacy and Technology LiteracyDocument5 pagesQ1 W2 Media Literacy Information Literacy and Technology LiteracyJunrey BelandoNo ratings yet
- MIL AssignmentDocument1 pageMIL AssignmentJlln MgnkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-in-MIL 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesReviewer-in-MIL 3rd QuarterBella PurisimaNo ratings yet
- 001 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument28 pages001 Introduction To Media and Information Literacyrecquelle danoNo ratings yet
- 02 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument36 pages02 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyJuicy SaniatanNo ratings yet
- Mil - Shs - q1 - w2 - Similarities and Differences Among Media - Information and Digital LiteracyDocument12 pagesMil - Shs - q1 - w2 - Similarities and Differences Among Media - Information and Digital LiteracyDONNAVIE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Mil Og ReviewerDocument6 pagesMil Og ReviewerMarian ColoradoNo ratings yet
- 02 A Introduction-to-Media-and-Information-LiteracyDocument24 pages02 A Introduction-to-Media-and-Information-LiteracyKenDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Briz MilDocument2 pagesBriz MilRaven FosterNo ratings yet
- White Red Simple Marketing Mix Venn DiagramDocument1 pageWhite Red Simple Marketing Mix Venn DiagramAnthonyalennNo ratings yet
- 3Q L2 Codes and ConventionsDocument8 pages3Q L2 Codes and Conventionsshanehfernandez18No ratings yet
- SICRITDocument26 pagesSICRITShann Brenan DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Q1 W2 Media Literacy Information Literacy and Technology LiteracyDocument5 pagesQ1 W2 Media Literacy Information Literacy and Technology LiteracyGreg Alvarez100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Mil Module 2 Lesson 1Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Mil Module 2 Lesson 1Yuan Andrei SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracySupport JYP Loud TraineesNo ratings yet
- Activity 21stDocument1 pageActivity 21stKhafzael VlazdemorNo ratings yet
- APPLECASDocument1 pageAPPLECAScas786715No ratings yet
- Reviewer For MilDocument2 pagesReviewer For MilHAZEL SANDRONo ratings yet
- MIL - Quarter 3 - Module 2Document7 pagesMIL - Quarter 3 - Module 2Darlene Dacanay David100% (1)
- Print Lesson 2 q1Document13 pagesPrint Lesson 2 q1Dorie Fe ManseNo ratings yet
- Mil. JoannaDocument3 pagesMil. JoannaJhanniah PinedaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media LiteratureDocument1 pageIntroduction To Media LiteratureMalabuyoc, Jullienne Denice D.No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument16 pages1 Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyOrange GriffinNo ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer Grad 12 (1st Quarter)Document4 pagesMIL Reviewer Grad 12 (1st Quarter)gallegos.elijahjerome.belenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information LiteracyAnjamae Miso Miramar PabuaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Venn Diagram PDFDocument1 pageQ3 Venn Diagram PDFJhanniah PinedaNo ratings yet
- Hobby PDFDocument13 pagesHobby PDFLorenzo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Mil Notes in Quarter 1Document6 pagesMil Notes in Quarter 1InfiniteNo ratings yet
- MITECDocument5 pagesMITECKate LlanetaNo ratings yet
- 3 Transitivity Analysis of Selected Privilege Speeches of Senator Miriam Defensor SantiagoDocument23 pages3 Transitivity Analysis of Selected Privilege Speeches of Senator Miriam Defensor SantiagoMatt OniaNo ratings yet
