Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 5 Elasticity and Its Application
Chap 5 Elasticity and Its Application
Uploaded by
Trần Trác Tuyền Vietnam Fanpage Sweet Dream0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views7 pagesChap 5 Elasticity and Its Application
Chap 5 Elasticity and Its Application
Uploaded by
Trần Trác Tuyền Vietnam Fanpage Sweet DreamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Chap 5: Elasticity and its application
*màu đỏ: công thức
*không in đậm: đọc lướt qua
1. Elasticity (hệ số co giãn)
- measures how much one variable responds to changes in another
variable.
- is a numerical measure of the responsiveness of Qd or Qs to one of its
determinants.
- một công cụ phản ánh mức độ phản ứng của người mua và người bán
trước những thay đổi của thị trường - cho phép chúng ta phân tích cung
và cầu với độ chính xác cao hơn
- Ở bất kỳ thị trường cạnh tranh nào, đường cung dốc lên biểu thị hành
vi của người bán và đường cầu dốc xuống biểu thị hành vi của người
mua.
- Giá hàng hóa điều chỉnh làm cho lượng cung và cầu cân bằng nhau
2. Price elasticity of demand = %∆Qd/%∆P (Q=quantity, P=price)
- !!! hệ số co giãn thường được ghi bằng số dương
- Measures the price-sensitivity of buyers’ demand
+ Cầu về một hàng hóa được coi là co giãn với giá cả nếu lượng cầu thay
đổi mạnh khi giá thay đổi.
+ Cầu được coi là không co giãn nếu lượng cầu chỉ thay đổi rất ít khi giá
thay đổi.
** Ví dụ: Giả sử sự gia tăng 10 phần trăm của giá một cốc kem làm cho
lượng kem mà bạn mua giảm 20 phần trăm. Chúng ta tính toán hệ số co
giãn giá của cầu trong trường hợp này như sau:
Hệ số co giãn của cầu = 20 phần trăm /10 phần trăm = 2
hệ số co giãn bằng 2 cho chúng ta biết rằng sự thay đổi của lượng cầu
lớn gấp hai lần sự thay đổi của giá cả. phần trăm thay đổi của giá là dương
10% (phản ánh sự tăng lên), phần trăm thay đổi của lượng là âm 20%
(phản ánh sự giảm đi).
3. Calculating percentage changes = [(end value – start value)/ start
value] x 100%
!!! Công thức trên đưa ra các kết quả khác nhau tùy thuộc vào điểm xuất
phát sử dụng công thức bên dưới để tránh trục trặc này vì nó không phụ
thuộc vào điểm xuất phát
* midpoint method = [(end value – start value) / trung bình cộng] x 100%
4. The determinants of price elasticity:
- the extent to which close substitutes are available (mức độ sẵn có của các
sp thay thế gần gũi)
- whether the good is a necessity or a luxury (sp là thiết yếu hay xa xỉ)
- how broadly or narrowly the good is defined (độ rộng/hẹp của hàng hóa)
- the time horizon – elasticity is higher in the long run than the short run
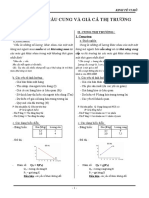
5. The variety of demand curves
- The price elasticity of demand is closely related to the slope of the
demand curve.
- Rule:
+ The flatter the curve, the bigger the elasticity. (Đường cong càng phẳng
thì độ co dãn càng lớn)
+ The steeper the curve, the smaller the elasticity (Đường cong càng dốc
thì độ co dãn càng nhỏ)
5 different classifications of D curves:
Q, P D curve Consumers’ Elasticity
price
sensitivity
Perfectly %Q=0 Vertical None E=0
inelastic (thẳng đứng)
demand
(nhu cầu
hoàn
toàn
không co
giãn)
(extreme
case)
Inelastic %∆Q < %∆P Relatively Relatively E<1
demand steep (dốc low
(nhu cầu xuống)
không co
giãn)
Unit %∆Q = %∆P Intermediate Intermediate E=1
elastic slope (dốc (vừa phải)
demand vừa phải)
(nhu cầu
co giãn
theo đơn
vị)
Elastic %∆Q > %∆P Relatively flat Relatively E>1
demand (tương đối high
(cầu co bằng phẳng)
giãn)
Perfectly %P=0 Horizontal Extreme E=infinity
elastic (nằm ngang)
demand
(hoàn
toàn co
giãn)
(extreme
case)
6. Elasticity of a linear demand curve
- The slope of a linear demand curve is
constant, but its elasticity is not. (Độ dốc
của đường cầu tuyến tính là không đổi,
nhưng độ co giãn của nó thì không.)
