Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction and Terminologies - NOTES 1
Uploaded by
Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction and Terminologies - NOTES 1
Uploaded by
Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction and Terminologies Population and sample
DSILYTC- FIRST MEETING
Population
Purpose of Statistics - Consists of the totality of all the
- To provide information elements or entities from which
- To provide comparisons you want to obtain an
- To help discern relationships information
- To aid in decision making
- To estimate unknown Sample
quantities - A subset of the population
- To justify claims or assertions
- To predict future outcomes A Car Company wants to know the
top 3 features of cars that are most
Statistics important to licensed drivers in the
- A science that deals with the Philippines. The Company
collection, organization, telephones 100 Alabang residents
presentation, analysis, and and asks a series of questions
interpretation of data
Analyze- extraction of data 1) Which of these is the
population in this survey?
Branches of Statistics Justify your answer.
(a) all licensed drivers in
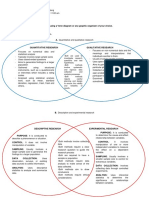
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Alabang
- Consists of methods (b) all residents in Alabang
concerned with collection, (c) all licensed drivers in the
organization, summarization, Philippines
and presentation of a set of (d) all residents of the
data Philippines
INFERENTIAL STATISTICS 2) Which of these is the
- Comprised of those methods sample in this survey? Justify
concerned with making your answer.
predictions or inferences about (a) 100 licensed drivers in
an entire population based on Alabang
information provided by the (b) all licensed drivers in
sample Alabang
(c) 100 licensed drivers in
the Philippines
(d) all licensed drivers in the Qualitative (Categorical)
Philippines - Variables variables that
indicate what kind of a given
CENSUS AND SURVEY characteristic an individual,
object, or event possesses.
Census
- the process of collecting Quantitative (Numerical) Variables
information from the population - variables that indicate how
much a given characteristic an
Survey individual, object, or event
- the process of collecting possesses
information from the sample
Types of quantitative variables
PARAMETER AND STATISTIC Discrete Variables
Paramater - variables whose values are
- a summary or numerical obtained through the process
measure used to describe a of counting
population Continuous Variables
- variables whose values are
Statistic obtained through the process
- a summary or numerical of measuring
measure used to describe a Dependent
sample - a variable which is affected by
another variable
CONSTANT - Ex. “test scores” is dependent
- A characteristic or property of on number of hours spent in
a population or sample which studying, IQ, attitude towards
makes the members similar to studying, etc…
each other Independent
- a variable which affects the
VARIABLES dependent variable
- any characteristic or - Ex. “number of hours spent in
information measurable or studying” affects test scores
observable on every element
of the population or sample
Scales of measurement of
variables
Nominal
- Variables whose values are
simply labels or names or
categories without any explicit
or implicit ordering of the
labels;
- Lowest level of measurement
known as categorical scale.
Ordinal
- Variables whose values are
simply labels or names or
categories with an implied
ordering in these labels;
- Ranking can be done on the
data
- Distance between two labels
can not be determined.
Interval
- Variables whose values can be
ordered and distance between
any two labels are of known
size;
- Always numeric and have no
true zero point.
Ratio
- Variables whose values have
all the properties of the interval
scale and the ratio of two
values is meaningful
- Has a true zero point;
- Highest level of measurement
You might also like
- Introduction To Business Statistics Through R Software: SoftwareFrom EverandIntroduction To Business Statistics Through R Software: SoftwareNo ratings yet
- Eda ReviewerDocument7 pagesEda ReviewerCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics ReviewerDocument2 pagesBusiness Statistics ReviewerCecilia VillarinoNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Its Role in Psychological ResearchDocument2 pagesStatistics and Its Role in Psychological ResearchAlexandra San PedroNo ratings yet
- Stats LectureDocument8 pagesStats LectureCathleen Drew TuazonNo ratings yet
- Stats Vid Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesStats Vid Lecture NotesPeaches PHNo ratings yet
- Notes On Engineering Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesNotes On Engineering Data Analysismae hope bangloyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Define The Given Statistical Terms BelowDocument2 pagesDefine The Given Statistical Terms BelowMT1-0622 LEE JIA HUINo ratings yet
