Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bab 2
Bab 2
Uploaded by
Brashella MadiliousOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bab 2
Bab 2
Uploaded by
Brashella MadiliousCopyright:
Available Formats
DBM 2643 PENGURUSAN OPERASI
BAB 2
Strategi Lokasi
Disediakan oleh; C. Brashella Madilious
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-1 07458
Outline
KEPENTINGAN LOKASI
FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI
KEPUTUSAN LOKASI
Produktiviti pekerja
Kadar Pertukaran dan risiko mata wang
Kos
Tingkah Laku
Hampir dengan Pasaran
Hampir dengan Pembekal
Hampir dengan Pesaing (Clustering)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-2 07458
Outline – samb..
KAEDAH PENILAIAN ALTERNATIF
LOKASI
The Factor-Rating Method
Location Break-Even Analysis
Center-of-Gravity Method
The Transportation Method
STRATEGI LOKASI PERKHIDMATAN
How Hotel Chains Select Sites
The Telemarketing Industry
Geographic Information Systems
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-3 07458
Objektif pembelajaran
Selepas menghabiskan bab ini, anda boleh:
Kenalpasti atau takrifkan:
Objektif strategi lokasi
Isu-isu lokasi antarabangsa
Clustering
Geographic Information Systems
Terangkan atau jelaskan:
Tiga kaedah menyelesaikan masalah lokasi
Factor-rating method
Locational breakeven analysis
Center -of-gravity method
terangkan faktor yang mempengaruhi keputusan
lokasi
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-4 07458
Federal Express
Kelebihan :
Membolehkan perkhidmatan kepada banyak
lokasi dengan kapal yang sikit
Membolehkan pemadanan kapal dengan
muatan
Mengurangkan kesilapan pengendalian dan
tangguhan transit disebabkan kawalan penuh
bungkusan dari tempat pemungutan dan
penghantaran
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-5 07458
Keputusan Lokasi Industri
Fokus Kos
Lokasi merupakan faktor kos
Affects shipping &
production costs (e.g., labor)
Costs vary greatly between
locations
© 1995 Corel Corp.
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-6 07458
Keputusan Lokasi Perkhidmatan
Fokus Keuntungan
Lokasi merupakan faktor keuntungan
Affects amount of
customer contact
Affects volume of
business
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-7 07458
Secara amnya- Keputusan Lokasi
Keputusan jangka masa panjang
Sukar ditarikbalik
Mempengaruhi kos berubah & tetap
Transportation cost
As much as 25% of product price
Other costs: Taxes, wages, rent etc.
Objektif: Memaksimumkan faedah lokasi kepada firma
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-8 07458
Rangkaian Keputusan Lokasi
Daerah/komuniti
Negara
Tapak
© 1995
Corel Corp. © 1995 Corel Corp.
© 1995
Corel Corp.
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-9 07458
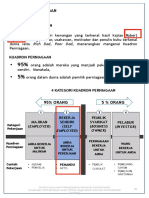
Faktor Mempengaruhi Keputusan Lokasi
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-10 07458
Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Keputusan
Lokasi
Produktiviti pekerja
Kadar Pertukaran dan risiko mata wang
Kos
Tingkah Laku
Hampir dengan Pasaran
Hampir dengan Pembekal
Hampir dengan Pesaing (Clustering)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-11 07458
Kaedah Pengukuran Lokasi
Factor-rating method
Locational break-even
analysis
Center of gravity method
Transportation model
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-12 07458 © 1995 Corel Corp.