7. Price elasticity and total revenue
- Revenue = PxQ
- A price increase has two effects on revenue:
+ Higher P means more revenue on each unit you sell.
+ But you sell fewer units (lower Q), due to Law of Demand.
(Which of these two effects is bigger? It depends on the price elasticity of
demand.)
7.1. If demand is elastic, then price elast. of
demand > 1
%∆Q > %∆P
The fall in revenue from lower Q is greater than
the increase in revenue from higher P, so revenue
falls.
When D is elastic, a price increase causes revenue
to fall.
7.2. If demand is inelastic, then price elast.
of demand < 1 %∆Q < %∆P
The fall in revenue from lower Q is smaller
than the increase in revenue from higher P, so
revenue rises.
When D is inelastic, a price increase causes
revenue to rise.
8. Interdiction and education impact on drugs
- Interdiction (sự can thiệp) reduces the supply of drugs P rises more
than Q falls an increase in total spending on drugs, and in drug-related
crime
- Education reduces the demand for drugs P&Q fall A decrease in total
spending on drugs, and in drug-related crime.
9. Price elasticity of supply = %∆Qd/%∆P
- Measure sellers’ price-sensitivity
Sử dụng midpoint method để tính % changes
- Cung về một hàng hóa được coi là co giãn nếu lượng cung thay đổi đáng kể
khi có sự thay đổi của giá cả.
- Cung được coi là không co giãn nếu lượng cung chỉ thay đổi chút ít khi giá
thay đổi.
*The variety of supply curves:
- The slope of the supply curve is closely related to price elasticity of
supply.
- Rule of thumb:
+ The flatter the curve, the bigger the elasticity. (Đường cong càng phẳng
thì độ co giãn càng lớn)
+ The steeper the curve, the smaller the elasticity (Đường cong càng dốc
thì độ co giãn càng nhỏ)
5 different classifications:
Q, P S curve Sellers’ price Elasticity
sensitivity
Perfectly %∆Q=0 Vertical None E=0
inelastic (dựng đứng)
(extreme)
Inelastic %∆Q < %∆P Relatively Relatively E<1
steep (tương low
đối dốc)
Unit %∆Q = %∆P Intermediate Intermediate E=1
elastic slope (dốc (vừa phải)
vừa phải)
Elastic %∆Q > %∆P Relatively Relatively E>1
flat (tương high
đối phẳng)
Perfectly %∆P=0 Horizontal Extreme E=infinity
elastic (nằm ngang)
(extreme)
10. How the price elasticity of supply can vary
- Supply often becomes less elastic as Q rises, due to capacity limits. (Cung
thường trở nên ít co giãn hơn khi Q (quantity) tăng do giới hạn công suất.)