- Introduction - Sesh 1Document17 pagesIntroduction - Sesh 1Eunice EstillerNo ratings yet
- Intro STAT POWER POINT 1Document28 pagesIntro STAT POWER POINT 1Nadezhda EscribanoNo ratings yet
- MATH 103 Module 1 - Statistics IntroductionDocument30 pagesMATH 103 Module 1 - Statistics IntroductionjexiwNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa Stats Q1Document4 pagesReviewer Sa Stats Q1sevketzuuu97No ratings yet
- Statistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringDocument5 pagesStatistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringLaila Joshbeth SandovalNo ratings yet
- Basic Business Statistics: Introduction and Data CollectionDocument33 pagesBasic Business Statistics: Introduction and Data CollectionMeiyati JamalNo ratings yet
- STATANL1STDocument5 pagesSTATANL1STandrea.huerto0730No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Basic StatisticsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Basic StatisticsRoxette Turingan TalosigNo ratings yet
- BUS 232 - Revision Lectures: Data and Data SetsDocument17 pagesBUS 232 - Revision Lectures: Data and Data SetsPame CorralNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To StatisticsJORENCE PHILIPP ENCARNACIONNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH 2nd CycleDocument4 pagesRESEARCH 2nd CycleJoana SamiaNo ratings yet
- Ie-Pc 121 Notes Quiz 1Document1 pageIe-Pc 121 Notes Quiz 1Andrea PepitoNo ratings yet
- Stats ReviewerDocument4 pagesStats ReviewerSheena DumayNo ratings yet
- ALAGOS - DEONNY KRIS - MMW - INTRODUCTION OF DATA MANAGEMENTDocument87 pagesALAGOS - DEONNY KRIS - MMW - INTRODUCTION OF DATA MANAGEMENTJairus Ivan MuchadaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods For Management: Term II 4 Credits MGT 408Document49 pagesQuantitative Methods For Management: Term II 4 Credits MGT 408Sandeep VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument14 pagesSTATISTICSJezelle Lois LacanariaNo ratings yet
- OACC4 - Module 1Document28 pagesOACC4 - Module 1Justine VersoNo ratings yet
- Collection Organization Presentation Analysis InterpretationDocument5 pagesCollection Organization Presentation Analysis InterpretationPhoebe Joane Paquiabas - MendezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Quiz StatisticsDocument7 pagesReviewer in Quiz StatisticsJohnallenson DacosinNo ratings yet
- Kemeng ReviewerDocument8 pagesKemeng ReviewerVinabie PunoNo ratings yet
- Math III - StatisticsDocument65 pagesMath III - StatisticsAndrea Hidalgo Ruiz100% (1)
- Basic Statistics 18 19 20Document6 pagesBasic Statistics 18 19 20Mirage LeeNo ratings yet
- Nature of StatisticsDocument5 pagesNature of StatisticsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics ReviewerDocument5 pagesBusiness Analytics ReviewerVernie N. PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1khxxdxrNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerCarl Johnave Manigbas MonzonNo ratings yet
- Math 4Document4 pagesMath 4Arceta, Alia Mae M.No ratings yet
- Research: Outcome Evaluation Cost-Effectiveness EvaluationDocument2 pagesResearch: Outcome Evaluation Cost-Effectiveness EvaluationJan Earl Darwin NazNo ratings yet
- Binder EdaDocument5 pagesBinder Edapalacioaya28No ratings yet
- PAS 111 Week 1Document3 pagesPAS 111 Week 1Franz PampolinaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Statistics (Notes)Document9 pagesPsychological Statistics (Notes)Faith Hannah OroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics: Lecturer Rubaiyat Mahjabeen Dept. of Economics, Fass, BupDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Statistics: Lecturer Rubaiyat Mahjabeen Dept. of Economics, Fass, BupRafee HossainNo ratings yet
- Types of AssessmentDocument5 pagesTypes of AssessmentJi YuNo ratings yet
- Stat Lesson 1Document20 pagesStat Lesson 1Indiana PremiumNo ratings yet
- Statistics: by Sir Lee KnowsDocument77 pagesStatistics: by Sir Lee KnowsEloiza Lajara RamosNo ratings yet
- Natividad Arlene Activity 2Document1 pageNatividad Arlene Activity 2Arlene Magalang NatividadNo ratings yet
- 605 CH 3 Methodology ADocument10 pages605 CH 3 Methodology Amoma3175No ratings yet
- Handouts 1 ENDATA130 Introduction To Data AnalysisDocument52 pagesHandouts 1 ENDATA130 Introduction To Data AnalysisCharle CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods in Management: Term II 4 Credits MGT 408 DAY - 2Document103 pagesQuantitative Methods in Management: Term II 4 Credits MGT 408 DAY - 2sudheer gottetiNo ratings yet
- MMW NotesDocument10 pagesMMW Noteslpanela.21No ratings yet
- 2ND TERM - Statistics & ProbabilityDocument19 pages2ND TERM - Statistics & ProbabilityefwefewfNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument21 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityKIRIL EytiNo ratings yet
- PR2 Final ReviewerDocument9 pagesPR2 Final ReviewerKristine Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year - CBMEDocument13 pages2nd Year - CBMEHo Sol JungNo ratings yet