Faktor Mempengaruhi Pemilihan Lokasi
Kos buruh (including wages, unionization,
productivity)
Kesediaan buruh (including attitudes, age,
distribution, and skills)
Berhampiran dengan bahan mentah dan pembekal
Berhampiran dengan pasaran
Polisi kewangan kerajaan (including incentives, taxes,
unemployment compensation)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-13 07458
Faktor Mempengaruhi Pemilihan Lokasi
– samb…
Peraturan persekitaran
Utiliti (including gas, electric, water, and
their costs)
Kos tapak (including land, expansion,
parking, drainage)
Kesediaan pengangkutan (including rail, air,
water, and interstate roads)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-14 07458
Faktor Mempengaruhi Pemilihan Lokasi
– samb…
Isu-isu kualiti hidup dalam komuniti (including all levels of education,
cost of living, health care, sports, cultural activities, transportation,
housing, entertainment, religious facilities)
Pertukaran asing termasuklah kadar dan kestabilan
Kualiti kerajaan (including stability, honesty, attitudes toward new
business - whether overseas or local)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-15 07458
Langkah-langkah
Kaedah Factor Rating
Senaraikan faktor yang relevan
Berikan pemberat kepada setiap faktor (such as 0 –
1)
Bangunkan skala setiap faktor (such as 1 – 100)
Skor setiap lokasi menggunakan faktor skala
Darabkan skor dengan pemberat untuk setiap faktor
& jumlahkan
Pilih lokasi dengan jumlah skor maksimum
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-16 07458
Kaedah Factor-Rating
Teknik lokasi yang banyak digunakan
Berguna untuk lokasi perkhidmatan &
industri
Kadar lokasi menggunakan faktor
Tangible (quantitative) factors
Example: Short-run & long-run costs
Intangible (qualitative) factors
Example: Education quality, labor skills
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-17 07458
Locational Break-Even Analysis
Kaedah analisis kos-kuantiti digunakan untuk
pemilihan lokasi industri
Langkah-langkah
Menentukan kos tetap & berubah untuk setiap lokasi
Plotkan jumlah kos untuk setiap lokasi (Cost on vertical axis,
Annual Volume on horizontal axis)
Pemilihan lokasi dengan jumlah kos terendah untuk jangkaan
kuantiti pengeluaran
Must be above break-even
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-18 07458
Kaedah Center of Gravity
Cari lokasi bagi single distribution center yang
memberi perkhidmatan kepada beberapa destinasi
Digunakan dalam perkhidmatan
Pertimbangan
Lokasi bagi destinasi yang wujud
Jumlah yang perlu dihantar
Jarak penghantaran (kos)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-19 07458
Transportation Model
Hitungkan jumlah yang perlu dihantar dari
beberapa sumber kepada beberapa destinasi
Digunakan bagi lokasi perindustrian
Sejenis linear programming model
Objective: Minimize total production
& shipping costs
Constraints
Production capacity at source (factory)
Demand requirement at destination
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-20 07458
Worldwide Distribution of
Volkswagens and Parts
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-21 07458
Components of Volume and
Revenue for a Service Firm
1. Purchasing power of customer drawing area
2. Service and image compatibility with demographics of the
customer drawing area
3. Competition in the area
4. Quality of the competition
5. Uniqueness of the firm’s and competitor’s locations
6. Physical qualities of facilities and neighboring businesses
7. Operating policies of the firm
8. Quality of management
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-22 07458
Location Strategies – Service vs. Industrial
Service/Retail/Professional Goods-Producing Location
Revenue Focus Cost Focus
Tangible costs
Volume/revenue Transportation cost of raw
Drawing area, purchasing materials
power Shipment cost of finished goods
Competition; Energy and utility cost; labor;
advertising/pricing raw material; taxes, etc.
Physical quality Intangible and future costs
Parking/access; security/ Attitude toward union
lighting; appearance/image Quality of life
Cost determinants Education expenditures by state
Rent Quality of state and local
government
Management caliber
Operations policies (hours,
wage rates)
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-23 07458
Location Strategies –Service vs. Industrial
Service/Retail/Professional Techniques Goods Producing Location
Regression models to determine Techniques
importance of various factors Linear Programming
Factor-rating method (Transportation method)
Traffic counts Factor-rating method
Demographic analysis of drawing
area Locational breakeven
Purchasing power analysis of analysis
drawing area Crossover charts
Center of gravity method
Geographic information systems
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-24 07458
Location Strategies –Service vs. Industrial
Service/Retail/Professional Goods-Producing Location
Assumptions Assumptions
Location is a major Location is a major
determinate of revenue determinate of cost
Most major costs can be
High customer-contact issues identified explicitly for
are critical each site
Costs are relatively constant Low customer contact
for a given area; therefore, the allows focus on identifiable
costs
revenue function is critical Intangible costs can be
evaluated
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-25 07458
Major Methods of Solving Location
Problems
Weighted methods which:
Assign weights and points to various factors
Determine tangible costs
Investigate intangible costs
Center of Gravity Method
Find best distribution center location
Location breakeven methods
Special case of breakeven analysis
Transportation method
A specialized linear programming method
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-26 07458
Telemarketing and Internet
Industries
Memerlukan kontek secara bersemuka dengan
pelanggan (atau pekerja)
Memperkenalkan perspektif baru terhadap masalah
lokasi
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-27 07458
Geographic Information Systems
Peralatan baru untuk membantu dalam analisis lokasi
Membolehkan kombinasi bagi banyak faktor/had
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-28 07458
Sekian
Terima kasih
© 2004 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J.