11. Other elasticities
11.1. Income elasticity of demand = %∆Qd/%∆income
- measures the response of Qd to a change in consumer income
- Income rises demand for normal good rises
+ For normal goods: income elasticity >0
+ For inferior goods: income elasticity <0
11.2. Cross-price elasticity of demand = %∆Qd for good 1/%∆Qd for
good 2
- hệ số co giãn của cầu theo giá chéo
- measures the response of demand for one good to changes in the price of
another good
You might also like
- Các Nội Dung Chính Cần Nhớ Và Không Nhầm Mentora+Document8 pagesCác Nội Dung Chính Cần Nhớ Và Không Nhầm Mentora+K60 NGUYỄN THỊ TÚNo ratings yet
- PE Chapter 5Document2 pagesPE Chapter 5kirisugutokisadaNo ratings yet
- CH 2.BEDocument72 pagesCH 2.BEk61.2215115255No ratings yet
- Chuong 3Document28 pagesChuong 3Nguyễn Văn KhoaNo ratings yet
- Chương 3.1Document42 pagesChương 3.1Hà Giang Ngô ThịNo ratings yet
- Chuong 3 He So Co GianDocument67 pagesChuong 3 He So Co GianDương ThùyNo ratings yet
- Ch4.BE new-SVDocument57 pagesCh4.BE new-SVK60 VÕ NGUYÊN KIỀU DIỄMNo ratings yet
- Co Gian KTVMDocument21 pagesCo Gian KTVMNguyễn Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Chương 1 - KT Vi Mô NG D NGDocument33 pagesChương 1 - KT Vi Mô NG D NGrubidi1609No ratings yet
- Ch03-Do Co Gian Của Cung Va Cau-presentation7eVn-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument91 pagesCh03-Do Co Gian Của Cung Va Cau-presentation7eVn-Đã Chuyển ĐổiHo Nguyen ThienNo ratings yet
- On Tap Kinh Te HocDocument4 pagesOn Tap Kinh Te HocHuyền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Chương 3 Độ Co Giãn Của Cung Và Cầu Vi MôDocument38 pagesChương 3 Độ Co Giãn Của Cung Và Cầu Vi MôHoàng Mai ThiNo ratings yet
- Chương 3 Độ Co Giãn Của Cung Và Cầu Vi MôDocument38 pagesChương 3 Độ Co Giãn Của Cung Và Cầu Vi MôHoàng Mai ThiNo ratings yet
- Chương 3 (phần 1)Document85 pagesChương 3 (phần 1)manhhung864212No ratings yet
- Chuong6 - HOC THUYET TY GIA-Ä Ã Chuyá ƑN Ä Á - IDocument75 pagesChuong6 - HOC THUYET TY GIA-Ä Ã Chuyá ƑN Ä Á - IThảo Đỗ Thị BíchNo ratings yet
- PHẦN ÔN TẬP KINH TẾ VI MÔ KHÓA 14 Năm 2023-2024Document4 pagesPHẦN ÔN TẬP KINH TẾ VI MÔ KHÓA 14 Năm 2023-2024qnhnhlngNo ratings yet
- Chuong 6Document81 pagesChuong 6Vy HuyềnNo ratings yet
- CHƯƠNG 5 kinh tế vi môDocument3 pagesCHƯƠNG 5 kinh tế vi môThiên CaoNo ratings yet
- KINH TẾ VI MÔDocument9 pagesKINH TẾ VI MÔphamvtruong876No ratings yet
- KTVM5 - Do Co Gian Va Ung DungDocument59 pagesKTVM5 - Do Co Gian Va Ung DungNT Thu HườngNo ratings yet
- KTVMDocument8 pagesKTVMphamvtruong876No ratings yet
- Hệ Số Co Giãn - Kế Trung NguyễnDocument8 pagesHệ Số Co Giãn - Kế Trung NguyễnK61 NGUYỄN XUÂN QUỲNHNo ratings yet
- Chương 3. Co Giãn Của Cầu Và CungDocument13 pagesChương 3. Co Giãn Của Cầu Và CungNguyen Huu Hoang PhucNo ratings yet
- Ec101 Slide Chuong4Document12 pagesEc101 Slide Chuong4Trương Mẫn.H VânNo ratings yet
- Bài Giảng Vtp1-Tuần 5 - newDocument43 pagesBài Giảng Vtp1-Tuần 5 - newLê Nguyễn Thái AnhNo ratings yet
- Chương 5 MicroDocument7 pagesChương 5 Micronguyennguyen.31231024658No ratings yet
- Chuong 4 Ty Gia Va Che Do Ty Gia - PDFDocument41 pagesChuong 4 Ty Gia Va Che Do Ty Gia - PDFyoonjeonghan520No ratings yet