- StatisticDocument13 pagesStatisticnandaaungwdnNo ratings yet
- Norm-Referenced Testing and Assessment:: NormsDocument3 pagesNorm-Referenced Testing and Assessment:: NormsAdam VidaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statistics ReviewerDocument12 pagesElementary Statistics ReviewerChristian ChavezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document44 pagesChapter 1hazriq hakimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- Glossary Quality Assurance TerminologyDocument17 pagesGlossary Quality Assurance TerminologyAditya JainNo ratings yet
- Hypothesistesting Notes5Document6 pagesHypothesistesting Notes5Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression Analysis - Notes8Document3 pagesMultiple Regression Analysis - Notes8Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation - Notes 2Document4 pagesData Presentation - Notes 2Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression - Notes6Document3 pagesCorrelation and Regression - Notes6Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques Notes4Document3 pagesSampling Techniques Notes4Ma. Christina Isabel EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pages3.5 Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Karush Kuhn TuckerDocument14 pagesKarush Kuhn TuckerAVALLESTNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics AssignmentDocument4 pagesBusiness Statistics AssignmentArun NalamaraNo ratings yet
- Empirical ResearchDocument2 pagesEmpirical ResearchAnonymous 2idBUjHi3No ratings yet
- 1MM 17 T00 Orientation HandoutDocument13 pages1MM 17 T00 Orientation HandoutAlyssaNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc-CS Stas-1 & 2 SyllabusDocument10 pagesF.Y.B.Sc-CS Stas-1 & 2 SyllabusRahul BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Analytical ChemistryDocument3 pagesThe Nature of Analytical ChemistryJULIA AUDREY PERALTANo ratings yet
- Least Squares Curve Fitting: Numerical MethodsDocument39 pagesLeast Squares Curve Fitting: Numerical MethodseyassadailehNo ratings yet
- MIT18 S096F13 CaseStudy7Document45 pagesMIT18 S096F13 CaseStudy7TheoNo ratings yet
- Taylor SeriesDocument3 pagesTaylor SeriesiamheretohelpNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 PDFDocument1 pageTutorial Sheet 1 PDFKaushik MishraNo ratings yet
- Base Stock PolicyDocument20 pagesBase Stock PolicyKaustubh PotnisNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Integration Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pages5.4 Integration Trigonometric Functionshariz syazwanNo ratings yet
- STAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFDocument3 pagesSTAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFeccentricftw4No ratings yet
- Exponential Smoothing Example:: Single Years Quarter Period Sales Avg A (T) /avgDocument6 pagesExponential Smoothing Example:: Single Years Quarter Period Sales Avg A (T) /avgchikomborero maranduNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Model Predictive Control-MorariDocument632 pagesNonlinear Model Predictive Control-MorarifenasikarimNo ratings yet
- Eee3001 Control-Systems Eth 1.0 37 Eee3001Document3 pagesEee3001 Control-Systems Eth 1.0 37 Eee3001dhoniNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Hyperbolic Functions PDFDocument7 pagesDerivative of Hyperbolic Functions PDFStevenzel Eala Estella100% (1)
- 5.2.1 Bayesian Linear RegressionDocument9 pages5.2.1 Bayesian Linear RegressionFrancisco JoséNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lectures Pmd-Pro-Guide-2nd-Edition - 1579881770Document205 pagesNotes For Lectures Pmd-Pro-Guide-2nd-Edition - 1579881770benNo ratings yet
- CIMA Strategic Analysis ToolsDocument16 pagesCIMA Strategic Analysis ToolsWYNBAD100% (1)
- ELEMSTADocument13 pagesELEMSTAWeslie VillejoNo ratings yet
- Modelling Functions Summative JANUARY 2016: Goal of The AssignmentDocument4 pagesModelling Functions Summative JANUARY 2016: Goal of The AssignmentHarjot DhillonNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and The Talent Management ProcessDocument25 pagesJob Analysis and The Talent Management ProcesssheryzaidNo ratings yet
- Random Motors Project: Rocinate 36Document2 pagesRandom Motors Project: Rocinate 36Keshav Sarda75% (12)
- Chaos PresentationDocument26 pagesChaos PresentationSiana Alinda AniseNo ratings yet
- 151 Implicit Differentiation Second DerivativesDocument7 pages151 Implicit Differentiation Second DerivativesEsa KhanNo ratings yet
- B-Spline Curves: Navsheen Mirakhur 02111604415 Semester 3rdDocument14 pagesB-Spline Curves: Navsheen Mirakhur 02111604415 Semester 3rdYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDE TextbookDocument392 pagesPDE Textbooksujit21kumarNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Decision Models: IntroductionDocument372 pagesOptimization and Decision Models: Introductionkellyanne MutwiriNo ratings yet