8-29 07458
You might also like
- Slide Taklimat KKMDocument62 pagesSlide Taklimat KKMHasrulAbRahman100% (1)
- Proses Penyediaan Spesifikasi: Bahagian Perolehan Kerajaan Kementerian Kewangan MalaysiaDocument39 pagesProses Penyediaan Spesifikasi: Bahagian Perolehan Kerajaan Kementerian Kewangan MalaysiaAhmad FauzanNo ratings yet
- TOT MyPerformance - Submodul SKUDocument73 pagesTOT MyPerformance - Submodul SKUMat idi100% (1)
- Nota Exam PSVDocument35 pagesNota Exam PSVSyamil DzulfidaNo ratings yet
- Case Study MMDocument18 pagesCase Study MMIrfan Harraz100% (1)
- PENGURUSAN BAHAN Buruh Overhed Part B OverhedDocument8 pagesPENGURUSAN BAHAN Buruh Overhed Part B OverhedFrank Chay100% (1)
- Kos OverheadDocument18 pagesKos OverheadNoor Lela Yahaya100% (1)
- Bab 10 - Perancangan Layout PabrikDocument28 pagesBab 10 - Perancangan Layout PabrikRafael sipayungNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Kau 2 4 Aspek AuDocument18 pagesBahan Ajar Kau 2 4 Aspek AuHendri SetyabudiNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas K2 PPAVDocument7 pagesNota Ringkas K2 PPAVNur Ainin Kamilia Binti KamalNo ratings yet
- Bdap Asas Perakaunan Pen Gurus AnDocument14 pagesBdap Asas Perakaunan Pen Gurus Ananbu_331100% (1)
- Tugasan MA 10Document3 pagesTugasan MA 10sabahankafahNo ratings yet
- DPK Chapter 7Document28 pagesDPK Chapter 7Amirul AdliNo ratings yet
- C4302 - Topik 2 Ekonomi PengangkutanDocument28 pagesC4302 - Topik 2 Ekonomi PengangkutanAdilenNo ratings yet
- Lampiran CDocument6 pagesLampiran CAshiteru BestNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To StatisticspeqaNo ratings yet
- Kulim P1 2018 SkemaDocument21 pagesKulim P1 2018 SkemaÎ Âm DurkaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 5 - ABCDocument26 pagesKuliah 5 - ABCwanaNo ratings yet
- Menggira Kos LogistikDocument43 pagesMenggira Kos LogistikroslyNo ratings yet
- Kertas Penerangan K1Document25 pagesKertas Penerangan K1Nili DawatiNo ratings yet
- PenghargaanDocument20 pagesPenghargaanEeta Azmi0% (1)
- SKSS Opmm PintasDocument6 pagesSKSS Opmm PintasMUHAMMAD AFIQ SYAHMI BIN MOHD SALLEH MoeNo ratings yet
- 4 Minggu - 2 - Strategi-SCM-1Document18 pages4 Minggu - 2 - Strategi-SCM-1Nicky AfrilliaNo ratings yet
- Rancanganperniagaan 130630030247 Phpapp01Document42 pagesRancanganperniagaan 130630030247 Phpapp01Mohammad Rusdi Yacob CarlosNo ratings yet
- Nota Kuliah 1Document7 pagesNota Kuliah 1m-6165626No ratings yet
- Fasa 1 - Pengurusan OperasiDocument23 pagesFasa 1 - Pengurusan OperasiBenNo ratings yet
- Konsep Biaya Dan Perilaku BiayaDocument19 pagesKonsep Biaya Dan Perilaku Biayashinta musyarofah50% (2)
- Tot Myperformance - Submodul Sku - Final 24052022-Suk GanuDocument57 pagesTot Myperformance - Submodul Sku - Final 24052022-Suk GanuAHMAD SAIFULLAHNo ratings yet
- Template PInTaS (Bengkel)Document1 pageTemplate PInTaS (Bengkel)Josepine MaryNo ratings yet
- Slide Penyediaan RP PENUH 2007Document46 pagesSlide Penyediaan RP PENUH 2007Raouf Datuk Saad100% (1)