- CH 3Document21 pagesCH 3Trâm BíchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02.3 - ElasticityDocument25 pagesChapter 02.3 - Elasticitynguyenthihoangnga07No ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG MÔN HỌC KINH TẾ LƯỢNG NEUDocument13 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG MÔN HỌC KINH TẾ LƯỢNG NEUHuệ LanNo ratings yet
- MIC5-MK-SV-kinh tế vi môDocument51 pagesMIC5-MK-SV-kinh tế vi môLê NhiNo ratings yet
- đề cương kinh tế vi môDocument40 pagesđề cương kinh tế vi môPhan Thanh ThùyNo ratings yet
- Kinh Tế Học Đại CươngDocument33 pagesKinh Tế Học Đại CươngTrúc Thái ThanhNo ratings yet
- F3 TCQDT 3Document50 pagesF3 TCQDT 3Two ZeroNo ratings yet
- Chương 1: Giới Thiệu: Kinh tế học thực chức và chuẩn tắc (positive & normative analysis)Document6 pagesChương 1: Giới Thiệu: Kinh tế học thực chức và chuẩn tắc (positive & normative analysis)Minh Hoa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bài Số 4. Đề Cương Bài GiảngDocument19 pagesBài Số 4. Đề Cương Bài Giảngnguyenthivui2702No ratings yet
- Hoá Lý Chương 2Document60 pagesHoá Lý Chương 2Khánh Nguyễn NgHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elasticity and its Application - Các thuật ngữ chínhDocument2 pagesChapter 5 Elasticity and its Application - Các thuật ngữ chínhkhine zin thawNo ratings yet
- CHƯƠNG 3. Đ Co GiãnDocument31 pagesCHƯƠNG 3. Đ Co Giãnlinhphung.25112000No ratings yet
- CHNG I NHP MON V KINH T HCDocument19 pagesCHNG I NHP MON V KINH T HCkhôi nguyênNo ratings yet
- LÝ THUYẾT VI MÔDocument19 pagesLÝ THUYẾT VI MÔPhuong DoanNo ratings yet
- Bài 3B - Hệ Số Co GiãnDocument10 pagesBài 3B - Hệ Số Co GiãnNguyễn Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu môn vi môDocument22 pagesTài liệu môn vi môHồ Thị OanhNo ratings yet
- 4.5.Từ Điển Economics CFADocument67 pages4.5.Từ Điển Economics CFAManh Hung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Congthuc OncaptocDocument17 pagesCongthuc OncaptocKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Công Thức Môn Quản Trị Vận Hành Doanh NghiệpDocument25 pagesCông Thức Môn Quản Trị Vận Hành Doanh NghiệpOanh Trịnh Vũ KiềuNo ratings yet
- UEB Chương 2 Phần IIDocument9 pagesUEB Chương 2 Phần IIKiều Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bai03 CogianDocument23 pagesBai03 Cogianngọc trầnNo ratings yet
- Mic5 MKDocument54 pagesMic5 MKTien NongNo ratings yet
- Tổng kết kiến thức chương 3 Co giãn cầu và cung - môn KT Vi môDocument8 pagesTổng kết kiến thức chương 3 Co giãn cầu và cung - môn KT Vi môNgọc Sơn BùiNo ratings yet
- Câu hỏi tự luận VLĐC IDocument8 pagesCâu hỏi tự luận VLĐC IVinhKhang ChuNo ratings yet
- Công TH CDocument6 pagesCông TH CkhueNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG KINH TẾ VĨ MÔDocument27 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG KINH TẾ VĨ MÔMinh vân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chuong 3Document17 pagesChuong 3Diệp DiệpNo ratings yet
- Kinh Te VI Mo 5876Document22 pagesKinh Te VI Mo 5876Hung HoangNo ratings yet
- - - - Bài tập cung cầuDocument12 pages- - - Bài tập cung cầuQuân HuniNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - ElasticityDocument19 pagesChap 3 - ElasticityQuốc Bảo NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chæ Æ NG IiDocument16 pagesChæ Æ NG Iinguyên hoàngNo ratings yet
- SV Chuong 4-Ty Gia Va Che Do Ty GiaDocument20 pagesSV Chuong 4-Ty Gia Va Che Do Ty GiaPhuong AnhNo ratings yet