- CM 654 - Quality Management Processes Plan Quality Management - Group-1 Module-2Document117 pagesCM 654 - Quality Management Processes Plan Quality Management - Group-1 Module-2leepatrickbanez0% (1)
- Banner, Brochure, Leaflet, and PhampletDocument20 pagesBanner, Brochure, Leaflet, and Phampletnurul husniahNo ratings yet
- MGT 2201 - Assignment 1Document3 pagesMGT 2201 - Assignment 1YousefNo ratings yet
- Doa NP 05 16 BS Fcom Rev 03 May PDFDocument3 pagesDoa NP 05 16 BS Fcom Rev 03 May PDFAmine ChabchoubNo ratings yet
- Baking Science and Technology, Volume 1 by E.J Pyler: Read Online and Download EbookDocument6 pagesBaking Science and Technology, Volume 1 by E.J Pyler: Read Online and Download EbookCamilo Higuera0% (1)
- Author 1. Florentino Ayson, Et. AlDocument2 pagesAuthor 1. Florentino Ayson, Et. AlMontarde, Hazel MaeNo ratings yet
- BAESystemsDocument12 pagesBAESystemssri chandanaNo ratings yet
- Walmart Failure in GermanyDocument4 pagesWalmart Failure in GermanyAnimesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Performance Linked Incentive Schemes of Icici and SbiDocument22 pagesPerformance Linked Incentive Schemes of Icici and Sbikaran_tiff100% (3)
- Ivey MSC Western UniversityDocument16 pagesIvey MSC Western UniversityDyanChenNo ratings yet
- Hoppe Brochure Motion-ControlDocument15 pagesHoppe Brochure Motion-ControlSerhiiNo ratings yet
- Upper Intermediate: KeynoteDocument2 pagesUpper Intermediate: KeynoteLexieNo ratings yet
- Orleans Jail Jan 19 ReportDocument111 pagesOrleans Jail Jan 19 ReportEthan BrownNo ratings yet
- M.Tech PPTDocument11 pagesM.Tech PPTDarkNo ratings yet
- Electric ReportDocument33 pagesElectric ReportAkshay bypNo ratings yet
- 43.0 - Temporary Structures v3.0 EnglishDocument14 pages43.0 - Temporary Structures v3.0 Englishchumairabbas100% (1)
- CRID PowerPoint Slides - Aviation Revenue Generation Presentation - 3 Lean MGTDocument58 pagesCRID PowerPoint Slides - Aviation Revenue Generation Presentation - 3 Lean MGTTobzNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Parenting SkillsDocument12 pagesEnhancing Parenting Skillsapi-26018051No ratings yet
- Effects of Outdoor Advertising: Does Location Matter?: Rick T. WilsonDocument25 pagesEffects of Outdoor Advertising: Does Location Matter?: Rick T. Wilsondhrruv kkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management 2 C Assignment QuestionsDocument3 pagesEngineering Management 2 C Assignment Questionsabhinav kumarNo ratings yet
- DMK ACHIEVEMENT PDFDocument154 pagesDMK ACHIEVEMENT PDFMakizhnan மகிழ்நன்No ratings yet
- Exam 3890Document36 pagesExam 3890Tauseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Edi GarmentDocument18 pagesEdi GarmentPrabal Kumar MajumdarNo ratings yet
- So You've Joined Toastmasters. Now What?: New Member OrientationDocument41 pagesSo You've Joined Toastmasters. Now What?: New Member OrientationDolgorsuren Tsogbadrakh100% (1)
- Business Plan Part 3Document5 pagesBusiness Plan Part 3Erika NietoNo ratings yet
- National Steel Corporation V. Court of Appeals G.R. No. 112287 December 12, 1997 Panganiban, J. DoctrineDocument12 pagesNational Steel Corporation V. Court of Appeals G.R. No. 112287 December 12, 1997 Panganiban, J. DoctrineIt'sRalph MondayNo ratings yet
- Mba-110 Full Solved AssementDocument4 pagesMba-110 Full Solved AssementAnkitKumarJha33% (3)
- Biodiversity & Intellectual Property RightsDocument34 pagesBiodiversity & Intellectual Property RightsSushil JindalNo ratings yet
- Aula II - Cognatos e PrefixosDocument12 pagesAula II - Cognatos e PrefixosClaudia MesquitaNo ratings yet