- Buletin BSFJ Bil 3 2008Document30 pagesBuletin BSFJ Bil 3 2008azcompNo ratings yet
- Eaa483 EstimatingDocument26 pagesEaa483 EstimatingIntan Farhana Mohd RoslanNo ratings yet
- Bab 4Document22 pagesBab 4Siti AishahNo ratings yet
- PB Susah 1Document10 pagesPB Susah 1wanmuhamadazwarNo ratings yet
- Jurnal NPV PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal NPV PDFShintyaTryCahyaniNo ratings yet
- CBCT2203Document17 pagesCBCT2203Ahmad Fuad100% (1)
- RP - Wiring AfiqDocument37 pagesRP - Wiring AfiqRaouf Datuk SaadNo ratings yet
- K3B Kerangka Kerja Konseptual S2 20212022Document32 pagesK3B Kerangka Kerja Konseptual S2 20212022HANIS HADIRAH BINTI HASHIMNo ratings yet
- Is1 - Konsep Asas KualitiDocument14 pagesIs1 - Konsep Asas Kualitinur atikahNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi StrategikDocument36 pagesSistem Informasi StrategikEka'kajuL'JuliantiNo ratings yet
- Nuralam Ud CVDocument3 pagesNuralam Ud CVnuralamsk484No ratings yet
- Instrumen Penilaian Bersepadu - PENSYARAHDocument1 pageInstrumen Penilaian Bersepadu - PENSYARAHkartini16No ratings yet
- Borang Permohonan Stepp 2022Document10 pagesBorang Permohonan Stepp 2022mysara othmanNo ratings yet
- Dialog Prestasi Peringkat SekolahDocument35 pagesDialog Prestasi Peringkat SekolahNOR AISAH BINTI JAMIL (N-PPDPD)100% (1)
- Sample Rancangan PerniagaanDocument26 pagesSample Rancangan PerniagaanDPMPAK10621 Nurhafizah Md NohNo ratings yet
- ColorscopeDocument6 pagesColorscopeBrizein Neni Sumalong0% (1)
- KP Cu04 Wa3Document13 pagesKP Cu04 Wa3idahothNo ratings yet
- Slaid Taklimat Permohonan PertukaranDocument31 pagesSlaid Taklimat Permohonan PertukaranAimi KhalidNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Kos Qualiti PDFDocument12 pagesBab 6 Kos Qualiti PDFMummy IechaNo ratings yet
- Template KIK (Jan 2013)Document111 pagesTemplate KIK (Jan 2013)Pearl BlackNo ratings yet
- Service Marketing Past Year QuestionDocument11 pagesService Marketing Past Year QuestionNur JieyaNo ratings yet
- SOALAN KAJIAN KES - Pemilihan LokasiDocument1 pageSOALAN KAJIAN KES - Pemilihan Lokasipandagurlzy elikNo ratings yet
- TOT MyPerformance - Submodul SKU - FINALDocument70 pagesTOT MyPerformance - Submodul SKU - FINALFikry FahmiNo ratings yet
- Arahan Projek KumpulanDocument2 pagesArahan Projek KumpulanMya MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Manual RFPDocument12 pagesManual RFPJayashri SelvendranNo ratings yet
- Assignment HRMDocument12 pagesAssignment HRMBasiir ShuhirNo ratings yet
- Isi 1Document10 pagesIsi 1intanyuslee100% (1)
- Bab 9Document47 pagesBab 9Brashella MadiliousNo ratings yet
- Bab 6Document14 pagesBab 6Brashella MadiliousNo ratings yet
- Bab 4Document32 pagesBab 4Brashella MadiliousNo ratings yet
- NamaDocument1 pageNamaBrashella MadiliousNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kepada Pengurusan OperasiDocument15 pagesPengenalan Kepada Pengurusan OperasiBrashella MadiliousNo ratings yet